Specific Heat Capacity (Edexcel IGCSE Physics (Modular)): Revision Note
Exam code: 4XPH1
Specific heat capacity
The specific heat capacity, c of a substance is defined as:
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of the substance by 1 °C per kilogram of mass (J/kg °C)
Different substances have different specific heat capacities
If a substance has a low specific heat capacity, it heats up and cools down quickly (ie. it takes less energy to change its temperature)
If a substance has a high specific heat capacity, it heats up and cools down slowly (ie. it takes more energy to change its temperature)
Examples of specific heat capacity
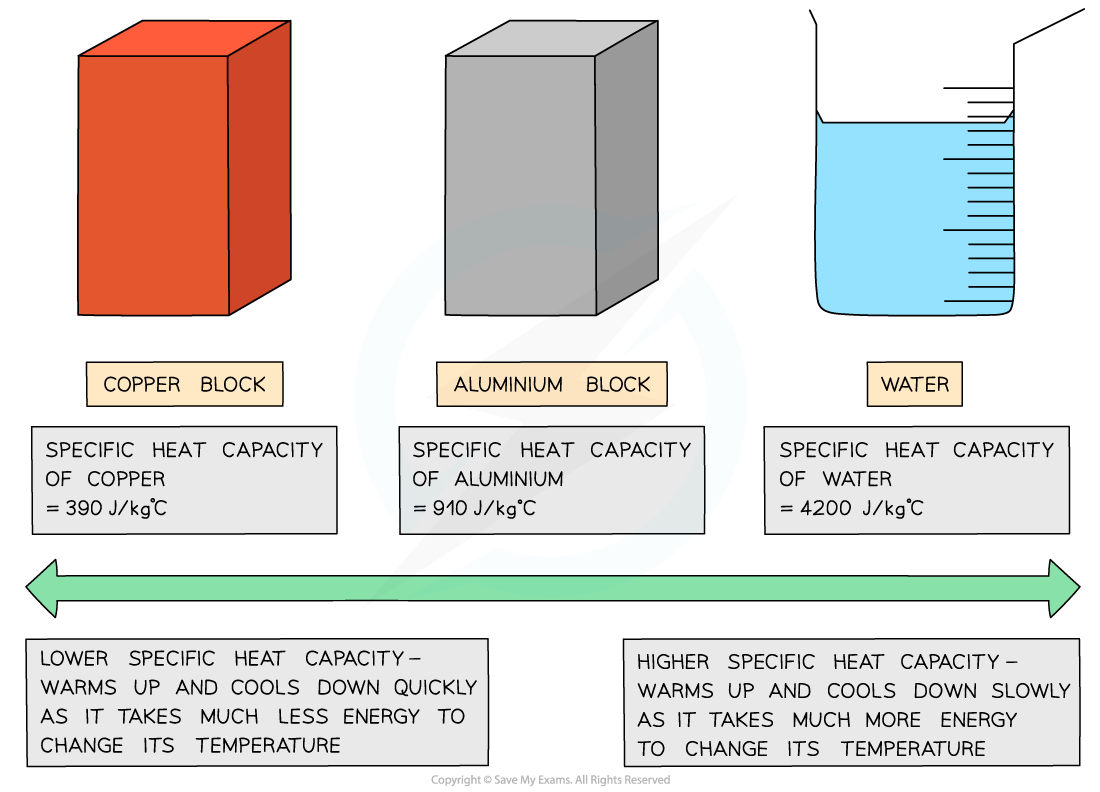
Low vs high specific heat capacity
How much the temperature of a system increases depends on:
The mass of the substance heated
The type of material
The amount of energy put into the system in the form of thermal energy
Calculating specific heat capacity
The specific heat capacity of a substance can be calculated using the equatiion:
Where:
ΔQ = change in thermal energy, in joules (J)
m = mass, in kilograms (kg)
c = specific heat capacity, in joules per kilogram per degree Celsius (J/kg °C)
ΔT = change in temperature, in degrees Celsius (°C)
Worked Example
Water of mass 0.48 kg is increased in temperature by 0.7 °C. The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J / kg °C.
Calculate the amount of thermal energy transferred to the water.
Answer:
Step 1: Write down the known quantities
Mass, m = 0.48 kg
Change in temperature, ΔT = 0.7 °C
Specific heat capacity, c = 4200 J/kg °C
Step 2: Write down the relevant equation
Step 3: Calculate the thermal energy transferred by substituting in the values
Step 4: Round the answer to 2 significant figures
Examiner Tips and Tricks
This equation will be given on your equation sheet, so don't worry if you cannot remember it, but it is important that you understand how to use it. You will always be given the specific heat capacity of a substance, so you do not need to memorise any values.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?