Isotopes (Edexcel IGCSE Physics (Modular)): Revision Note
Exam code: 4XPH1
Isotopes
For a particular element, the number of protons is always the same, but the number of neutrons can be different
This is because the number of protons determines the element e.g. carbon atoms have 6 protons and iron atoms have 26 protons
An isotope is defined as:
An atom, or atoms, of the same element that have an equal number of protons but a different number of neutrons
Each element can have more than one isotope
Isotopes of hydrogen
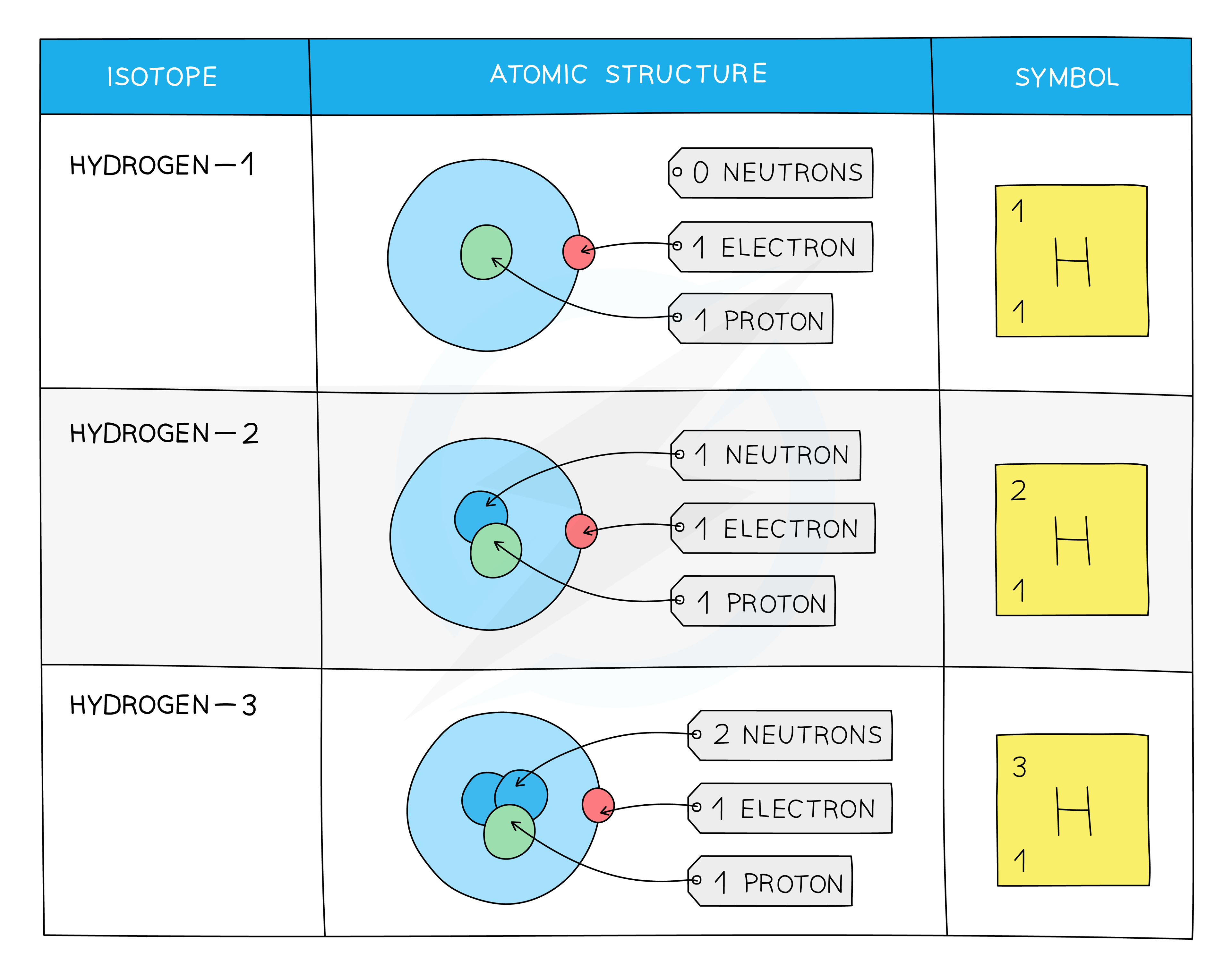
Some isotopes are more unstable than others due to the imbalance of protons and neutrons, which means
They may be more likely to decay
They may be less likely to occur naturally
For example, about 2 in every 10 000 atoms of hydrogen are the isotope deuterium
The isotope tritium is even rarer (about 1 in every billion billion atoms of hydrogen)
Worked Example
State the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in these two isotopes of chlorine:
,
Answer:
Step 1: Determine the number of protons
The atomic number is the number of protons
Both chlorine-35 and chlorine-37 have 17 protons
Step 2: Determine the number of neutrons
The mass number is the number of protons and neutrons
Number of neutrons in chlorine-35 = 35 − 17 = 18
Number of neutrons in chlorine-37 = 37 − 17 = 20
Step 3: Determine the number of electrons
The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons
Both chlorine-35 and chlorine-37 have 17 electrons

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?