Alcohols (Oxford AQA IGCSE Combined Science Double Award): Revision Note
Exam code: 9204
The Alcohol Functional Group
All alcohols contain the hydroxyl (-OH) functional group which is the part of alcohol molecule that is responsible for their characteristic reactions
Alcohols are a homologous series of compounds that have the general formula CnH2n+1OH
They differ by one -CH2 in the molecular formulae from one member to the next
The -OH group in alcohols

The first three alcohols
The names and structures of the first threealcohols are shown below
In terms of naming, the same system is used as for alkanes and alkenes, with the final ‘e’ being replaced with ‘ol’
Table to show the name, formula and displayed formula of the first four alcohols
Name | Formula | Displayed formula |
|---|---|---|
Methanol | CH3OH |  |
Ethanol | C2H5OH |  |
Propanol | C3H7OH |  |
Uses of Alcohols
Alcohols are colourless liquids that dissolve in water to form neutral solutions
The first four alcohols are commonly used as fuels
School laboratories use ethanol in spirit burners as it burns cleanly and without strong odours
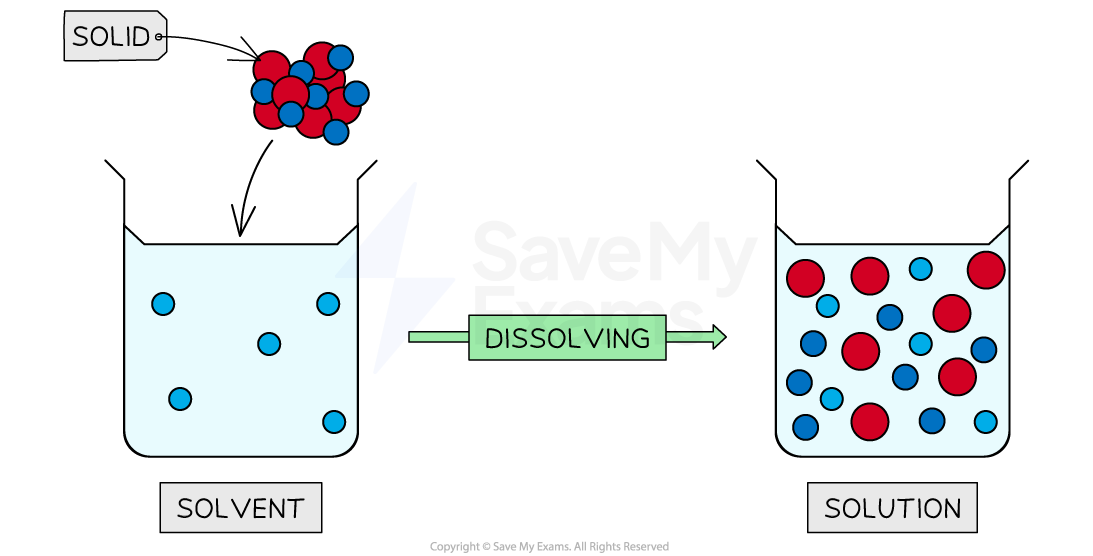
Methanol and ethanol are also used extensively as solvents
This is because they can dissolve many substances that water cannot such as fats and oils, but can also dissolve most of the substances that water can
Diagram to show the process of dissolving
Alcohol is also used to make alcoholic beverages
Ethanol is the main alcohol used
Alcohols react with sodium metal to produce hydrogen gas and a metal salt
The word equation for the reaction of methanol with sodium is:
sodium + methanol → sodium methoxide + hydrogen
Oxidation of Ethanol
Microbial oxidation occurs when a substance is oxidised by microbes such as bacteria or yeast
When ethanol undergoes oxidation, ethanoic acid is formed
Ethanoic acid is the main acid in vinegar
The bacteria Acetobacter causes this reaction to take place
Oxidising agents such as acidified potassium dichromate can be used to form carboxylic acids from alcohols
We can use [O] in an equation to represent oxidation
Oxidation is also the removal of hydrogen from the ethanol, this is why water is formed
The equation for this reaction is:
C2H5OH + 2[O] → CH3COOH + H2O
Ethanol being oxidised to ethanoic acid


Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?