Differentiation (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 0580 & 0980
Did this video help you?
Differentiation
What is a gradient function?
Recall that the equation of a curve gives the y-coordinate of a point when you substitute in its x-coordinate
For example,
Substitute
in to get
The point
lies on the curve
A gradient function gives the gradient of the curve at a point when you substitute in its x-coordinate
A gradient function is written as
pronounced "dy by dx"
This refers to the change in y over change in x
For example, the gradient function
Substitute
in to get
The gradient at the point where
is 7
The gradient function
can also be called the derivative or derived function
What is differentiation and how does it work?
Differentiation is an algebraic method that changes the equation of a curve,
, into a gradient function,
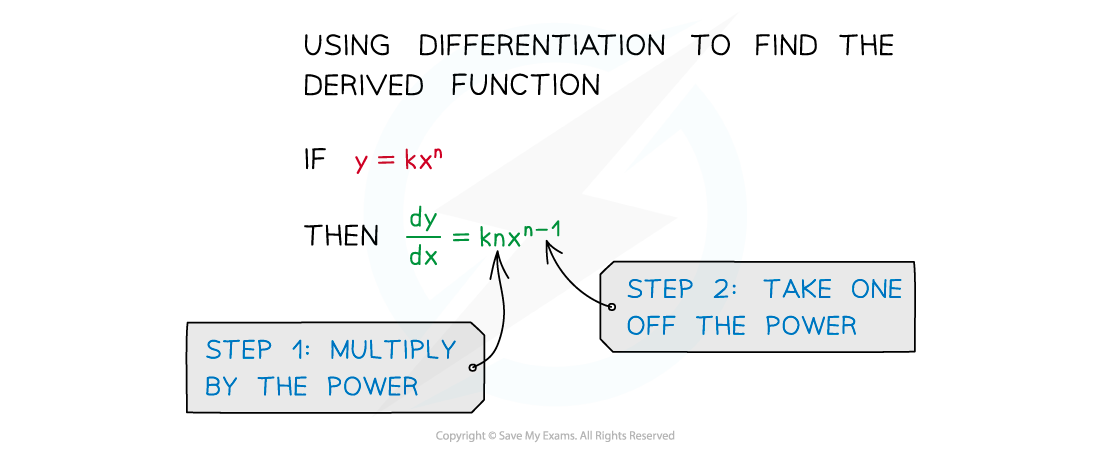
To differentiate a power of
, bring down the power and reduce the power by 1
Differentiating
gives
Differentiating
gives
Differentiating
gives
Any number that is already in front of
is multiplied by the power that was brought down
Differentiating
gives
Differentiating
gives
Differentiating
gives
Be careful with two special cases:
Differentiating
gives
The
disappears leaving just a number
For example,
differentiates to
This makes sense, the gradient of the straight line
is 2
Differentiating just a number (a constant term),
, gives
Numbers disappear!
For example,
differentiates to
This makes sense, the gradient of the horizontal line
is zero
How do I differentiate sums and differences of terms?
The equation of a curve may include a number of different terms
You can differentiate each term individually
Differentiating
gives
Differentiating
gives
Remember the two special cases of:
differentiating to just
and constant terms,
, differentiating to zero
E.g. differentiating
gives
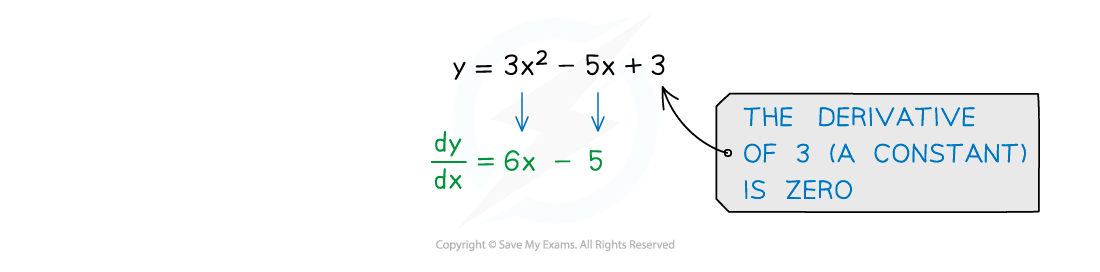
How do I find the gradient of a curve using the gradient function?
