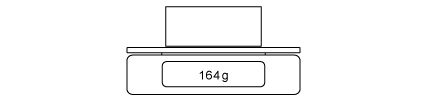
Extended tier only
Explain the difference between speed and velocity
Extended tier only
Identify the scalar quantities.
Tick all the boxes that apply.
time
weight
acceleration
distance
Extended tier only
State:
(i) one example of a vector quantity.
[1]
(ii) one other example of a scalar quantity.
[1]
Extended Only
Fig. 1.1 shows a vector diagram for the effects of two forces.

Fig. 1.1
Calculate the resultant force.
resultant force = ....................................
Was this exam question helpful?