Position & Displacement Vectors (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Maths) : Revision Note
Position & Displacement Vectors
What are position vectors?
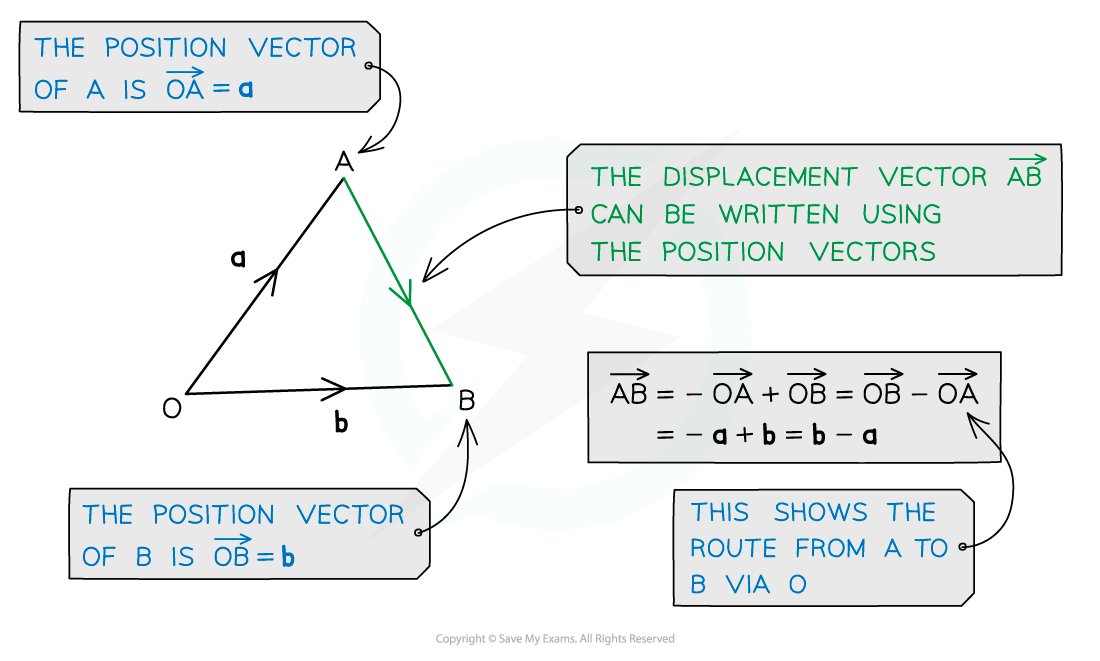
A position vector describes where a specific point, A , is, relative to a fixed origin, O
Lower-case bold (or underlined) letters are used
The point A has position vector a =
Their components are equal to their coordinates
The point with coordinates (3, -2) has position vector
from the origin
What are displacement vectors?
A displacement vector describes the direction and distance between two points
The displacement vector from A to B is
How to get from A to B
If the points A and B have position vectors a and b relative to O
then A to B is the same as A to O (-a) followed by O to B (b)
This is a useful rule to remember
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You may need to draw an origin, O , on to a diagram to be able to sketch position vectors.
Worked Example
The points and
have position vectors
and
respectively.
Find and simplify the vector .
Let and
be position vectors of P and Q
is the displacement vector from P to Q
Use the rule that
Substitute in and
Expand and simplify
You can also get this answer by seeing what vector must be added to to get

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

