Refraction of Light (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences (Double Award)): Revision Note
Exam code: 0654 & 0973
Defining refraction
Refraction is defined as:
The change in direction of a light ray passing from one medium to another
In refraction, angles are measured between the ray (showing the direction of the wave) and the normal line
The angle of the wave approaching the boundary is called the angle of incidence (i)
The angle of the wave leaving the boundary is called the angle of refraction (r)
When drawing a ray diagram an arrow is used to show the direction the wave is travelling
An incident ray has an arrow pointing towards the boundary
A refracted ray has an arrow pointing away from the boundary
The angles of incidence and refraction are usually labelled i and r respectively
Refraction ray diagram
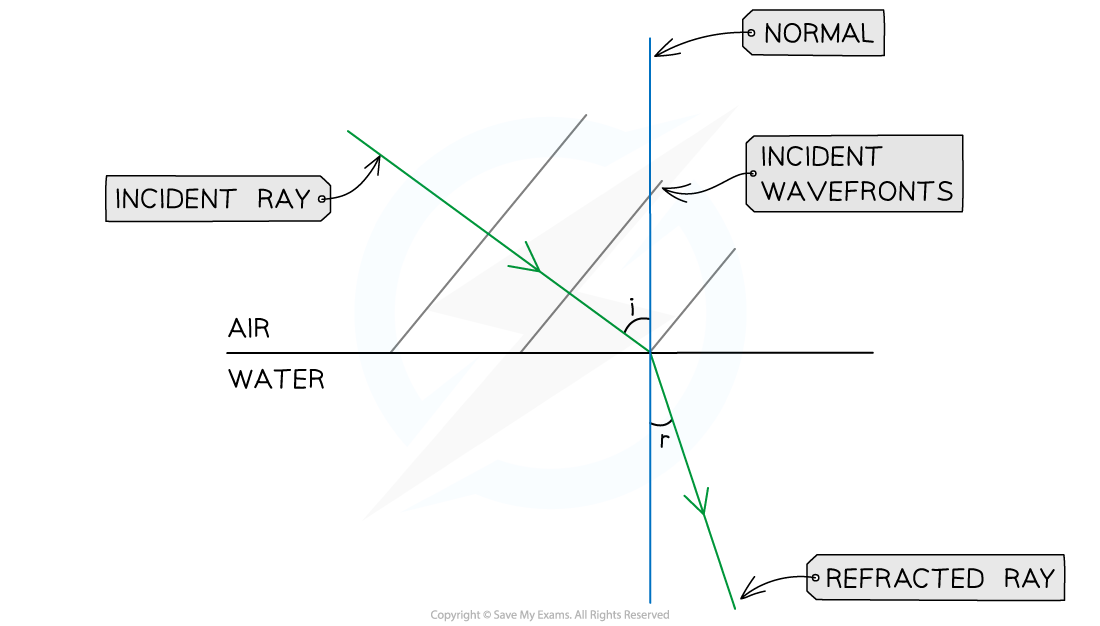
A ray diagram for light refracting at a boundary, showing the normal, angle of incidence and angle of refraction
Did this video help you?
Refraction of light
The change in direction depends on the difference in density between the two media:
From less dense to more dense (e.g air to glass), light bends towards the normal
From more dense to less dense (e.g. glass to air), light bends away from the normal
When passing along the normal (perpendicular) the light does not bend at all
Note that when a light wave enters and leaves the glass block there are two boundaries
The refracted ray at the first boundary becomes the incident ray at the second boundary
Refraction diagram of light from air through a glass block
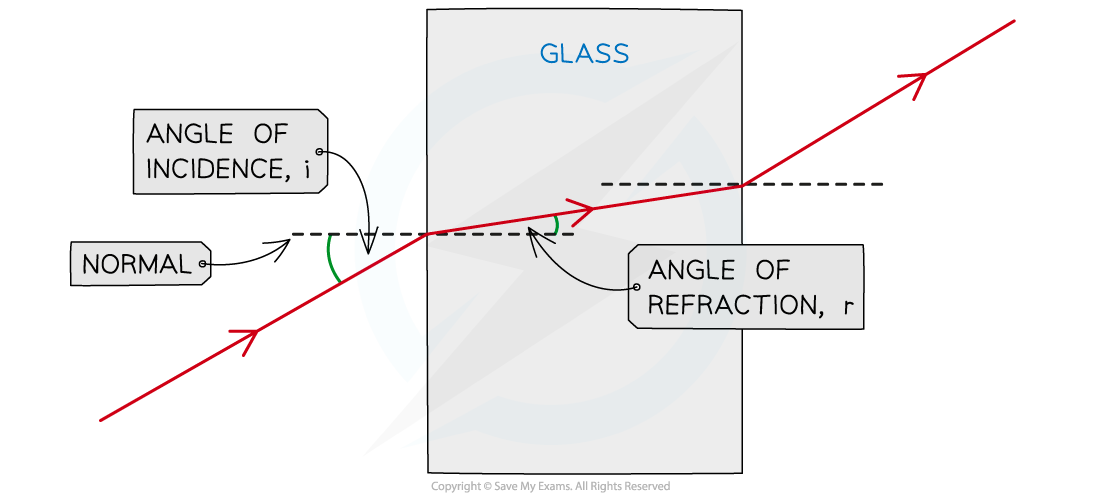
How to construct a ray diagram showing the refraction of light as it passes through a rectangular block
The change in direction occurs due to the change in speed when travelling in different substances
When light passes into a denser substance, the waves will slow down; hence, they bend towards the normal
The only properties that change during refraction are speed and wavelength – the frequency of waves does not change
Different frequencies account for different colours of light (red has a low frequency, whilst blue has a high frequency)
When light refracts, it does not change colour (think of a pencil in a glass of water), therefore, the frequency does not change
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Practice drawing refraction diagrams as much as you can! It's very important to remember which way the light bends when it crosses a boundary:
As the light enters the block it bends towards the normal line
Remember: Enters Towards
When it leaves the block it bends away from the normal line
Remember: Leaves Away
You only need to know about light passing through the boundaries between two media.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