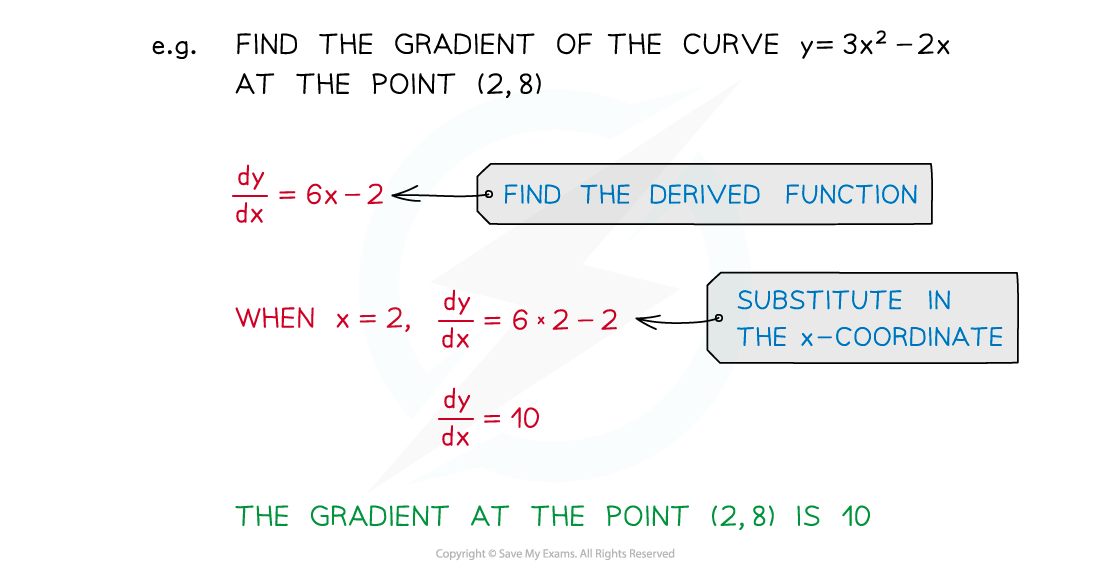
Find the x-coordinate of the point on the curve you're interested in
Use differentiation to turn the equation of the curve,
, into the gradient function,
Substitute the x-coordinate into the gradient function to find the gradient
The y-coordinate is not needed
If instead you are given a gradient and asked to find the x-coordinate
set
equal to that gradient and solve the equation
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Don't forget to write the left-hand sides of and
to avoid mixing up the curve equation with the gradient function!
How is the gradient function related to drawing tangents?
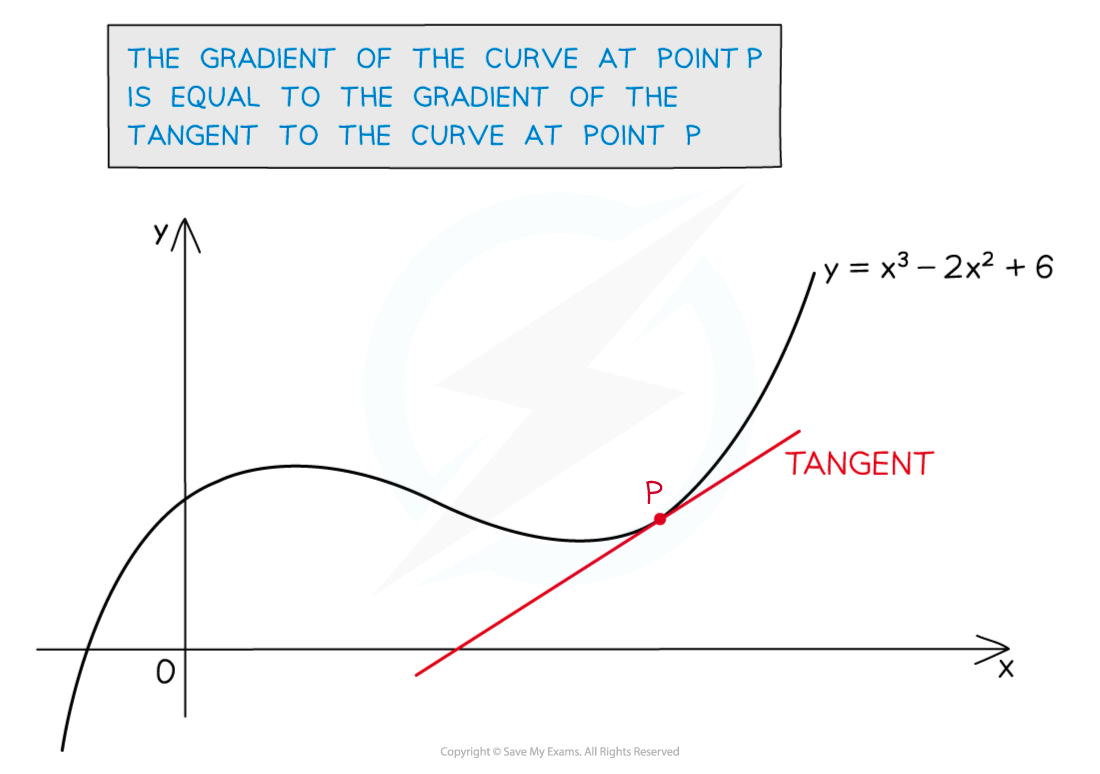
The gradient of a curve changes as you move along the curve
To find the gradient at a particular point you can draw a tangent and find its gradient
This is a graphical method that is not accurate
It depends on how well you draw the tangent
Instead, you can use differentiation to find the gradient function, then substitute the x-coordinate of the point into the gradient function to find the gradient
This is an algebraic method that is exact
For example, to find the gradient of the curve
at the point P where
either try to draw a tangent at
and measure its gradient (see below)
or differentiate the equation to get
Substitute in
to get
The gradient is 4
Worked Example
A curve has the equation .
(a) Find the gradient of the curve at the point .
Find the gradient function using differentiation
Substitute into the gradient function
The gradient when is -7
(The y-coordinate of the point is not needed)
The gradient at is -7
(b) Find the coordinates of the two points on the curve with a gradient of 5.
This is saying that
(This is not the same as substituting in )
Form an equation using from above
This is a quadratic equation
Bring the terms to one side and solve (for example, by factorisation)
These are the -coordinates of the two points on the curve with gradient 5
Substitute into
to find the
-coordinate of this point
Similarly, substitute into the equation for
Write out the two sets of coordinates
The points and
have a gradient of 5

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
