Total Internal Reflection (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences (Double Award)): Revision Note
Exam code: 0654 & 0973
Did this video help you?
Total internal reflection
Extended tier only
Sometimes, when light is moving from a denser medium towards a less dense one, instead of being refracted, all of the light is reflected
This phenomenon is called total internal reflection
Total internal reflection (TIR) occurs at the boundary between two media when:
All the incident ray in medium 1 is reflected back into medium 1
Comparing refraction and total internal reflection

Refraction happens when the angle of incidence is smaller and total internal reflection happens when the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If asked to name the phenomena make sure you give the whole name – total internal reflection
Remember: total internal reflection occurs when light travels from a denser material to less dense material and ALL of the light is reflected.
Critical angle
Extended tier only
The critical angle is defined as
the angle of incidence at which the angle of refraction is 90°
and
above which all light is totally internally refracted
At the boundary between two media, as the angle of incidence is increased, the angle of refraction also increases until it gets closer to 90°
When the angle of refraction is exactly 90° the light is refracted along the boundary
At this point, the angle of incidence is known as the critical angle c
Obtaining total internal reflection examples

As the angle of incidence increases it will eventually surplus the critical angle and lead to total internal reflection of the light
When the angle of incidence is larger than the critical angle, the refracted ray is now reflected
This is total internal reflection
Worked Example
A glass cube is held in contact with a liquid and a light ray is directed at a vertical face of the cube. The angle of incidence at the vertical face is 39° and the angle of refraction is 25° as shown in the diagram. The light ray is totally internally reflected for the first time at X.
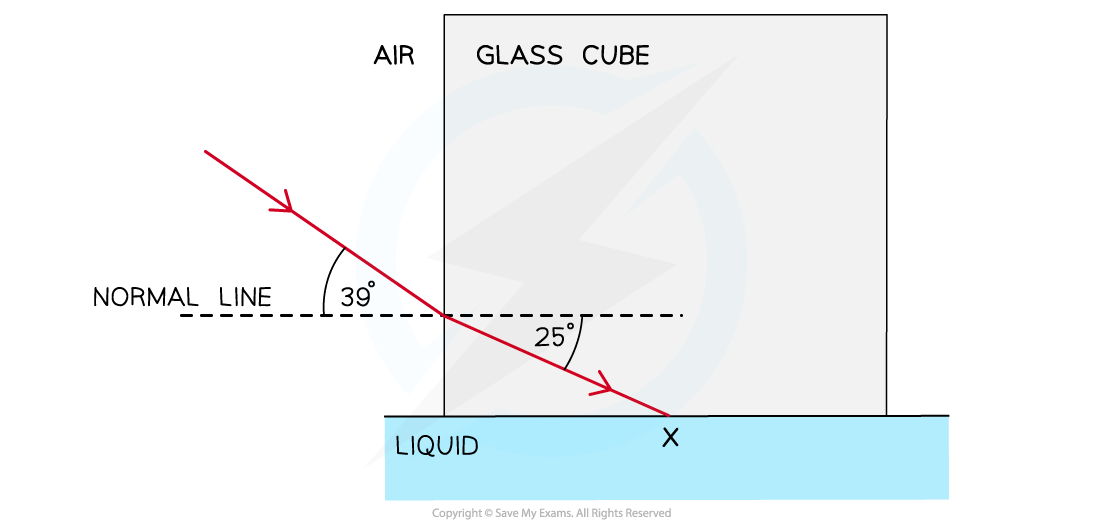
Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray beyond X to the air and calculate the critical angle for the glass-liquid boundary.
