Set Notation & Venn Diagrams (Edexcel IGCSE Maths A (Modular)) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Set Notation
What is a set?
A set is a collection of elements
Elements could be anything
Numbers, letters, coordinates, ...
You could describe a set by writing its elements inside curly brackets {}
{1, 2, 3, 6} , is the set of factors of 6
If the set of elements follow a rule then you can write this using a colon inside the curly brackets {... : ...}
The bit before the colon is the type of element
The bit after the colon is the rule
{x is a positive integer : x2 < 30} is the set of positive integers which, when squared, are less than 30
This is equal to {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
The colon is often read as 'such that'
If no type is specified, x can take any value (fractions, decimals, irrationals, ...)
{x: x2 < 30} means any value whose square is less than 30
{ (x, y) : y = mx + c } would mean the coordinates (x, y) where y = mx + c
I.e. The set of all possible coordinates that lie on the line y = mx + c
A colon can also be replaced by a vertical bar
{x | x2 < 30}
What do I need to know about set notation?
is the universal set (the set of everything)
For example, if we are only interested in factors of 24 then
= {1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24}
You may see alternative notations used for
U is a common alternative (different to
for union!)
S or the Greek letter ξ (xi) may also be seen
We use upper case letters to represent sets (A, B, C, ...) and lower case letters to represent elements (a, b, c, ...)
n(A) is the number of elements in set A
For example, if
= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}, A = {1, 4, 9}, B = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
n(A) = 3, n(B) = 6
means "is an element of"
And
means "is not an element of"
E.g.
and
is the empty set
This is the set which does not contain any elements
A
B means "A is a subset of B"
Set A is a subset of set B if all the elements of A are also present in B
E.g. If A = {1,2,3} and B = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4}, then A
B
A
B means "A is not a subset of B"
A
B means the intersection of A and B (the overlap of A and B)
This is the set of elements that are in both set A and set B
E.g. If A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and B = {-1, 1, 4, 7, 8}, then A
B = {1, 4}
A
B means the union of A and B (everything in A or B or both)
This is the set of elements that are in at least one of the sets
This includes elements in both sets (in the intersection)
E.g. If A = {5, 6, 7, 8} and B = {3, 7, 11}, then A
B = {3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 11}
A' means the complement of A
It is the set of all elements in the universal set
that are not in A
E.g. If
= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and A = {1, 3}, A' = {2, 4, 5}
Sets & Venn Diagrams
What is a Venn diagram?
A Venn diagram is a way to illustrate all the elements within sets and any intersections
A Venn diagram consists of
a rectangle representing the universal set (
)
a circle for each set
Circles may or may not overlap depending on which elements are shared between sets
What do the different regions mean on a Venn diagram?
is represented by the region where the A and B circles overlap
is represented by the regions that are in A or B or both

Worked Example
Two sets A and B are shown in the Venn diagram.
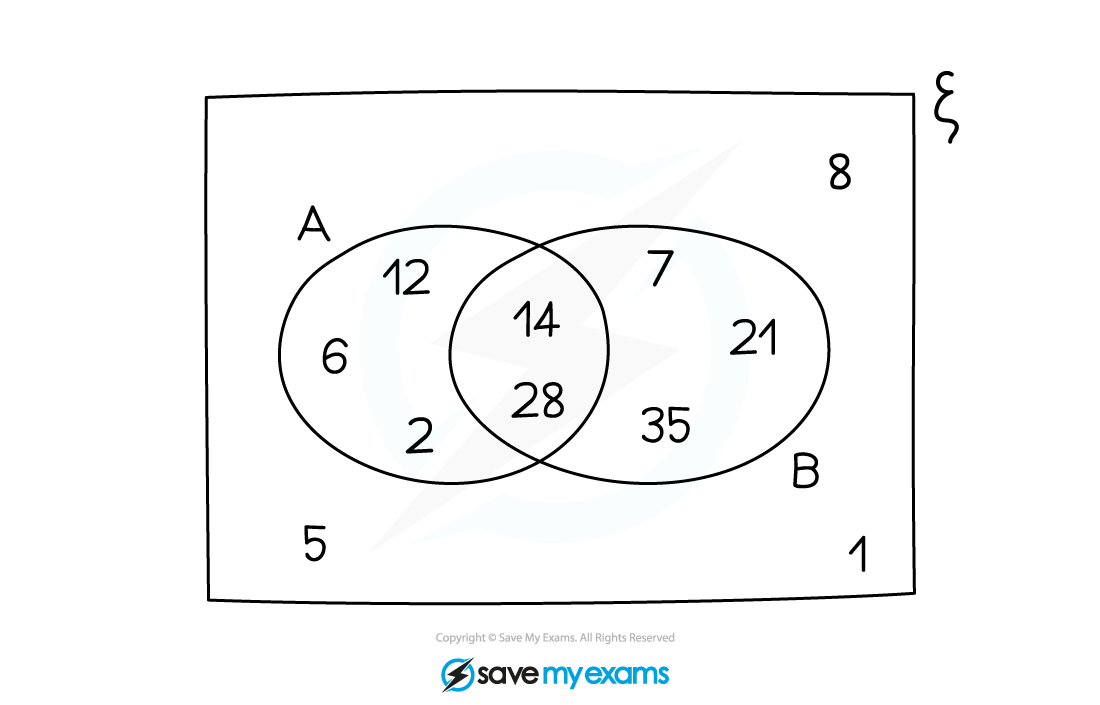
(a) Write down n(A).
The elements of A are anything inside the A circle
A = {2, 6, 12, 14, 28}
n(A) means the number of elements in A
There are 5 elements in A
n(A) = 5
(b) Use set notation to complete the sentence {14, 28} = ...
14 and 28 are the elements that are both in A and B
This means they are in the intersection of A and B
{14, 28} = A ∩ B
(c) Write down the elements that are in set A U B.
A = {2, 6, 12, 14, 28} and B = {7, 14, 21, 28, 35}
A U B is the set of elements that are in at least one of the sets
For elements in both, only write them out once
A U B = {2, 6, 7, 12, 14, 21, 28, 35}
(d) Jamie states that A'
B' =
.
Explain if this statement is correct or not.
The statement means Not A and Not B is equal to an empty set
i.e. There are no elements that are Not A and Not B
However, there are 3 elements that are neither A nor B
There are 3 elements that aren't in A or BA'
B' = {1, 5, 8}
Therefore the statement is incorrect
Worked Example
Consider the following sets.
= {letters of the alphabet}
= {t, e, a, m}
= { i }
= {m, e}
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate set.
(i)
(ii)
The symbol means "is a subset of", so all of the elements of one feature in the other
The symbol means "is not a subset of"
The element in is not in
All the elements of are also in

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

