The Pressure Law (Edexcel IGCSE Physics (Modular)) : Revision Note
The pressure law
If the volume V of an ideal gas is constant, the pressure law is given by:
P ∝ T
This means the pressure is proportional to the temperature
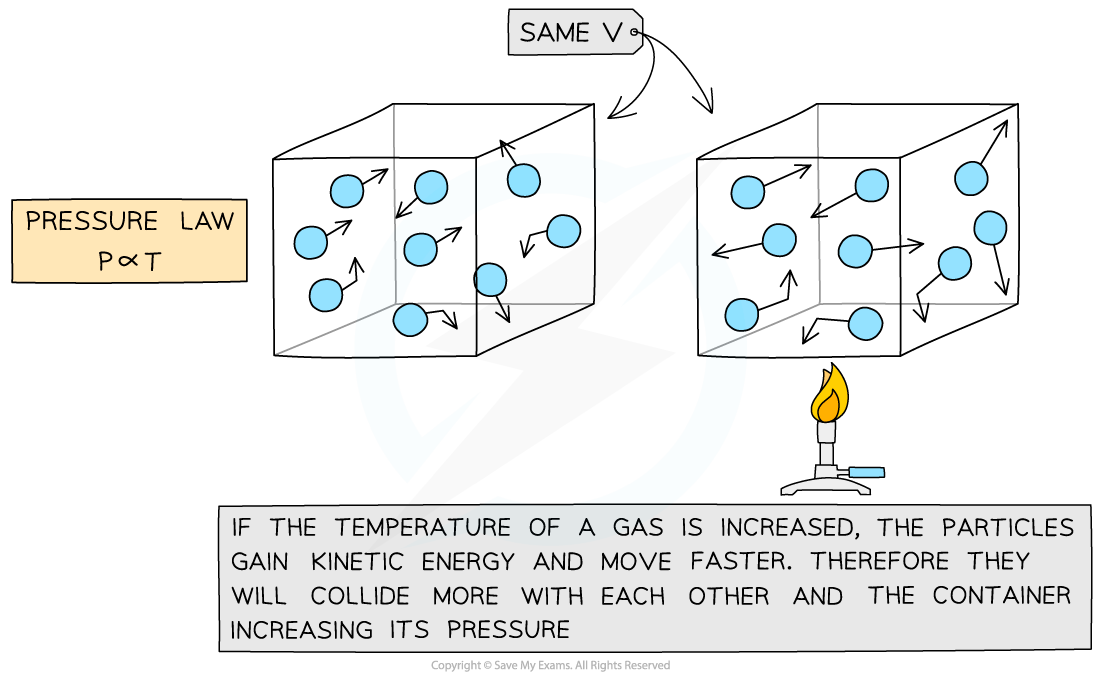
Pressure and temperature are proportional. Doubling temperature also doubles the pressure for a gas in a fixed volume.
The relationship between the pressure and (Kelvin) temperature for a fixed mass of gas at constant volume can also be written as:
Where:
p1 = initial pressure (Pa)
p2 = final pressure (Pa)
T1 = initial temperature (K)
T2 = final temperature (K)

Pressure law graph representing temperature (in °C) directly proportional to the volume
Worked Example
The pressure inside a bicycle tyre is 5.10 × 105 Pa when the temperature is 279 K. After the bicycle has been ridden, the temperature of the air in the tyre is 299 K. Calculate the new pressure in the tyre, assuming the volume is unchanged.
Answer:
Step 1: Choose the correct ideal gas law
Volume is constant, so the pressure law must be used
Step 2: Write down the known quantities
p1 = 5.10 × 105 Pa
T1 = 279 K
T2 = 299 K
Step 3: Rearrange for p2 and substitute values into the pressure law
To make p2 the subject, multiply both sides by T2 to cancel out the T2 in the fraction under p2
Substitute the known quantities
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember when using gas laws the temperature T must always be in kelvin (K)!

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

