Acceleration (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 0625 & 0972
Did this video help you?
Acceleration
Extender tier only
Acceleration describes how the velocity of an object changes over time
Acceleration is defined as:
The rate of change of velocity
In other words, acceleration is the change in velocity per unit time
The acceleration of an object is often changing throughout an object's journey
Therefore, is it often useful to know the average acceleration
Where:
= acceleration in metres per second squared (m/s2)
= change in velocity in metres per second (m/s)
= time taken in seconds (s)
Formula triangle for acceleration, change in velocity and change in time

To use a formula triangle, simply cover up the quantity you wish calculate and the structure of the equation is revealed
Information on how to use a formula triangle can be found in Speed & velocity
Change in velocity
The change in velocity is the difference between the initial and final velocity:
Where:
= change in velocity in metres per second (m/s)
= final velocity in metres per second (m/s)
= initial velocity in metres per second (m/s)
Speeding up & slowing down
An object can change its velocity in several ways:
speeding up
slowing down
changing direction
Any change in an object's velocity is an acceleration
When an object speeds up, it is accelerating
This is positive acceleration
When an object slows down, it is decelerating
This is negative acceleration
Acceleration is positive if its direction is in the same direction as the motion of the object
Acceleration of different objects
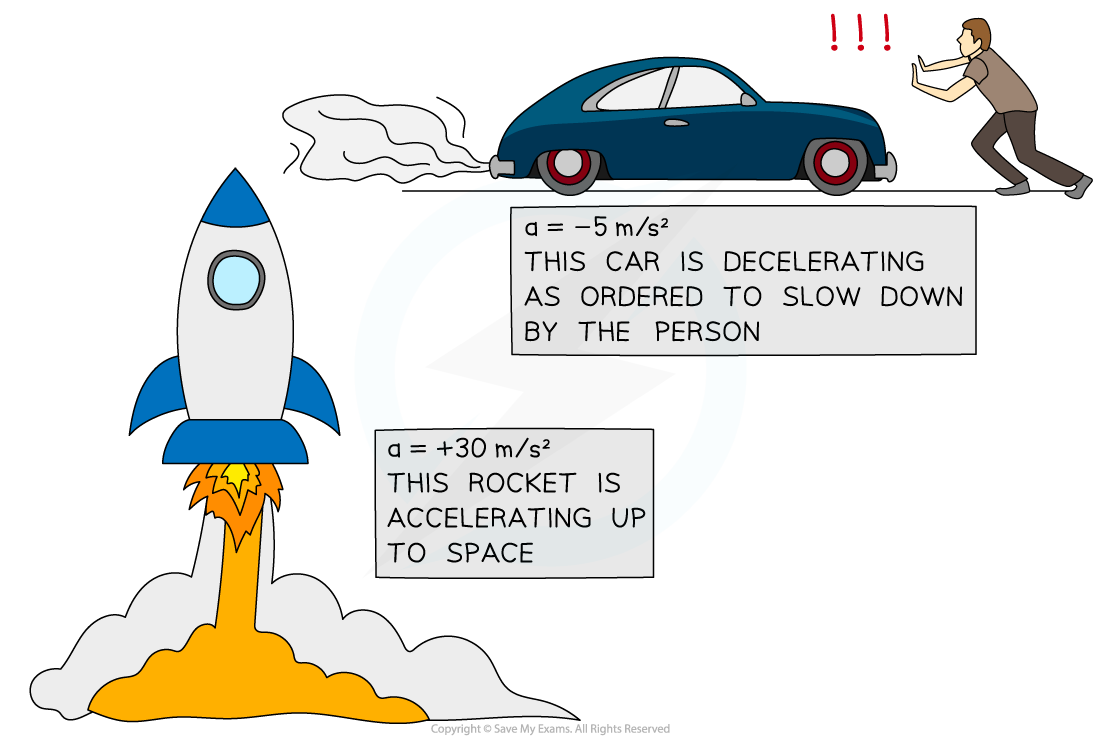
A rocket speeding up (accelerating) and a car slowing down (decelerating)
Worked Example
A Japanese bullet train decelerates at a constant rate in a straight line. The velocity of the train decreases from 50 m/s to 42 m/s in 30 seconds.
(a) Calculate the change in velocity of the train.
(b) Calculate the deceleration of the train, and explain how your answer shows the train is slowing down.
Answer:
Part (a)
Step 1: List the known quantities
Initial velocity,
Final velocity,
Step 2: Write the equation for change in velocity
Step 3: Substitute values for final and initial velocity
Part (b)
Step 1: List the known quantities
Change in velocity,
Time taken,
Step 2: Write the equation for acceleration
Step 3: Substitute the values for change in velocity and time
Step 4: Interpret the value for deceleration
The answer is negative, which indicates the train is slowing down
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember, the units for acceleration are metres per second squared, m/s2. In other words, acceleration measures how much the velocity (m/s) changes every second, so the units are metres per second per second (m/s/s).

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?