Kinetic Energy (Edexcel IGCSE Physics (Modular)) : Revision Note
Kinetic energy
Energy in an object's kinetic store is defined as:
The amount of energy an object has as a result of its mass and speed
This means that any object in motion has energy in its kinetic energy store
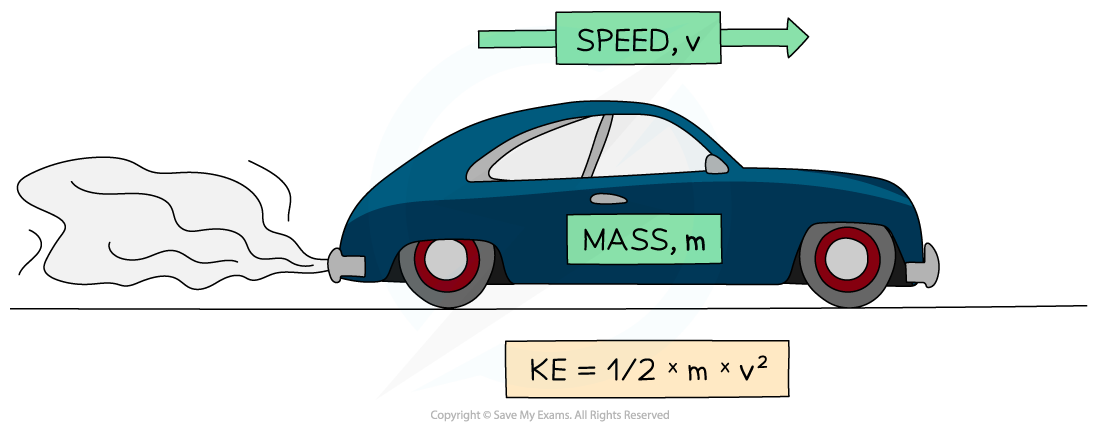
Kinetic energy can be calculated using the equation:
Where:
KE = kinetic energy in joules (J)
m = mass of the object in kilograms (kg)
v = speed of the object in metres per second (m/s)
Worked Example
Calculate the kinetic energy stored in a vehicle of mass 1200 kg moving at a speed of 27 m/s.
Step 1: List the known quantities
Mass of the vehicle, m = 1200 kg
Speed of the vehicle, v = 27 m/s
Step 2: Write down the equation for kinetic energy
Step 3: Calculate the kinetic energy
Step 4: Round the final answer to 2 significant figures
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When performing calculations using the kinetic energy equation, always double-check that you have squared the speed. Forgetting to do this is the most common mistake that students make.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?

