Doppler Shift (Edexcel IGCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 4PH1
Doppler shift
Usually, when an object emits waves, the wavefronts spread out symmetrically
If the wave source moves, the waves can become squashed together or stretched out
Therefore, when a wave source moves relative to an observer there will be a change in the observed frequency and wavelength
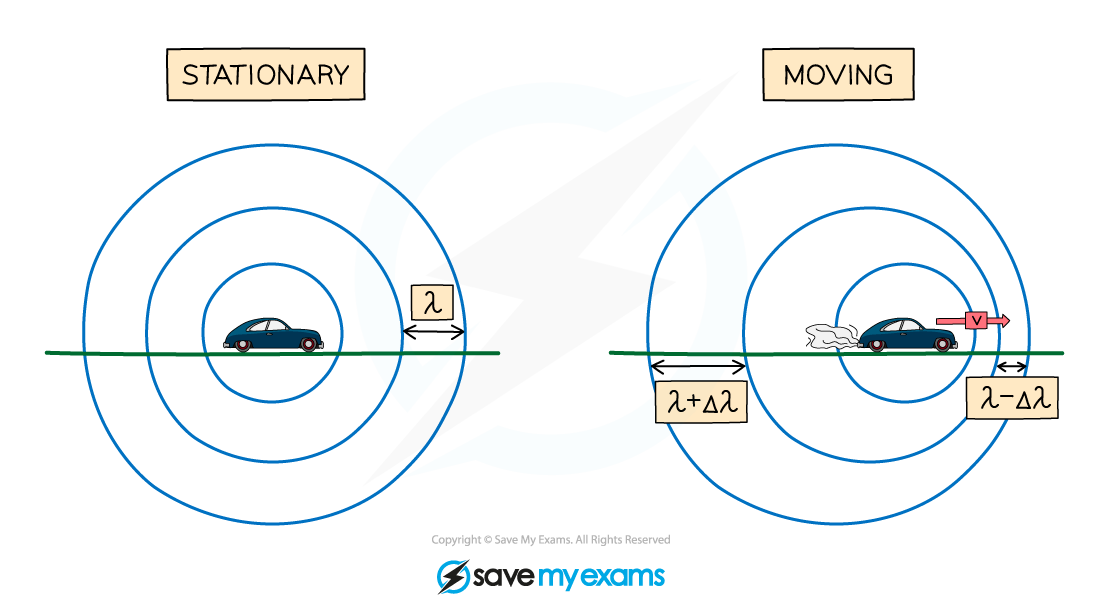
Wavefronts are even in a stationary object but are closer together in the direction of the moving wave source
A moving object will cause the wavelength, λ, (and frequency) of the waves to change:
The wavelength of the waves in front of the source decreases (λ – Δλ) and the frequency increases
The wavelength behind the source increases (λ + Δλ) and the frequency decreases
This effect is known as the Doppler effect or Doppler shift
Note: Δλ means 'change in wavelength'
Calculating Doppler shift of light
Doppler shift can be calculated using the Doppler effect equation:
Where:
λ = observed wavelength of the source in metres (m)
λ0 = reference wavelength in metres (m)
Δλ = change in wavelength in metres (m)
v = velocity of a galaxy in metres per seconds (m/s)
c = the speed of light in metres per second (m/s)
This means that the change in wavelength, Δλ:
Δλ = λ – λ0
The doppler shift equation can be used to calculate the velocity of a galaxy if its wavelength can be measured and compared to a reference wavelength
Since the fractions have the same units on the numerator (top number) and denominator (bottom number), the Doppler shift has no units
Worked Example
Light emitted from a star has a wavelength of 435 × 10-9 m. A distance galaxy emits the same light but has a wavelength of 485 × 10-9 m.
Calculate the speed at which the galaxy is moving relative to Earth.
The speed of light = 3 × 108 m/s.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Observed wavelength, λ = 485 × 10−9 m
Reference wavelength, λ0 = 435 × 10−9 m
Step 2: Write out the Doppler effect equation
Step 3: Rearrange for the relative speed of the galaxy, v
Step 4: Substitute the values into the equation for v
Examiner Tips and Tricks
This Doppler effect equation will be provided for you in the exam, but make sure you understand how to use it, in particular, make sure you know the difference between shifted λ and unshifted λ0 wavelength terms and get lots of practice using it

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?