Contact & Non-Contact Forces (Oxford AQA IGCSE Physics) : Revision Note
Contact & Non-Contact Forces
What is a force?
A force is defined as:
A push or a pull that acts on an object due to the interaction with another object
Forces acting on objects can change the object's
Speed
Direction
Shape
For example:
The force exerted by an engine (thrust) can increase the speed of a vehicle
A comet’s direction can be affected by gravitational attraction
A spring can have its shape changed by the force from a heavy load
Effects of forces

All forces can be categorised into one of two types:
Contact forces
Non-contact forces
Contact forces
A contact force is defined as:
A force which acts between objects that are physically touching
Friction:
is a force that opposes motion
occurs when the surfaces of objects rub against each other
Drag:
is a type of friction
occurs when particles in a fluid (a gas or a liquid) collide with an object moving through a fluid
Air resistance:
is a type of friction and a type of drag
occurs when air particles collide with an object moving through air
Tension:
occurs when a pair of forces pull from opposite ends of an object
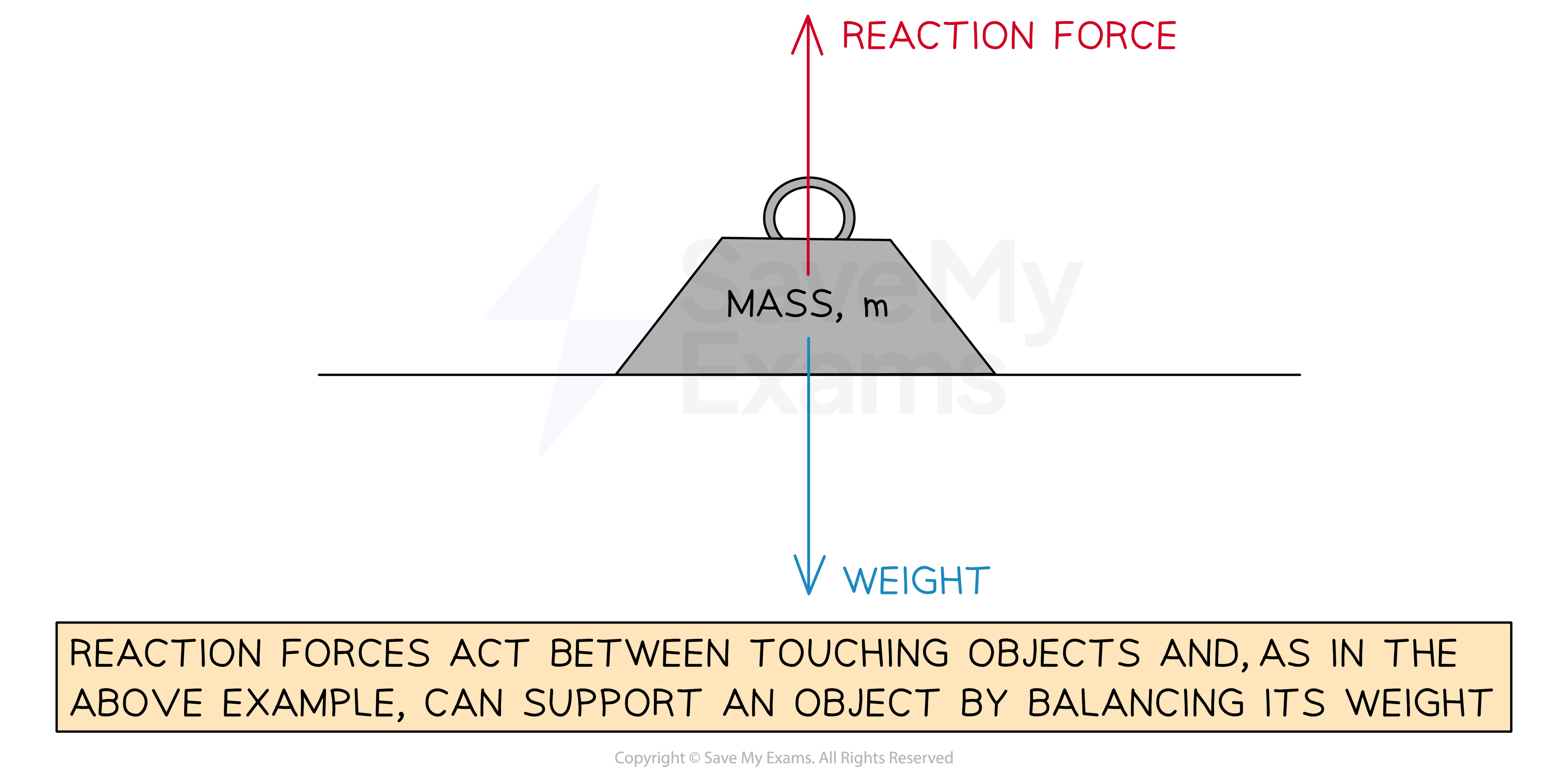
Normal contact force:
is sometimes called the reaction force
occurs when objects are supported by a surface
Friction and air resistance

Normal contact force
Non-contact forces
A non-contact force is defined as:
A force which acts at a distance, without any contact between bodies, due to the action of a field
All non-contact forces act at a distance due to the presence of fields
Weight:
is the force that acts on an object with mass when placed in a gravitational field
Electrostatic force:
is a force experienced by charged objects when placed in an electric field
For example, the attraction between a proton and an electron
Magnetic force:
is a force experienced by a magnetic pole when placed in a magnetic field
For example, the attraction between the North and South poles of magnets
Non-contact forces acting on objects

Worked Example
A child pulls a sledge by a rope as they climb up a snowy hill.
Describe the contact and non-contact forces involved in this scenario.
Answer:
Step 1: Identify the contact forces
The force of tension acts on the rope as the child pulls from one end and the sledge pulls from the other end
The normal contact force of the ground acts on the child and the sledge
The force of friction acts between the snow and the sledge as their surfaces rub past one another
The force of friction acts between the child's shoes and the ground as their surfaces rub past one another
The force of air resistance acts on the child and the sledge as they move through the air
Step 2: Identify the non-contact forces
The force of weight acts on the child and the sledge as they are both objects with mass in the Earth's gravitational field
Friction
Friction is a force that opposes the motion of an object
Friction slows down the motion of the object
Friction causes heating in the objects
Friction between solid surfaces is caused by imperfections in the surfaces of the objects moving over one another
Friction between solid surfaces

Gases and liquids are known as fluids
Fluids are different to solids because the particles in fluids can move around
Friction acts on objects moving through fluids as the particles collide with the object
This type of friction is called drag
Air resistance is a type of friction that slows the motion of an object moving specifically through air
Particles bump into the object as it moves through the air
As a result, the object heats up due to the work done against the frictional forces
Air resistance of a rocket through the atmosphere


You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

