Hooke's Law (Edexcel IGCSE Physics (Modular)): Revision Note
Exam code: 4XPH1
Hooke's law
The relationship between the extension of an elastic object and the applied force is defined by Hooke's Law
Hooke's Law states that:
The extension of an elastic object is directly proportional to the force applied, up to the limit of proportionality
Directly proportional means that as the force is increased, the extension increases
If the force is doubled, then the extension will double
If the force is halved, then the extension will also halve
The limit of proportionality is the point beyond which the relationship between force and extension is no longer directly proportional
This limit varies according to the material
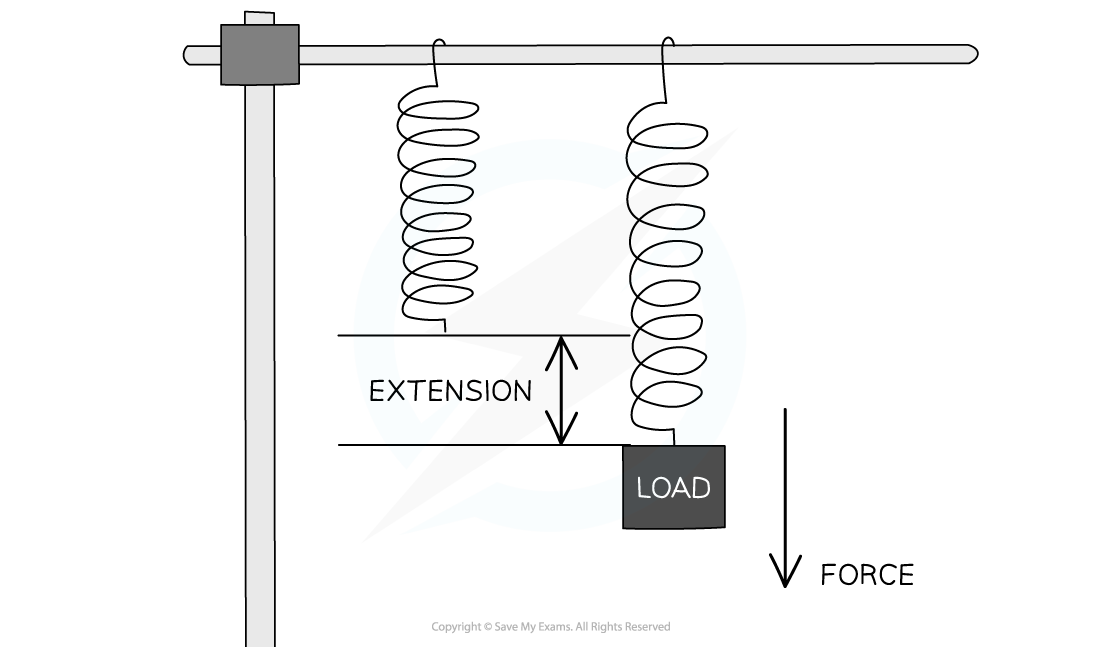
Hooke's Law states that a force applied to a spring will cause it to extend by an amount proportional to the force
The force-extension graph
Hooke’s law is the linear relationship between force and extension
This is represented by a straight line on a force-extension graph
Any material beyond its limit of proportionality will have a non-linear relationship between force and extension
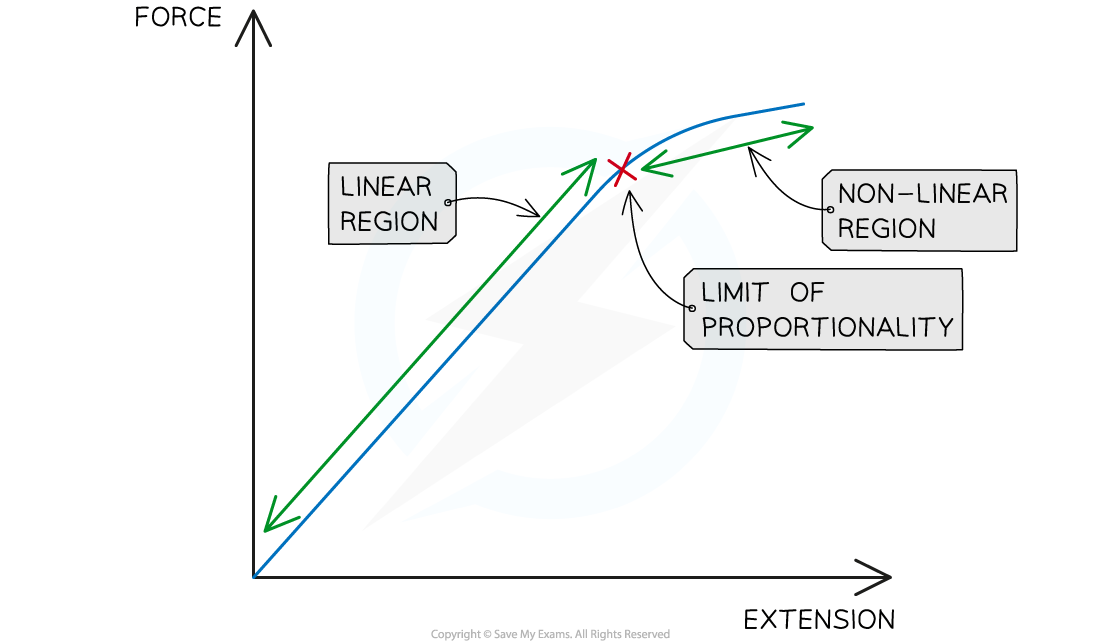
Hooke's Law is associated with the linear region of a force-extension graph. Beyond the limit of proportionality, Hooke's law no longer applies
Elastic behaviour
Elastic behaviour is the ability of a material to recover its original shape after the forces causing the deformation have been removed
Deformation is a change in the original shape of an object
Deformation can be either:
elastic
inelastic
Elastic Deformation
Elastic deformation is when the object does return to its original shape after the deforming forces are removed
Elastic deformation results in a change in the object's shape that is not permanent
Examples of materials that undergo elastic deformation are:
Rubber bands
Fabrics
Steel springs
Inelastic Deformation
Inelastic deformation is when the object does not return to its original shape after the deforming forces are removed
Inelastic deformation results in a change in the object's shape that is permanent
Examples of materials that undergo inelastic deformation are:
Plastic
Clay
Glass
Elastic behaviour of a spring

The spring on the right has undergone inelastic deformation, it's shape has been permanently deformed

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?