Stopping Distance (Edexcel IGCSE Physics (Modular)) : Revision Note
Stopping distance
The stopping distance of a car is defined as:
The stopping distance of a car is the total distance travelled during the time it takes to stop in an emergency
The stopping distance is the sum of the distance travelled as the driver makes the decision to stop plus the distance travelled as the driver applies the brakes
Stopping distance formula
The stopping distance is calculated using the following formula:
Stopping distance = Thinking distance + Braking distance
Thinking distance
Thinking distance is defined as
Thinking distance is the distance travelled in the time it takes the driver to react to an emergency and prepare to stop
The main factors affecting thinking distance are:
The speed of the car
The reaction time of the driver
The reaction time is defined as:
A measure of how much time passes between seeing something and reacting to it
The average reaction time of a human is 0.25 s
Reaction time is increased by:
Tiredness
Distractions (e.g. using a mobile phone)
Intoxication (i.e. consumption of alcohol or drugs)
Braking distance
Braking distance is defined as
the distance travelled under the braking force in metres (m)
For a given braking force, the greater the speed of the vehicle, the greater the stopping distance
Calculating stopping distance
For a given braking force, the speed of a vehicle determines the size of the stopping distance
The greater the speed of the vehicle, the larger the stopping distance
The Effect of speed on stopping distance
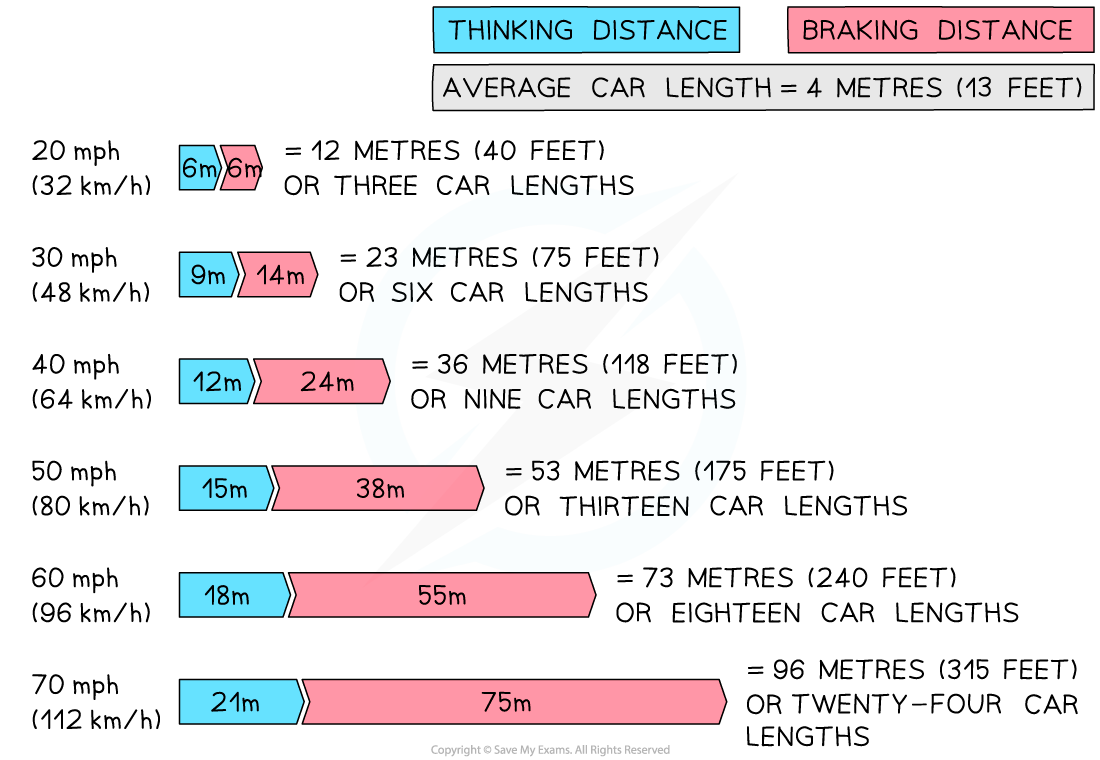
A vehicle's stopping distance increases with speed. At a speed of 20 mph the stopping distance is 12 m, whereas at 60 mph the stopping distance is 73 m (reproduced from the UK Highway Code)
A Table Showing Speed and Stopping Distance
Speed (mph) | Speed (m/s) | Stopping Distances (m) |
20 | 9 | 12 |
30 | 14 | 23 |
40 | 18 | 36 |
50 | 22 | 53 |
60 | 27 | 73 |
Worked Example
At a speed of 20 m/s, a particular vehicle had a stopping distance of 40 metres. The car travelled 14 metres whilst the driver was reacting to the incident in front of him.
What was the braking distance?
A 54 m
B 34 m
C 26 m
D 6 m
ANSWER: C
Step 1: Identify the different variables
Stopping distance = 40 m
Thinking distance = 14 m
Step 2: Rearrange the formula for stopping distance
Stopping distance = Thinking distance + Braking distance
Braking distance = Stopping distance – Thinking distance
Step 3: Calculate and identify the correct braking distance
Braking distance = 40 – 14
Braking distance = 26 metres
Therefore, the answer is C
Factors affecting stopping distance
There are various factors which can affect a vehicle's stopping distance
Vehicle speed
The greater the speed, the greater the vehicle's braking distance will be
This is because the brakes will need to do more work to bring the vehicle to a stop
Vehicle mass
The more massive the vehicle, the more distance it will travel as it comes to a stop
Road conditions
Wet or icy roads make the brakes less effective and the vehicle travels further as it comes to a stop
Driver reaction time
Thinking distance is increased if the driver is distracted, for example by a phone, satnav, radio or a person
Thinking distance is increased if the driver is tired, on certain types of medication, or is under the influence of alcohol or drugs

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

