Did this video help you?
Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2023
First exams 2025
Distance-Time & Speed-Time Graphs (CIE IGCSE Maths: Extended)
Revision Note
Distance-Time Graphs
How does a distance-time graph work?
- Distance-time graphs show distance from a fixed point at different times
- Distance is on the vertical axis, and time is on the horizontal axis.
- The gradient of the graph is the speed
- A positive gradient represents the object (or person) moving away from the starting point
- If the graph is a horizontal line the object is stationary (not moving)
- A negative gradient represents the object (or person) moving towards the starting point
- If the graph is a straight line the speed is constant
- If the graph is a curve you can draw the tangent at a point on the graph and find its gradient
- This will be an estimate of the speed at that point
Examiner Tip
- It is easy to get confused between different types of graph.
- Look at the label on the vertical axis to make sure you are looking at a DISTANCE-time graph (not speed-time)
Worked example
One afternoon Mary cycled to her grandparents' house, 8 km from her own home.
Part of her travel graph for her journey is shown below.

Mary stayed at her grandparents' house for half an hour.
She then cycled home at a steady speed, without stopping, arriving home at 4 pm.


Did this video help you?
Speed-Time Graphs
What is a speed-time graph?
- Speed-time graphs show speed at different times
- Speed is on the vertical axis, and time is on the horizontal axis
- The gradient of the graph is the acceleration
-
- If the graph is a curve you can draw the tangent at a point on the graph and find its gradient
- This will be an estimate of the acceleration at that point
- A positive gradient shows positive acceleration (speeding up)
- A horizontal line on a speed-time graph shows constant speed (no acceleration)
- A negative gradient shows negative acceleration, or deceleration (slowing down)
- The distance covered can be found by finding the area under the graph
Examiner Tip
- It is easy to get confused between different types of graph.
- Look at the label on the vertical axis to make sure you are looking at a SPEED-time graph (not distance-time)
Worked example
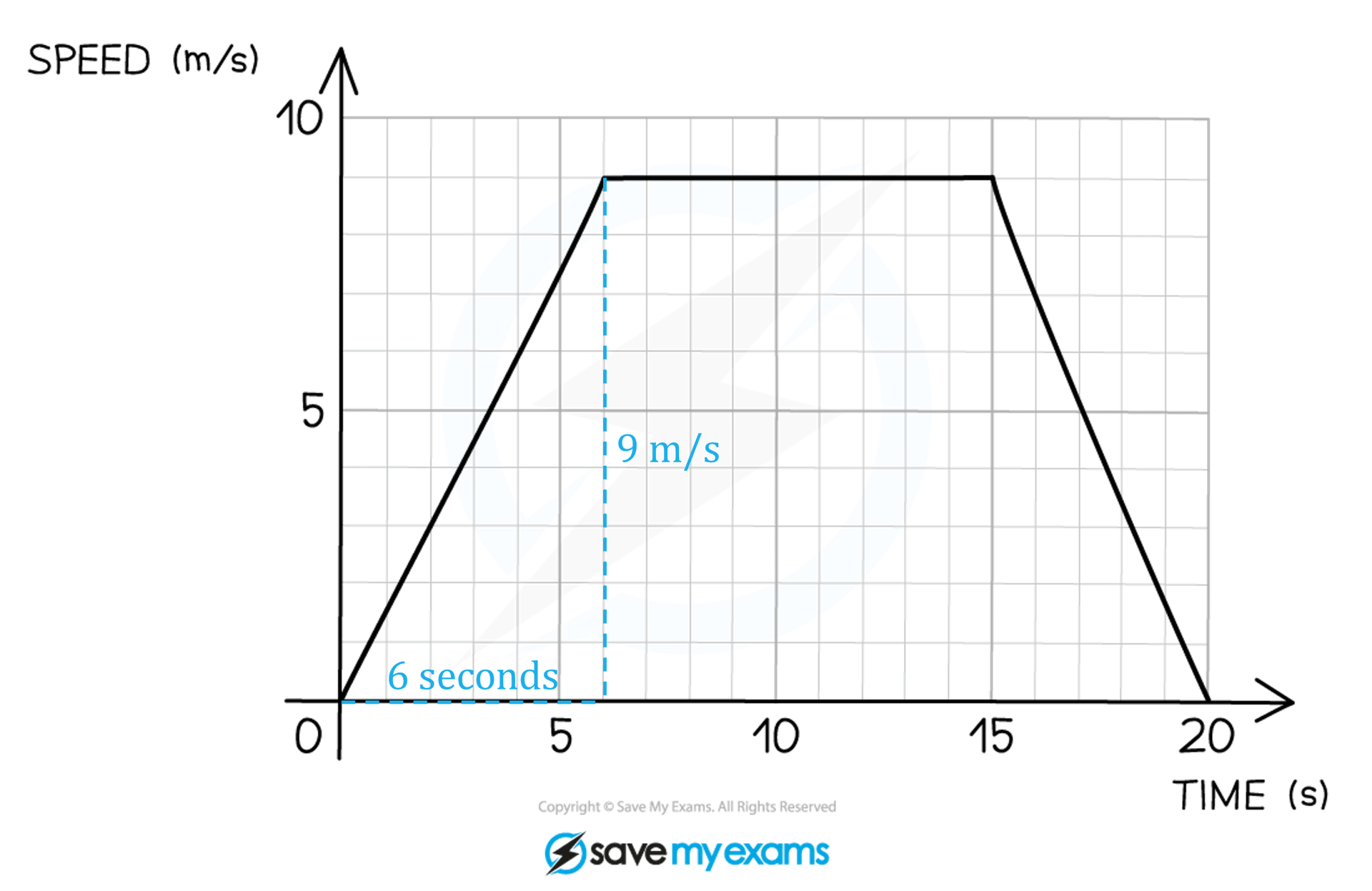
The speed-time graph for a car travelling between two sets of traffic lights is shown below.


You've read 0 of your 10 free revision notes
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