Answer:
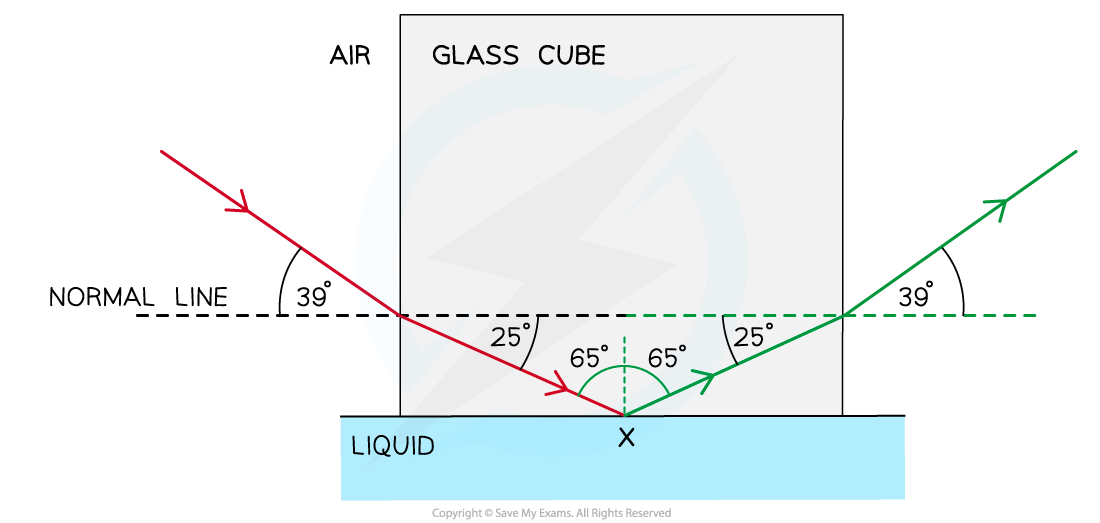
Step 1: Draw the reflected angle at the glass-liquid boundary
When a light ray is reflected, the angle of incidence = angle of reflection
Therefore, the angle of incidence (or reflection) is 90° – 25° = 65°
Step 2: Draw the refracted angle at the glass-air boundary
At the glass-air boundary, the light ray refracts away from the normal
Due to the reflection, the light rays are symmetrical to the other side
Step 3: Calculate the critical angle
The question states the ray is “totally internally reflected for the first time” meaning that this is the lowest angle at which TIR occurs
Therefore, 65° is the critical angle
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you are asked to explain what is meant by the critical angle in an exam, you can be sure to gain full marks by drawing and labelling the same diagram above (showing the three semi-circular blocks)
Optical fibres
Extended tier only
