Compound Measures (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 0580 & 0980
Did this video help you?
Compound measures
What is a compound measure?
A compound measure is something that is calculated by using more than one measurement
Compound measures can be used to measure rates
This measures how much one quantity changes when the other is increased by 1
Examples include:
Speed – how much the distance changes for each unit of time
Flow rate – how much the volume changes for each unit of time
Population density – how many people there are for each unit of area
Fuel consumption - volume of fuel used for each unit of distance travelled
How do I find the units for a compound measure?
You can use the formula for a compound measure to derive its units
Use the units for the quantities in the formula to derive the units of the compound measure
Write a division as a/b or ab-1 and pronounce it as “a per b”
Examples include:
If the distance is measured in km and the time is measured in minutes then the speed is measured in km/min or km min-1
If the volume is measured in m3 and the time is measured in minutes then the flow rate is measured in m3/min or m3min-1
How do I find the formula for a compound measure?
You can use the units for a compound measure to help remember its formula
You just need to remember what each unit measures
If the unit is a/b then the formula will be the quantity that a measures divided by the quantity that b measures
Examples include:
Density can be measured in kg/cm3
kg is a measure of mass and cm3 is a measure of volume
Therefore
Population density can be measured in "people per km2"
The formula must be
E.g. The population of France is approximately 67 million
The area of France is approximately 550 000 km2
Population density of France =
What is a formula triangle?
A formula triangle shows the relationship between the different measures in a compound formula
E.g. for Speed, Distance and Time
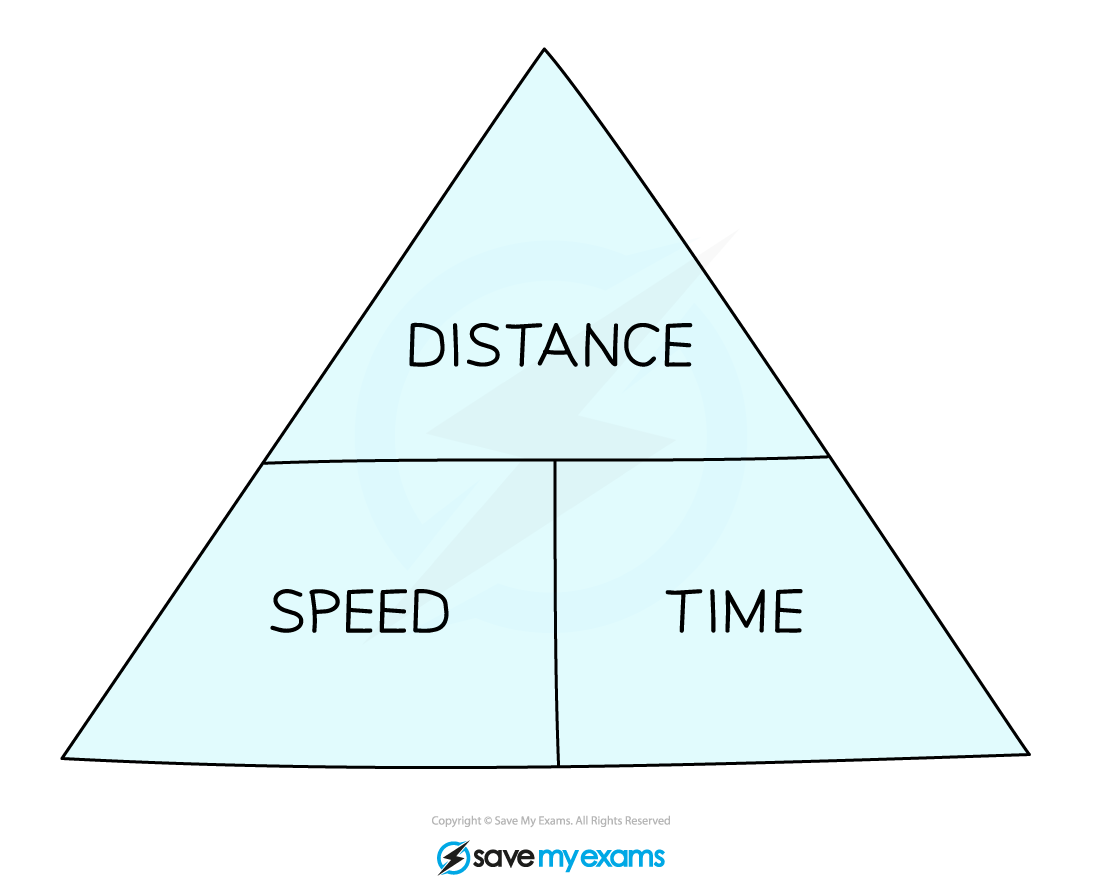
If you are calculating a variable on the top of the triangle, multiply the two variables on the bottom
For example,
If you are calculating a variable on the bottom of the triangle, divide the top by the other variable on the bottom
For example,
and
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Check in the exam to see if the answer needs to be in different units.
For example, the question may use metres and seconds but want the answer in km/h.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You need to remember the relationship between speed, distance and time.
Worked Example
A high-speed racing car has an average fuel consumption of 3 km per litre during a race.
1 lap of the racing circuit is 5.9 km in length.
(a) Calculate the volume of fuel used, in litres, to complete 15 laps of the circuit.
Answer:
The units for the fuel consumption are km per litre, which suggests the formula is
Calculate the total distance covered for the 15 laps
Use the above formula to find the volume of fuel, litres, used
Rearrange the equation by multiplying both sides by , and dividing both sides by 3
29.5 litres of fuel
The race car then requires a pit-stop to refuel to complete the final laps of the race.
The flow rate of the fuel pump is 720 litres per minute, and fuel is pumped into the car for 3.1 seconds.
(b) Calculate the volume of fuel, in litres, pumped into the car in this time.
Answer:
The flow rate is 720 litres per minute which suggests the formula is
Before we can use the formula, we need to change the units of time to both be the same
Change 720 litres per minute, into litres per second (to match the time fuel is pumped for, which is in seconds)
If 720 litres are pumped in 1 minute, 60 times less will be pumped in 1 second
Substitute these values into the formula
Multiply both sides by 3.1
37.2 litres

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?