The Scale of the Universe (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences (Double Award)): Revision Note
Exam code: 0654 & 0973
The Milky Way
The Universe
The Universe is defined as
A large collection of billions of galaxies
It is also the name given to the entirety of space
Galaxies
A galaxy is defined as
A large collection of billions of stars
Stars are large astronomical objects, such as the Sun
The Milky Way
The Milky Way is one of many billions of galaxies making up the Universe
The Sun is one of many billions of stars making up the Milky Way
Other stars in the Milky Way galaxy are much further away from Earth than the Sun is
Some of these stars also have planets which orbit them
Hierarchy of the Solar System
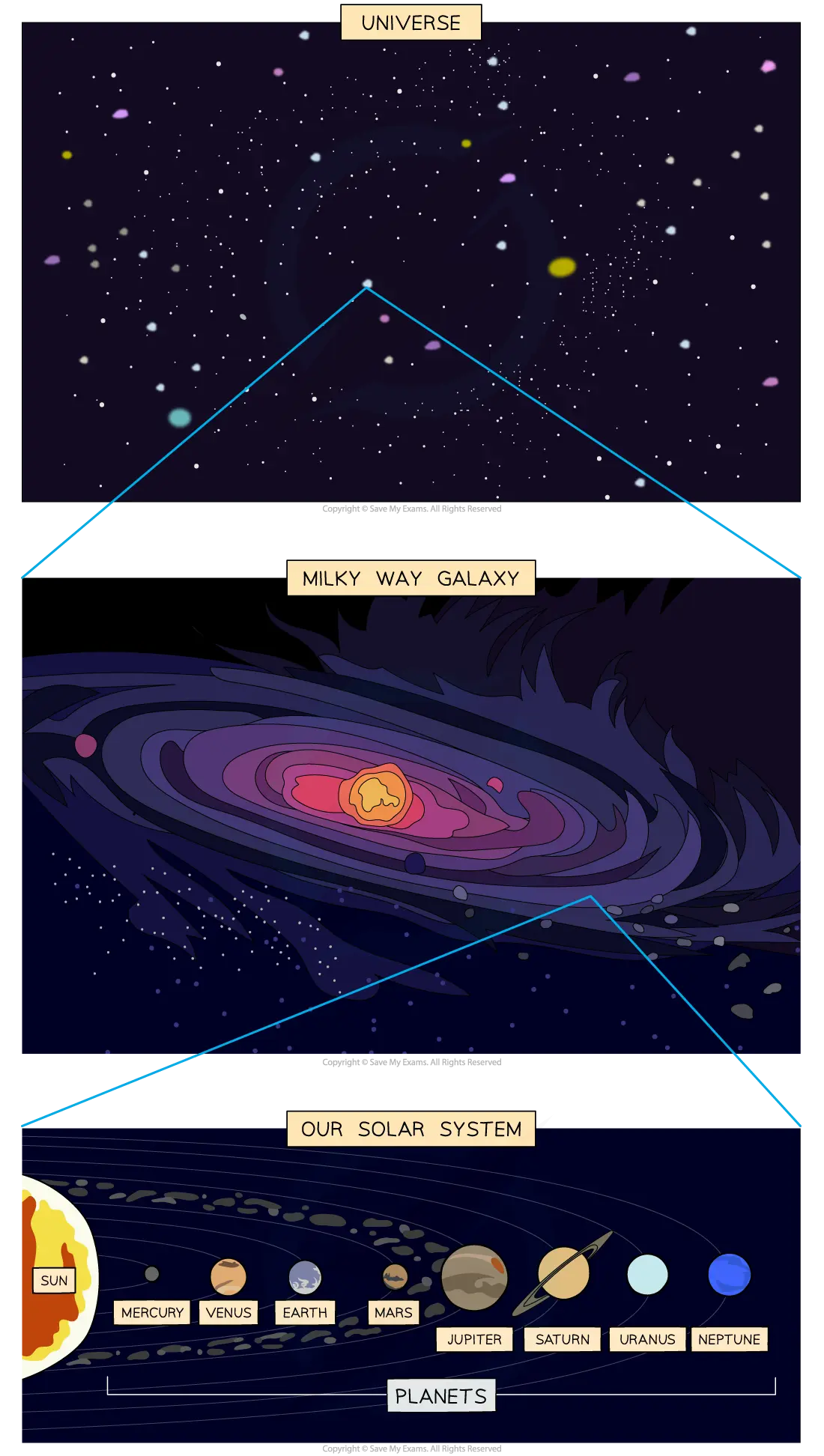
The Universe is a large collection of galaxies and a galaxy is a large collection of stars. The Sun is a star at the centre of our Solar System in the Milky Way galaxy
Astronomical distances
Astronomical distances, such as the distances between stars and galaxies, are extremely large
To describe these distances, astronomers use a special unit called the light year
One light-year is defined as:
The distance travelled by light in one year
The diameter of the Milky Way is approximately 100 000 light-years
This means that light would take 100 000 years to travel from one side of the Milky Way to the other
Worked Example
The centre of our galaxy is 30 000 light years away.
(a) How long does it take light to reach the Earth?
(b) How far away, in light years, is the edge of the Milky Way from Earth?
Answer:
Part (a)
The centre of our galaxy is 30 000 light years away
It takes light 30 000 years to reach the Earth from the centre of our galaxy
Part (b)
The diameter of the Milky Way is 100 000 light years
The radius of the Milky Way is 50 000 light years
Therefore, the edge of the Milky Way closest to the Earth is 50 000 – 30 000 = 20 000 light years
ORThe edge of the Milky Way furthest from the Earth is 100 000 – 20 000 = 80 000 light years

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
