The copper(II) carbonate in the mineral, malachite, reacts with hydrochloric acid according to this equation.
CuCO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) → CuCl2 (aq) + H2O (g) + CO2 (g)
Some students investigate the effect of changing the concentration of acid on the rate of this reaction. The diagram shows the apparatus they use.

This is the method they use:
set the balance to zero
add an excess of malachite lumps to the conical flask and replace the cotton wool
start a timer and record the balance reading after one minute
The experiment is repeated using different concentrations of hydrochloric acid. The mass and number of malachite lumps are kept the same in each experiment.
The table shows the results obtained in one series of experiments.

State why the balance readings have negative values.
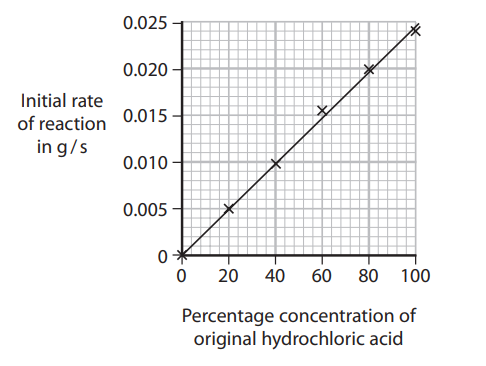
The graph shows the results of this series of experiments.

The circled point indicates an anomalous result.
i) Suggest one mistake the students could have made to produce this result.
(1)
ii) State the relationship shown by the graph.
(1)
Explain why an increase in the concentration of the acid causes an increase in the rate of the reaction. You should use the particle collision theory in your answer.
Did this page help you?