Sexual Reproduction (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences (Double Award)) : Revision Note
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction can be described as
A process involving the fusion of the nuclei of two gametes to form a zygote
Sexual reproduction results in the production of offspring that are genetically different from each other
Sexual reproduction and species
Sexual reproduction can contribute to the success of a species in the wild as it increases the genetic variation present in a population
A species is a group of organisms that can reproduce to produce fertile offspring
Haploid & Diploid Cells: Extended
Extended Tier Only
The nuclei of gametes are haploid
They contain half the number of chromosomes of a normal body cell
In humans, this is 23 chromosomes
The nucleus of a zygote is diploid
It contains the same number of chromosomes as a normal body cell
In humans, this is 23 pairs of chromosomes
The zygote continues to stay diploid as it grows into a fetus and embryo during pregnancy
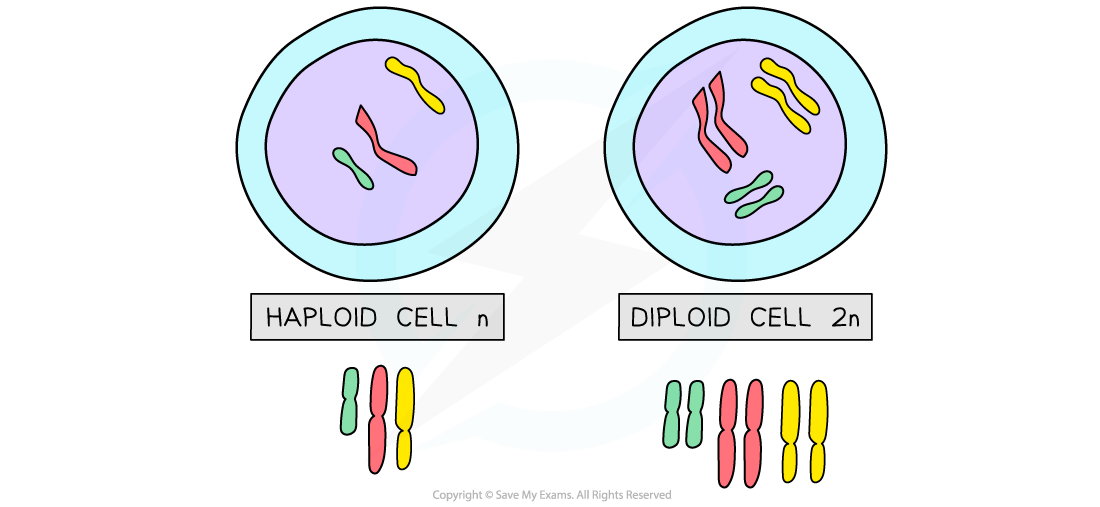
Gametes nuclei are haploid, zygote nuclei are diploid
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It is important to note the use of the word "nucleus" when describing gametes and zygotes - it is their nucleus that is either haploid or diploid, so do be sure to sure to describe this in full.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Sexual Reproduction: Extended
Extended Tier Only
Advantages and disadvantages of sexual reproduction to a population in the wild include:


You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
