Changes of State (Edexcel IGCSE Physics) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Changes of state
When a solid is heated it melts to form a liquid
Thermal energy transfer takes place and supplies the particles in the solid with energy in their kinetic store
This breaks the rigid bonds between the particles meaning they can now flow over each other
When a liquid is heated it evaporates to form a gas
Thermal energy transfer takes place and supplies the particles on the surface of the liquid with energy in their kinetic store
This removes the bonds between the particles meaning they can move about randomly and spread far apart
When a liquid boils to form a gas bubbles are produced within the liquid
Particles do not evaporate from the surface
Changing between states of matter

Changing the temperature of a solid, liquid or gas changes its state
Heat & temperature
Heating a system will change the energy stored in a system by increasing the kinetic energy of its particles
The temperature of the material, therefore, is related to the average kinetic energy of the molecules
This increase in kinetic energy (and therefore energy stored in the system) can:
Cause the temperature of the system to increase
Or, produce a change of state (solid to liquid or liquid to gas)
The higher the temperature, the higher the average kinetic energy of the molecules and vice versa
This means they move around faster
The relationship between temperature and internal energy
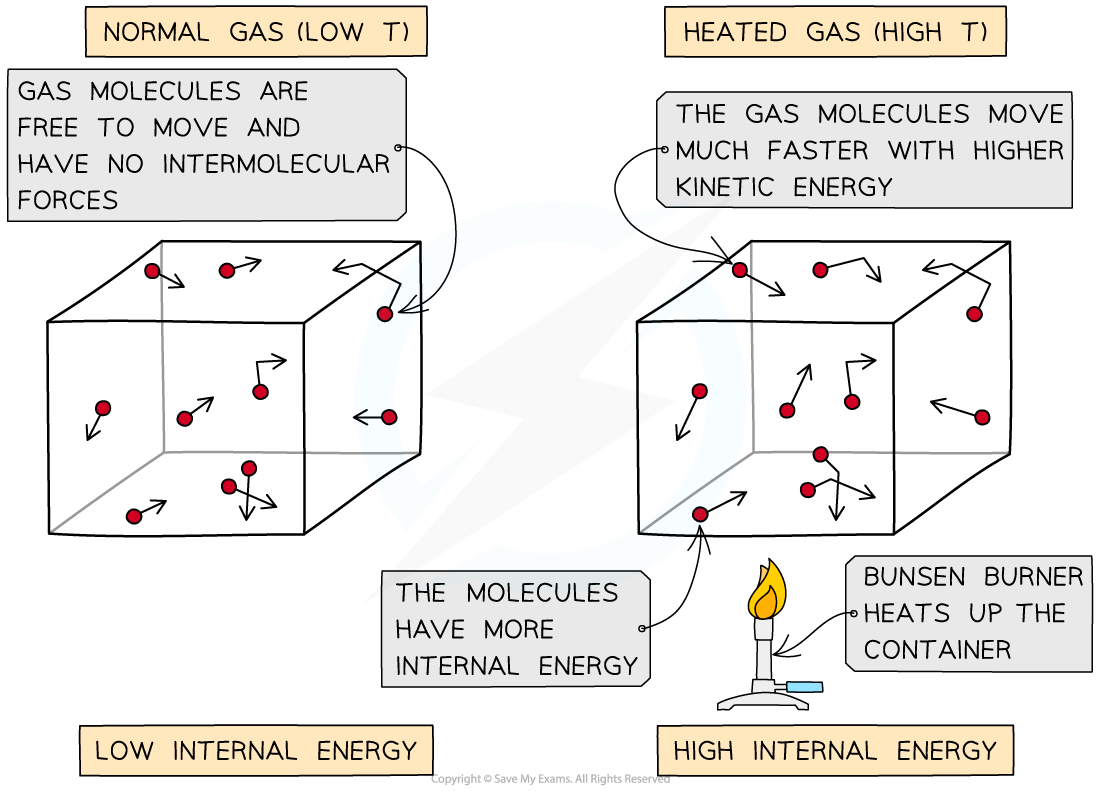
As the container is heated up, the gas molecules move faster with higher kinetic energy. The energy stored within the system - the internal energy - therefore increases
Worked Example
A student measures the mass of a beaker of water twice, leaving 24 hours between the readings. The temperature in the room remained constant between readings, however, they notice a decrease in the mass of the beaker of water.

Which of the following is not a correct conclusion that can be drawn from the experiment?
A The difference in mass is equal to the mass of the water that evaporated
B The total energy within the beaker decreased
C The density of water in the air increased
D The total number of water molecules in the air and water decreased
Answer: D
A is true because the mass lost from the beaker is due to those water molecules evaporating
B is true because evaporation causes the most energetic particles to leave the beaker
The total number of particles in the beaker decreased
C is true because additional water molecules were added to the air, without a significant change in the volume of the air
D is not true because no mass is lost during evaporation - it is only changed from a liquid to a gas state
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Heating a system will always increase the energy stored within the system. Remember this increase in 'internal energy' can have two effects: either the temperature of the system will increase, or the system will change state (e.g. from a solid to a liquid, or a liquid to a gas)

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
