Purity of Substances (Oxford AQA IGCSE Combined Science Double Award) : Revision Note
Purity of Substances
A change of state refers to a substance changing its state between solid, liquid or gas
Changes of state happen at the melting and boiling points of a pure substance
The purity of a substance affects its melting and boiling point
Changes of state

Pure substances
In everyday language, we use the word pure to describe when something is natural or clean and to which nothing else has been added
In Physics and Chemistry, a pure substance may consist of a single element or compound which contains no other substances
For example, a beaker of a sample of pure water contains only H2O molecules and nothing else
If salt were added to the beaker then the saltwater solution would be a mixture
A mixture consists of two or more elements or compounds that are physically mixed together, they are not chemically combined
Air is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen and some other gases such as carbon dioxide and argon
The chemical properties of the substances in a mixture remain unchanged
Substances in mixtures can be separated by physical means (e.g. filtration or distillation)
Compounds and mixtures

The heating and cooling curve of a pure substance
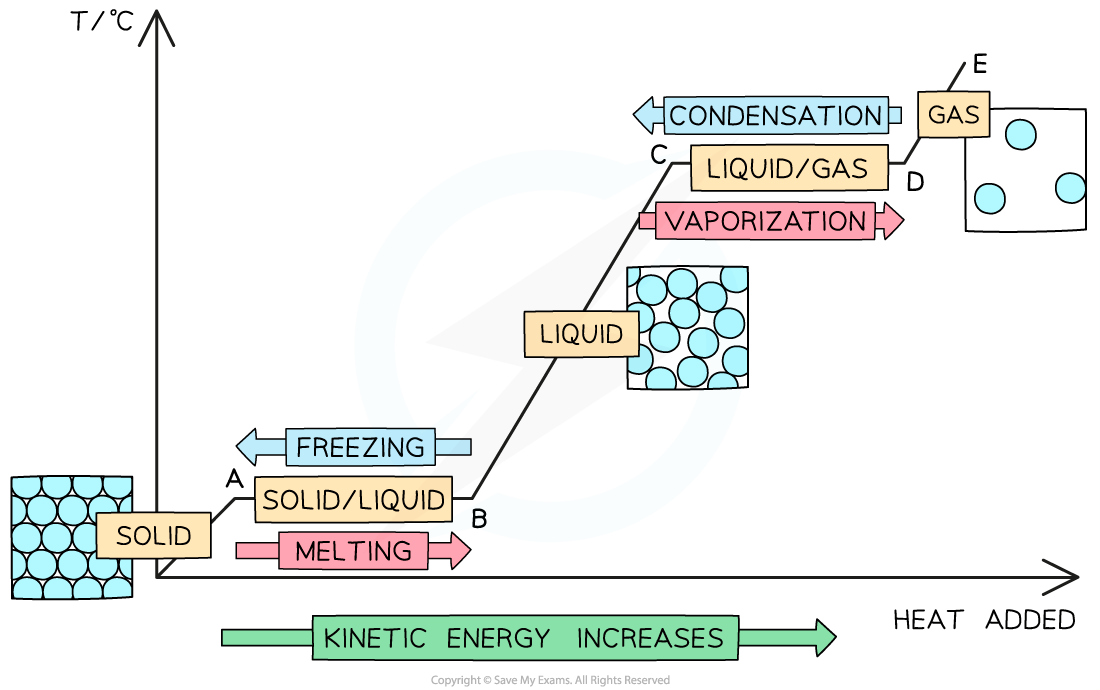
Distinguishing purity
Pure substances melt and boil at specific temperatures e.g. pure water has a boiling point of 100°C and a melting point of 0°C
Measuring the melting and boiling temperature of water

Mixtures have a range of melting and boiling points as they consist of different substances that tend to lower the melting point and broaden the melting point range
Melting and boiling point data can therefore be used to distinguish pure substances from mixtures
Melting point analysis is routinely used to assess the purity of drugs
This is done using a melting point apparatus which allows you to slowly heat up a small amount of the sample, making it easier to observe the exact melting point
This is then compared to data tables
The closer the measured value is to the actual melting or boiling point then the purer the sample is
Worked Example
When roads are icy, salt is spread on the icy patches to make them safer to drive on.
Explain the purpose of using a salt mixture in this process.
Answer:
When salt is added to the ice it forms a salt-ice mixture
This mixture has a lower melting point than pure ice
So the ice melts at a lower temperature making the roads safer to drive on

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

