Five identical spheres are placed between two blocks in order to measure their diameter.

What is the diameter of a single sphere?
2.0 cm
2.1 cm
2.2 cm
2.3 cm
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: 0625 & 0972
Select a download format for Physical Quantities & Measurement Techniques
Select an answer set to view for
Physical Quantities & Measurement Techniques
Five identical spheres are placed between two blocks in order to measure their diameter.

What is the diameter of a single sphere?
2.0 cm
2.1 cm
2.2 cm
2.3 cm
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A student wants to take a particularly accurate measurement of the volume of liquid in a measuring cylinder.
Which of the following procedures would make her measurement less accurate?
Aligning her eye level with the height of the liquid in the cylinder.
Reading the liquid level from the bottom of the meniscus.
Using the largest measuring cylinder she could find.
Using a set-square to make sure the cylinder is perfectly vertical.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A student is timing the rate of cooling of a beaker of water. On a repeat run of the investigation, the student forgets to zero the stopwatch.
The readings on the stopwatch at the start time and the end time are shown in Fig. 1.1

Calculate how long it took the beaker to cool.
11 minutes
11 minutes and 8 seconds
12 minutes
12 minutes and 8 seconds
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Extended tier only
Identify the physical quantity that is not scalar.
speed
time
weight
energy
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Extended tier only
Identify the physical quantity that is a scalar.
weight
distance
velocity
acceleration
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A lump of modelling clay is moved from a small measuring cylinder to a large measuring cylinder that has twice the diameter.
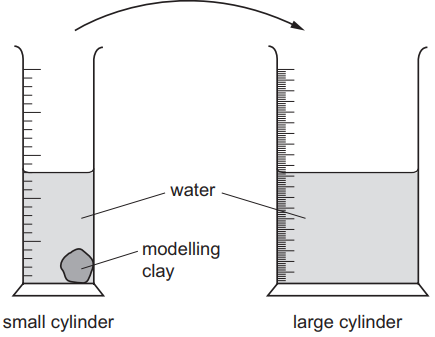
The reading on the small measuring cylinder goes down by 20 cm3.
By how much does the reading on the large cylinder go up?
10 cm3
20 cm3
40 cm3
80 cm3
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which measuring devices are most suitable for determining the length of a swimming pool and the thickness of aluminium foil?
| length of a swimming pool | thickness of aluminium foil |
A | ruler | measuring cylinder |
B | tape measure | micrometer screw gauge |
C | tape measure | ruler |
D | ruler | micrometer screw gauge |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A person wishes to roast a chicken. The chicken requires 1 hour and 20 minutes in the oven to be properly cooked.
The oven must be switched on 10 minutes before any food is put in, in order to pre-heat, and reach the correct temperature for cooking.
The chicken needs to be ready at 4:30 pm. At what time must the oven be switched on?
2:00 pm
2:10 pm
3:00 pm
3:10 pm
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A particularly diligent student wants to measure the volume of some liquid for an experiment. She has two measuring cylinders available, a large 250 ml one and a small 50 ml one. The liquid will fit into either of the two measuring cylinders.
As expected, the liquid forms a meniscus where it touches the sides of either measuring cylinder.
Which cylinder should the student use to get the most accurate result, and from where should she measure the liquid level?
| Measuring cylinder | Reading taken from |
A | large | Top of meniscus |
B | large | Bottom of meniscus |
C | small | Top of meniscus |
D | small | Bottom of meniscus |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A geologist wants to measure the volume of a particularly interesting pebble she has found in a river.
She uses the apparatus shown below.

What is the volume of the pebble?
6 cm3
11 cm3
17 cm3
23 cm3
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A scientist is trying to determine the volume of three identical pieces of a new material. She places them in a measuring cylinder, as shown in the diagram.
The first cylinder shows the level of water in the measuring cylinder before the pieces are added, and the second cylinder shows the measuring cylinder with the pieces of the new material inside.

What is the volume of each piece of the new material?
13.3 cm3
16.7 cm3
30.0 cm3
40.0 cm3
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A length of string is measured between two points on a ruler.
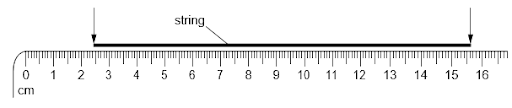
When the length of string is wound closely around a pen, it goes round six times.
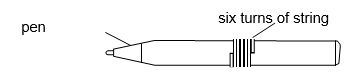
What is the distance once round the pen?
2.2 cm
2.6 cm
13.2 cm
15.6 cm
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Extended Tier Only
On the diagram shown, what is the magnitude of the resultant force of the two vectors?
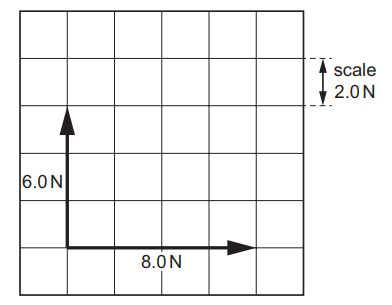
2.0 N
7.0 N
10 N
14 N
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Three blocks are placed into three measuring cylinders. These are shown below.

Which row in the table shows the blocks in order of increasing volume?
| Smallest volume | → | Largest volume |
A | X | Y | Z |
B | Y | X | Z |
C | Z | Y | X |
D | Z | X | Y |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A student is trying to see how quickly they can run 5.0 km on a standard 400 m running track.
They reason that, if they know how fast they can run one lap, they can assume they will run at the same speed for 5.0 km, and can calculate their predicted time.
They, correctly, reason that they will not be able to maintain their initial pace throughout the whole 5.0 km, so they decide to time lap 5.
The diagram shows the reading on the stopwatch at the beginning and the end of lap 5.

Calculate how long it should take the student to run 5.0 km.
36 minutes 52.5 seconds
24 minutes 22.5 seconds
13 minutes 0 seconds
9 minutes 45 seconds
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
An Olympic cyclist rides around a velodrome track 5 times.
The diagram below shows the reading on the stopwatch, which was used to time the laps. Unfortunately, the person using the stopwatch started it a little early, so the stopwatch reads 2 seconds when the cyclist starts.

What is the average time to complete one lap of the velodrome?
16.24 s
14.04 s
15.84 s
15.21 s
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A student uses a ruler to determine the circumference of a wooden dowel.
She puts a mark onto the dowel, then rolls it along the ruler three times, before reading the position on the ruler at which it stopped.

What is the circumference of the dowel?
12 cm
12.3 cm
37 cm
36 cm
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?