Electrical Power (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences (Double Award)): Revision Note
Exam code: 0654 & 0973
Electrical power equation
The power of an appliance is defined as:
The rate at which energy is transferred by an appliance
Power can be calculated in terms of energy:
Where:
= power, measured in watts (W)
The watt is equivalent to joules per second (J/s)
= energy transferred, measured in joules (J)
= time, measured in seconds (s)
Power can also be calculated in terms of work done:
Where:
= work done, which is equivalent to energy transferred, measured in joules (J)
The power of an electrical device is the energy transferred per second by the device
The power dissipated by an electrical component can be calculated by:
Where:
= dissipated power, measured in watts (W)
= current, measured in amps (A)
= potential difference, measured in volts (V)
Worked Example
Two lamps are connected in series to a 150 V power supply.
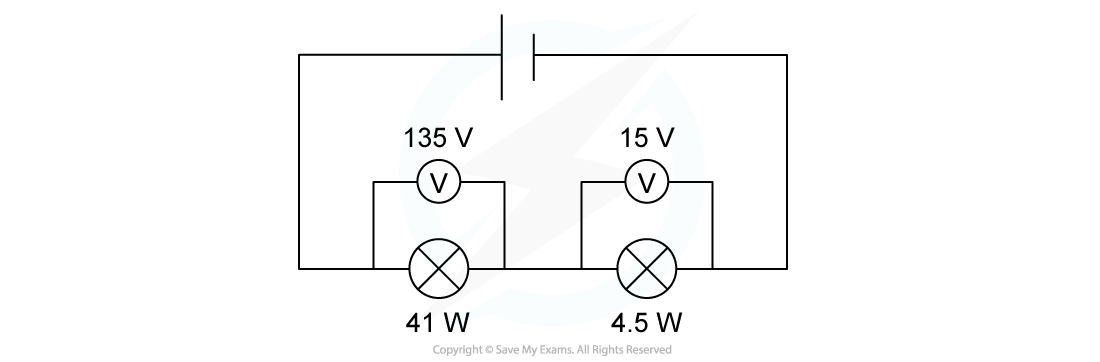
Which statement most accurately describes what happens?
A. Both lamps light normally
B. The 15 V lamp blows
C. Only the 41 W lamp lights
D. Both lamps light at less than their normal brightness
Answer: A
Step 1: Calculate the current required for both lamps to operate
For the 41 W lamp, with 135 V
For the 4.5 W lamp, with 15 V
Step 2: Determine the outcome of the bulbs
For both bulbs to operate at their normal brightness, a current of 0.3 A is required
The lamps are connected in series, so the same current would flow through both
Therefore, the lamps will light at their normal brightness
This is option A
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When doing calculations involving electrical power, remember the unit is Watts W, therefore, you should always make sure that the time is in seconds
Measuring energy usage
Energy measured in joules
Electrical energy transferred is often calculated with units of joules
One joule is equivalent to one-watt second
Consider an average lightbulb with a power of 60 W, which is left on for 6 hours in a house
1 hour is 3600 s
The energy transferred over this time is 1.296 × 106 J
This number is large and that is only one lightbulb for a single day
A household uses many appliances all year round; the energy transferred per month in joules would be inconveniently large
Energy measured in kilowatt-hours
To make these large values more relatable to daily use:
Power can be measured in kilowatts (kW)
Time can be measured in hours (h)
In this case, energy has units of kilowatt-hours (kW h)
The lightbulb from before receives 0.36 kW h of energy over the 6 hours
This value is much easier to understand for consumers and energy providers; thinking in terms of hours of use is more practical than seconds
Calculating with kWh
As has been stated previously, the equation for energy transferred is:
But here, different units are considered:
= energy transferred, measured in kilowatt hours (kW h)
= power of the appliance, measured in kilowatts (kW)
= time, measured in hours (h)
The usual unit of energy is joules (J), which is one watt-second
To find the number of joules in 1 kW h, convert the power and time to watts and seconds
1000 watts multiplied by 3600 seconds is equal to 1000 multiplied by 3600, in watt-seconds
Therefore, 1 kWh = 3.6 × 106 J
To convert from kW h to J:
To convert from J to kW h:
The kW h is a large unit of energy, and is mostly used for energy in homes, businesses and factories
Worked Example
A cooker transfers 1.2 × 109 J of energy electrically to the thermal store of the heating element during its use over a year.
Assume that 1 kW h costs 14.2 p.
100 p = £1 (100 pence = 1 pound)
Calculate the cost of using the oven for the year.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Energy in joules,
Cost per kW h,
Step 2: Convert the energy used from J to kW h
Step 3: Calculate the price
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The kilowatt hour is a tricky concept to get your head around, so make sure you are comfortable with the conversions between kW h and J well before your exam.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?