Environmental Factors & the Rate of Photosynthesis (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences (Double Award)) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Environmental Factors & the Rate of Photosynthesis
The rate of photosynthesis is affected by factors in the environment, e.g.
Light intensity
Photosynthesis involves the conversion of light energy into chemical energy, so an increase in light intensity will increase the rate of photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide concentration
Carbon dioxide is one of the raw materials for photosynthesis, so an increase in carbon dioxide concentration will increase the rate of photosynthesis
Temperature
Temperature affects the rate of enzyme-controlled reactions, of which photosynthesis is an example
As temperature increases molecules have more energy, so collide with each other more often, increasing the rate of photosynthesis
If temperature increases too far then enzymes may denature, resulting in a decreased rate of photosynthesis
Investigating the effect of environmental factors on the rate of photosynthesis
It is possible to use plant shoots to investigate the effect of environmental factors on the rate of photosynthesis
Aquatic plants such as Elodea or Cabomba can be used; this is because the oxygen that they produce during photosynthesis forms bubbles in the water
The number of bubbles produced per unit time, e.g. per minute, gives a measure of the rate of photosynthesis
The more bubbles produced per minute, the faster the rate of photosynthesis
A more accurate version of this experiment is to collect the oxygen released in a tube inverted over the top of the pondweed over a longer period of time and then measure the volume of oxygen collected using a gas syringe
Investigating the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis
Light intensity can be varied by positioning a lamp at different distances from a beaker containing pondweed

The effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis can be investigated by placing a lamp at different distances and measuring oxygen production in an aquatic plant
Investigating the effect of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis
Temperature can be varied by altering the temperature of the water in the beaker, e.g. using a water bath
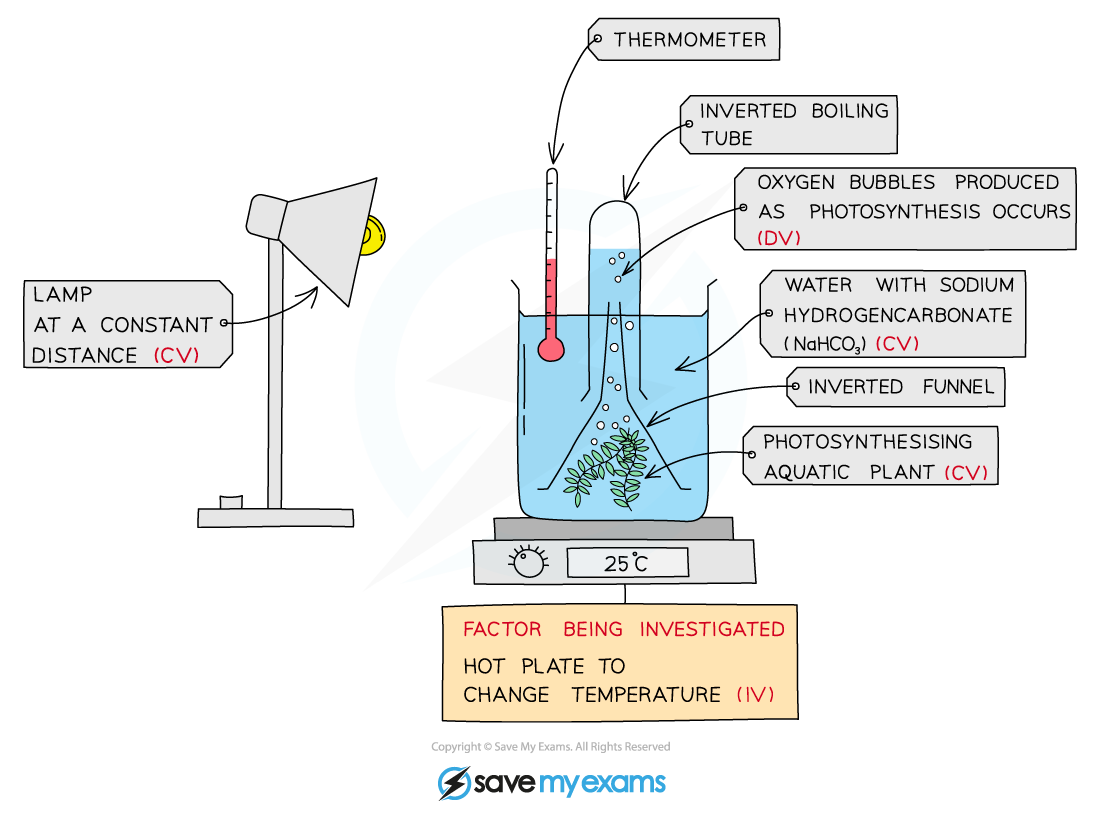
The effect of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis can be investigated by changing the temperature of a water bath and measuring oxygen production in an aquatic plant
Investigating the effect of carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis
The carbon dioxide concentration of the water in a beaker can be controlled by dissolving different amounts of sodium hydrogen carbonate in the water

The effect of carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis can be investigated by changing the sodium hydrogen carbonate concentration and measuring oxygen production in an aquatic plant
Care must be taken when investigating a condition to keep all other variables constant in order to ensure a fair test
For example, when investigating changing light intensity, a glass tank should be placed in between the lamp and the beaker to absorb heat from the lamp and so avoid changing the temperature of the water as well as the light intensity

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
