Scalars & Vectors (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 0625 & 0972
Did this video help you?
Scalar & vector quantities
Extended tier only
All quantities can be one of two types:
A scalar
A vector
Scalars
Scalar quantities have only a magnitude
Mass is an example of a scalar quantity because it has magnitude without direction
Energy and volume are also examples of scalar quantities
Vectors
Vector quantities have both magnitude and direction
Weight is an example of a vector quantity because it is a force and therefore has both magnitude and direction
Acceleration and momentum are also examples of vector quantities
Distance and displacement
Distance is a measure of how far an object has travelled, regardless of direction
Distance is the total length of the path taken
Distance, therefore, has a magnitude but no direction
So, distance is a scalar quantity
Displacement is a measure of how far it is between two points in space, including the direction
Displacement is the length and direction of a straight line drawn from the starting point to the finishing point
Displacement, therefore, has a magnitude and a direction
So, displacement is a vector quantity
What is the difference between distance and displacement?
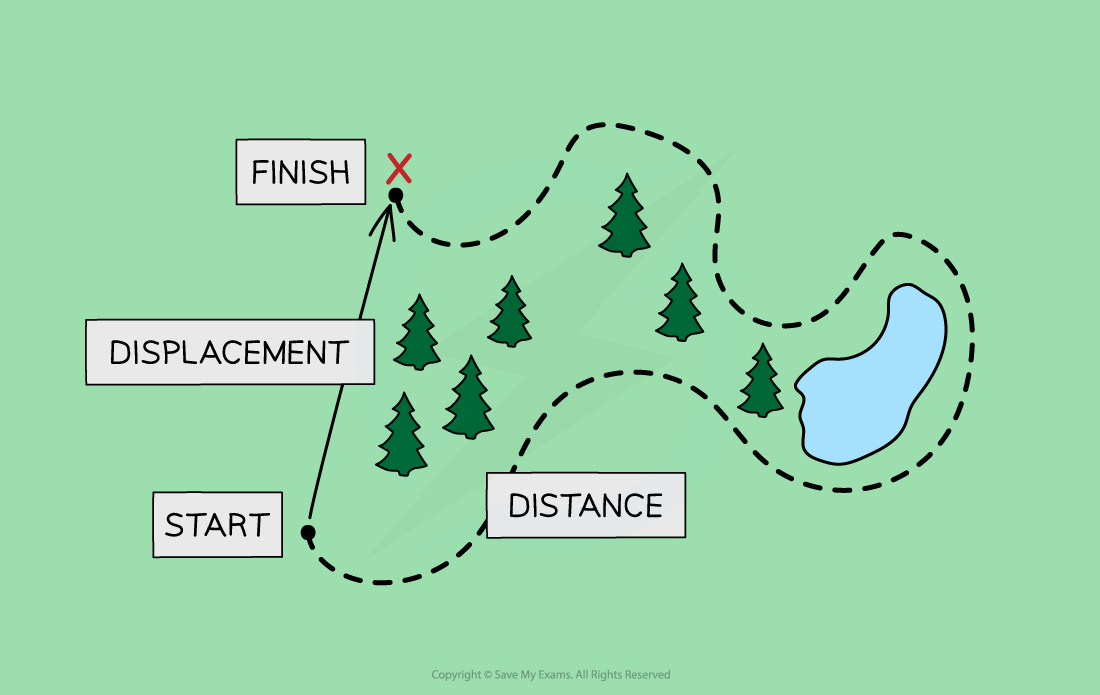
Displacement is a vector quantity, while distance is a scalar quantity
When a student travels to school, there will probably be a difference between the distance they travel and their displacement
The overall distance they travel includes the total lengths of all the roads, including any twists and turns
The overall displacement of the student would be a straight line between their home and school, regardless of any obstacles, such as buildings, lakes or motorways, along the way
Speed and velocity
Speed is a measure of the distance travelled by an object per unit time, regardless of the direction
The speed of an object describes how fast it is moving, but not the direction it is travelling in
Speed, therefore, has magnitude but no direction
So, speed is a scalar quantity
Velocity is a measure of the displacement of an object per unit time, including the direction
The velocity of an object describes how fast it is moving and which direction it is travelling in
An object can have a constant speed but a changing velocity if the object is changing direction
Velocity, therefore, has magnitude and direction
So, velocity is a vector quantity
Examples of scalars & vectors
Extended tier only
The table below lists some common examples of scalar and vector quantities
Corresponding scalars and their vector counterparts are aligned in the table where applicable
Table of scalars and vectors
Scalar | Vector |
|---|---|
distance | displacement |
speed | velocity |
mass | weight |
| force |
| acceleration |
| momentum |
| electric field strength |
energy |
|
volume |
|
density |
|
temperature |
|
power |
|
Worked Example
An instructor is in charge of training junior astronauts. For one of their sessions, they would like to explain the difference between mass and weight.
Suggest how the instructor should explain the difference between mass and weight, using definitions of scalars and vectors in your answer.
Answer:
Step 1: Recall the definitions of a scalar and vector quantity
Scalars are quantities that have only a magnitude
Vectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction
Step 2: Identify which quantity has magnitude only
Mass is a quantity with magnitude only
So mass is a scalar quantity
The instructor might explain to their junior astronauts that their mass will not change as their location in the Universe changes
Step 3: Identify which quantity has magnitude and direction
Weight is a quantity with magnitude and direction (it is a force)
So weight is a vector quantity
The instructor might explain that their weight, the force on them due to gravitational field strength, will vary depending on their location. For example, the force of weight acting on them would be less on the Moon than it is on Earth
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure you are comfortable with the differences between similar scalars and vectors.
The most commonly confused pairings tend to be:
distance and displacement
speed and velocity
weight and mass

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?