Total internal reflection is used to reflect light along optical fibres, meaning they can be used for
communications
endoscopes
decorative lamps
Light travelling down an optical fibre is totally internally reflected each time it hits the edge of the fibre
Total internal reflection example: optical fibre
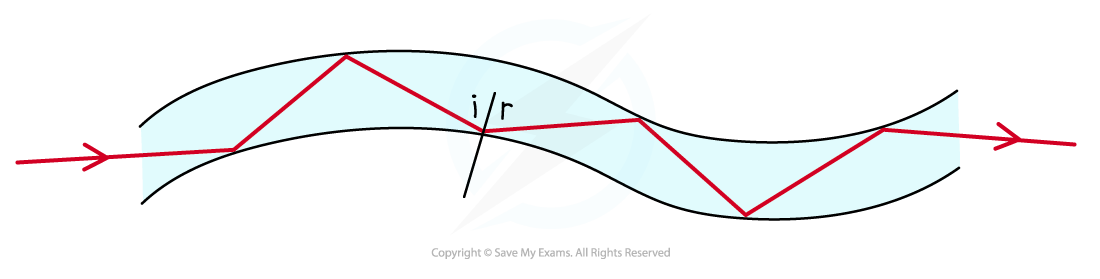
Optical fibres utilise total internal reflection for communications
Endoscopes are used to look within the human body
Total internal reflection example: endoscope
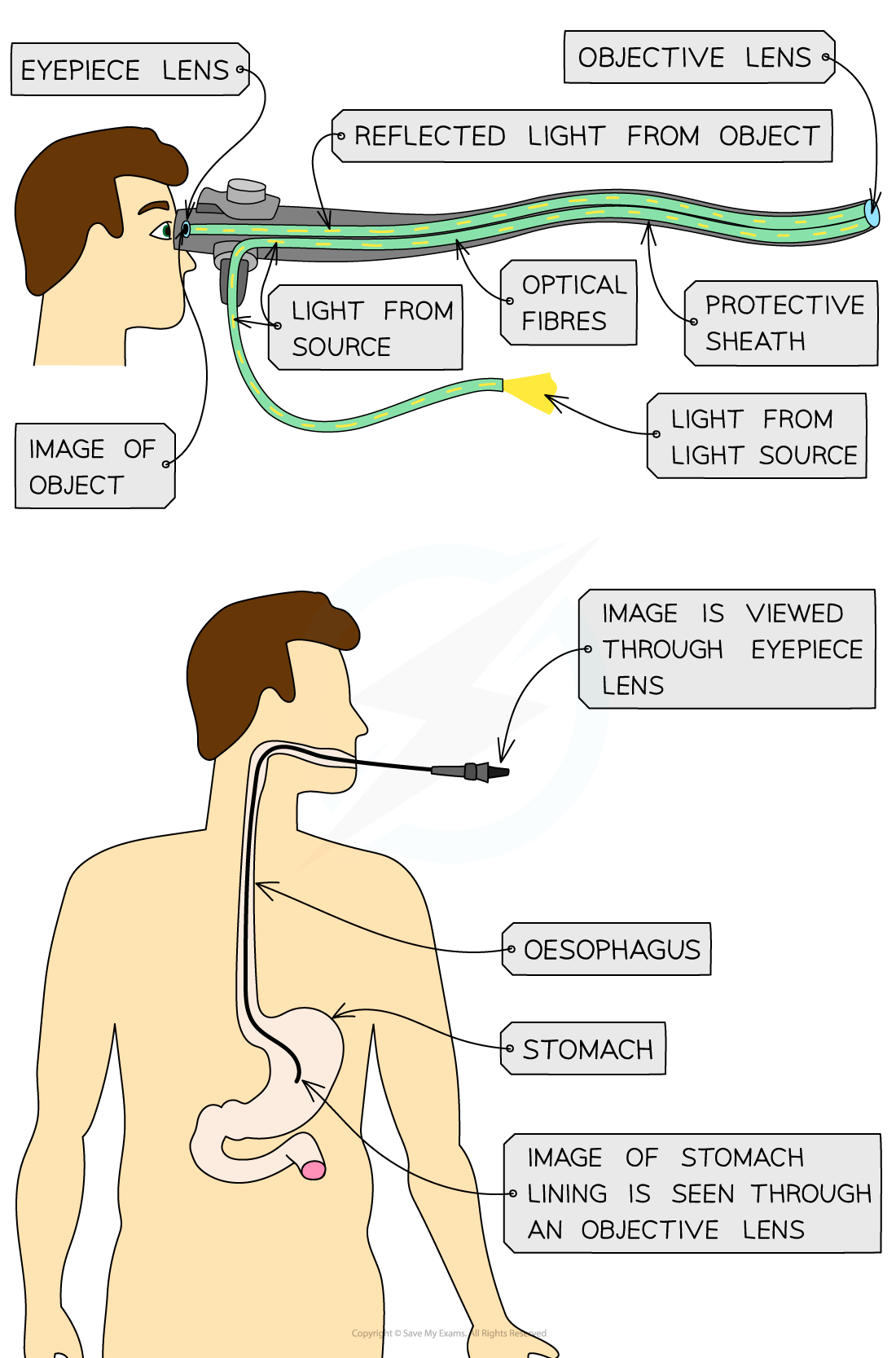
Endoscopes utilise total internal reflection to see inside a patient's body
Optical fibres can be used in communications to transmit:
Home (landline) telephone signals
Internet signals
Cable television signals
Total internal reflection example: telegraph poles

Fibre optic cables can be found in the phone cables attached between the telephone poles and the street

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?