Electric Charge (Edexcel IGCSE Physics (Modular)) : Revision Note
Electric forces between charges
The charge of a particle can be:
positive
negative
neutral (no charge)
Electrons are negatively charged particles, whilst protons are positive and neutrons are neutral
This is why in a neutral atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons
This is so the equal (but opposite) charges cancel out to make the overall charge of the atom zero
Diagram of a model of an atom
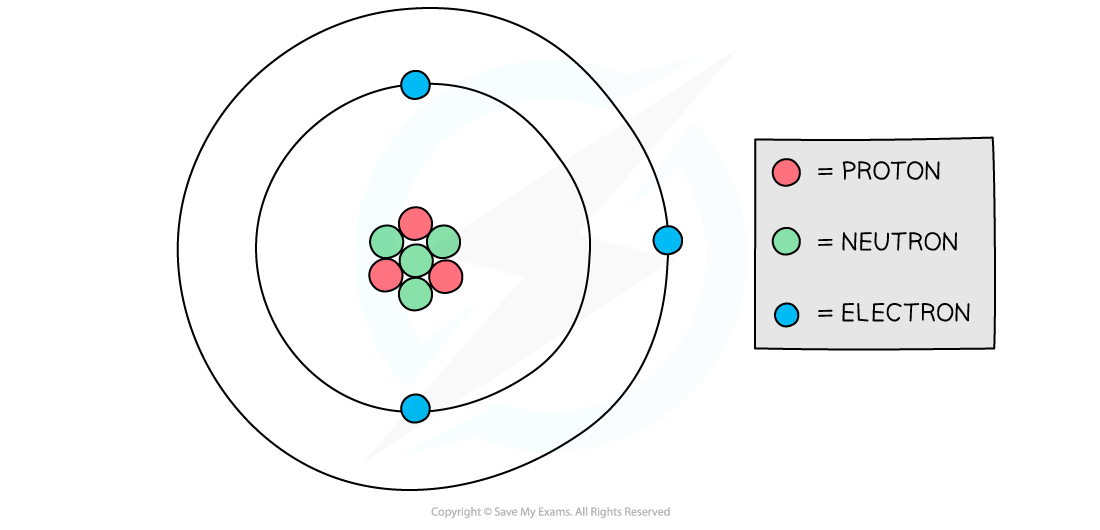
The number of negative electrons in an atom balances the number of positive protons
Therefore, an object becomes negatively charged when it gains electrons and positively charged when it loses electrons
When two charged particles or objects are close together, they also exert a force on each other
This force could be:
Attractive (the objects get closer together)
Repulsive (the objects move further apart)

Opposite charges attract, like charges repel
Whether two objects attract or repel depends on their charge
If the charges are the opposite, they will attract
If the charges are the same, they will repel – charges which are the same (e.g. both positive) are often referred to as like charges
The force is stronger if the objects are closer together
Attraction or repulsion summary table
Charge of object 1 | Charge of object 2 | Attract or repel? |
positive | positive | repel |
positive | negative | attract |
negative | positive | attract |
negative | negative | repel |
Attraction and repulsion between two charged objects are examples of a non-contact force
This is a force that acts on an object without being physically in contact with it
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember the saying “opposites attract” when answering questions about forces between charged particles.
Production of static
Static electricity refers to the accumulation of charge on an object, which then attracts other objects or can even produce sparks
When certain insulating materials are rubbed against each other they become electrically charged
This is called charging by friction
The charges remain on the insulators and cannot immediately flow away
One becomes positive and the other negative
An example of this is a plastic or polythene rod being charged by rubbing it with a cloth
Both the rod and cloth are insulating materials

A polythene rod may be given a charge by rubbing it with a cloth
This occurs because negatively charged electrons are transferred from one material to the other
The material, in this case, the rod, gains electrons
Since electrons are negatively charged, the rod becomes negatively charged
As a result, the cloth has lost electrons and therefore is left with an equal positive charge
Examiner Tips and Tricks
At this level, if asked to explain how things gain or lose charge, you must discuss electrons and explain whether something has gained or lost them. Remember when charging by friction, it is only the electrons that can move, not any 'positive' charge, therefore if an object gains a negative charge, something else must have gained a positive charge by losing negative electrons.
Movement of electrons
All objects are initially electrically neutral, meaning the negative and positive charges are evenly distributed
However, when the electrons are transferred through friction, one object becomes negatively charged and the other positively charged
The object the electrons are transferred to becomes negatively charged
The object the electrons transfer from becomes positively charged
This difference in charges leads to a force of attraction between itself and other objects which are also electrically neutral
This is done by attracting the opposite charge to the surface of the objects they are attracted to
In the example below, when the cloth and acetate rod are rubbed together, the electrons are transferred from the rod to the cloth
This results in an attractive force between the two objects once separated

Electrons are transferred from the rod to the cloth as they are rubbed together. This leaves the cloth negatively charged and the rod positively charged

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

