Conduction (Oxford AQA IGCSE Combined Science Double Award) : Revision Note
Conduction
Thermal conduction is the process of energy transfer by vibrating particles in a substance
It is the main method of thermal energy transfer in solids
The direction of energy transfer is always from hot to cold
Conduction occurs when:
Two objects, or substances, of different temperatures come in contact with one another, thermal energy is transferred from the hotter object to the cooler object
Conduction in solids
When a substance is heated, the particles, start to move around (vibrate) more
The atoms at the hotter end of the solid will vibrate more than the atoms at the cooler end
The vibrating particles transfer energy from their kinetic store to the kinetic store of neighbouring particles as they collide
Eventually, thermal equilibrium is achieved throughout the substance
This occurs in all solids, metals and non-metals alike
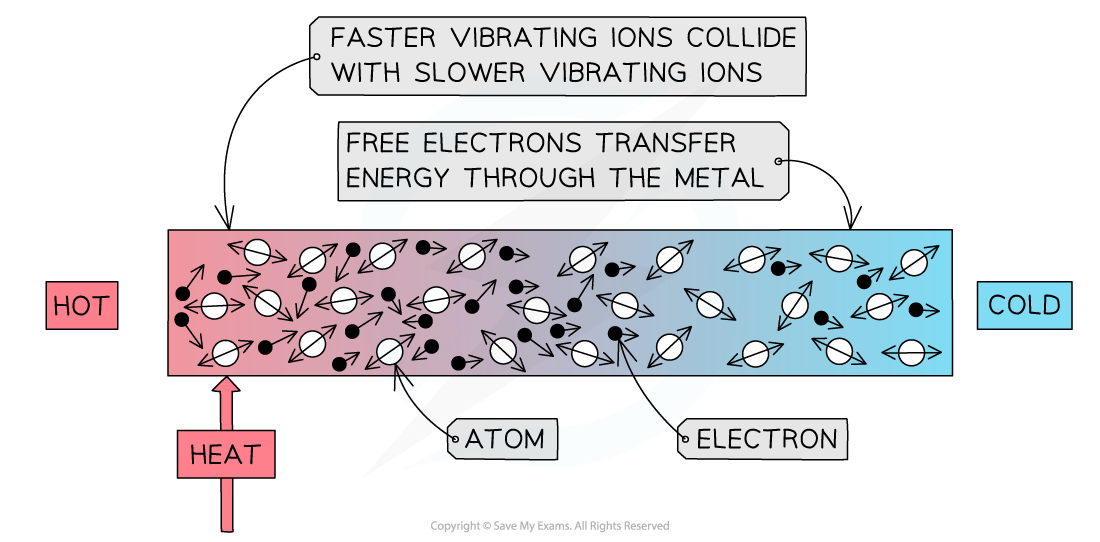
Conduction in metals
Metals are the best thermal conductors
This is because they have a high number of free electrons
When a metal is heated, the free electrons gain energy and pass through the structure of the metal
They collide with other electrons and metal ions that make up the metal, transferring energy with each collision
This speeds up the transfer of energy throughout the metal
Free electrons in a metal
Conduction in liquids and gases
Both types of fluid (liquid or gas) are poor conductors of heat
For thermal conduction to occur in a fluid the particles need to be close together so that when they vibrate the vibrations are passed along
In liquids, particles are close but slide past each other
Therefore, liquids are generally better conductors than gases
In gases, particles have much more space in between them
Therefore, gases are generally poor conductors
Conductors to insulators
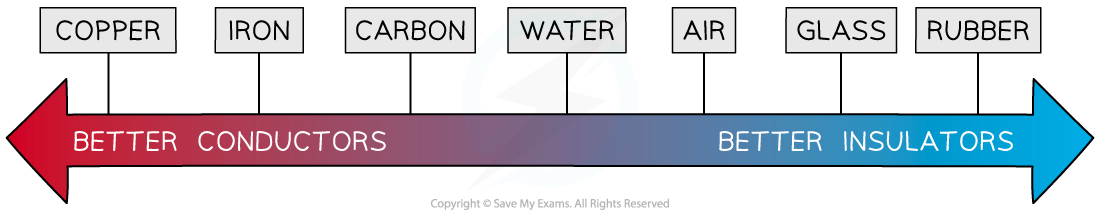
Insulators
There are many situations where energy transfers are unwanted:
Keeping a house warm
Keeping a hot drink hot or cold
Dressing to stay warm in cold weather
Insulated mug

An insulator is a substance that is a poor thermal conductor
Examples include wool, plastic, wood
Insulators are used to reduce energy transfers, for example, to keep a house warm or build a soundproof room
This is why in cold weather, a woollen jumper is worn to retain body heat and keep warm
Good insulators which keep the energy transfer through them as low as possible have:
A low thermal conductivity
Layers that are as thick as possible
Examiner Tips and Tricks
A common mistake when explaining how an insulator keeps something warm is to state something along the lines of “The object warms up the insulator which then warms the object up”.
Avoid giving this kind of answer!
The real explanation is:
The insulator contains trapped air, which is a poor thermal conductor
This reduces the rate of energy transfer from the object, meaning that it will stay warmer for longer

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

