Electric Charge (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 0625 & 0972
Did this video help you?
Positive & negative charges
There are two types of electric charge: positive and negative
Inside an atom, there are
negatively charged electrons
positively charged protons
neutral (no charge) neutrons
Atoms contain equal numbers of protons and electrons as they have equal and opposite charges
These charges cancel out so the overall charge of an atom is zero
Structure of an atom
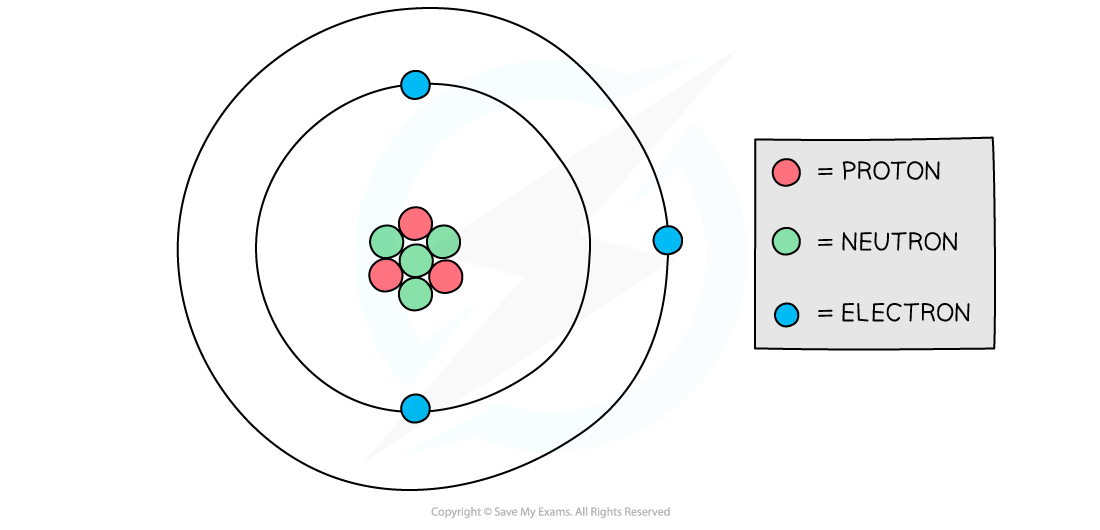
The number of negative electrons in an atom balances the number of positive protons
Attraction and repulsion
When two charges are close together, they exert a force on each other, this could be:
Attractive (the objects get closer together)
Repulsive (the objects move further apart)
Electric forces between charges

Opposite charges attract, like charges repel
Whether two objects attract or repel depends on their charge
If the charges are the opposite, they will attract
If the charges are the same, they will repel
Attraction or repulsion summary table
Charge of object 1 | Charge of object 2 | Attract or repel? |
|---|---|---|
positive | positive | repel |
positive | negative | attract |
negative | positive | attract |
negative | negative | repel |
The table shows that:
Positive charges repel other positive charges and attract negative charges
Negative charges repel other negative charges and attract positive charges
Extended tier only
Electric charge is measured in units called coulombs (C)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember the saying “opposites attract” when answering questions about forces between charged particles.
While electrostatic forces share many similarities with magnetic forces, they are different phenomena – do not confuse the two!

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?