Types of Graphs (Edexcel IGCSE Maths A): Revision Note
Exam code: 4MA1
Did this video help you?
Types of graphs
What types of graphs do I need to know?
You need to be able to recognise, sketch, and interpret the following types of graph:
Linear (
)
or
Quadratic (
)
Cubic (
)
Reciprocal (
)

You must also be able to recognise the three basic trigonometric graphs, covered in a separate section
Where are the asymptotes on reciprocal graphs?
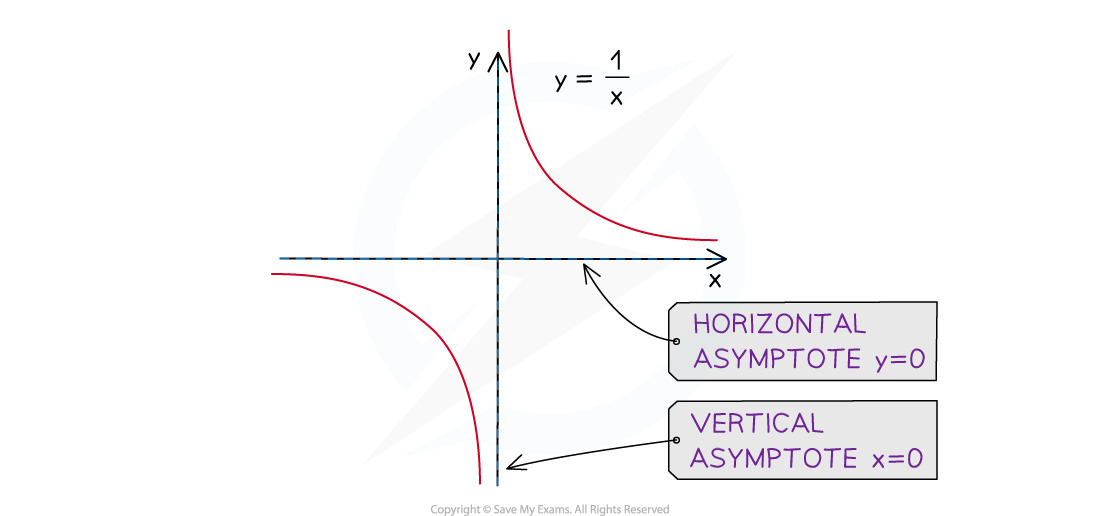
An asymptote is a line on a graph that a curve becomes closer to but never touches
These may be horizontal or vertical
The reciprocal graph,
(where
is a constant)
does not have a y-intercept
and does not have any roots
This graph has two asymptotes
A horizontal asymptote at the x-axis:
This is the limiting value when the value of x gets very large (or very negative)
A vertical asymptote at the y-axis:
This is the value that causes the denominator to be zero
The reciprocal graph,
(where
and
are both constants)
is the same shape as
but is shifted upwards by
units
would be
shifted down by 3 units
This means the horizontal asymptote also shifts up by
units
The vertical asymptote remains on the y-axis
The graph of
is similar to
but has two key differences
is steeper than
is always positive, even when
is negative

What does the graph of a cubic look like?
A cubic is a function of the form
and
are constants
It is sometimes referred to as a polynomial of degree (order) 3
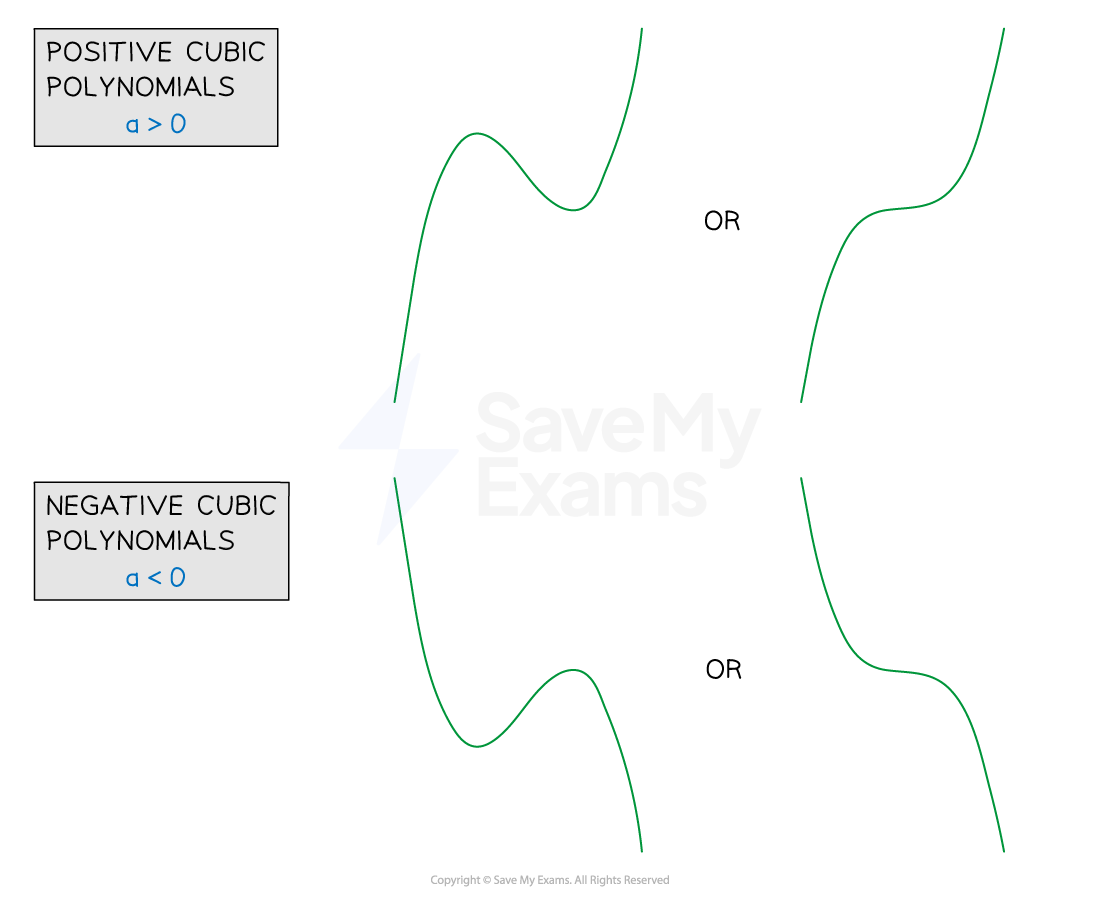
In general the graph of a cubic will take one of the four forms
All are smooth curves
The exact form of a particular cubic will depend on:
The number (and value) of roots (
-axis intercepts)
The
-axis intercept
The sign of the coefficient of the
term (
)
If
the graph is a positive cubic ('starts' in the bottom left, 'ends' in the top right)
If
the graph is a negative cubic ('starts' in the top left, 'ends' in the bottom right)
The turning points
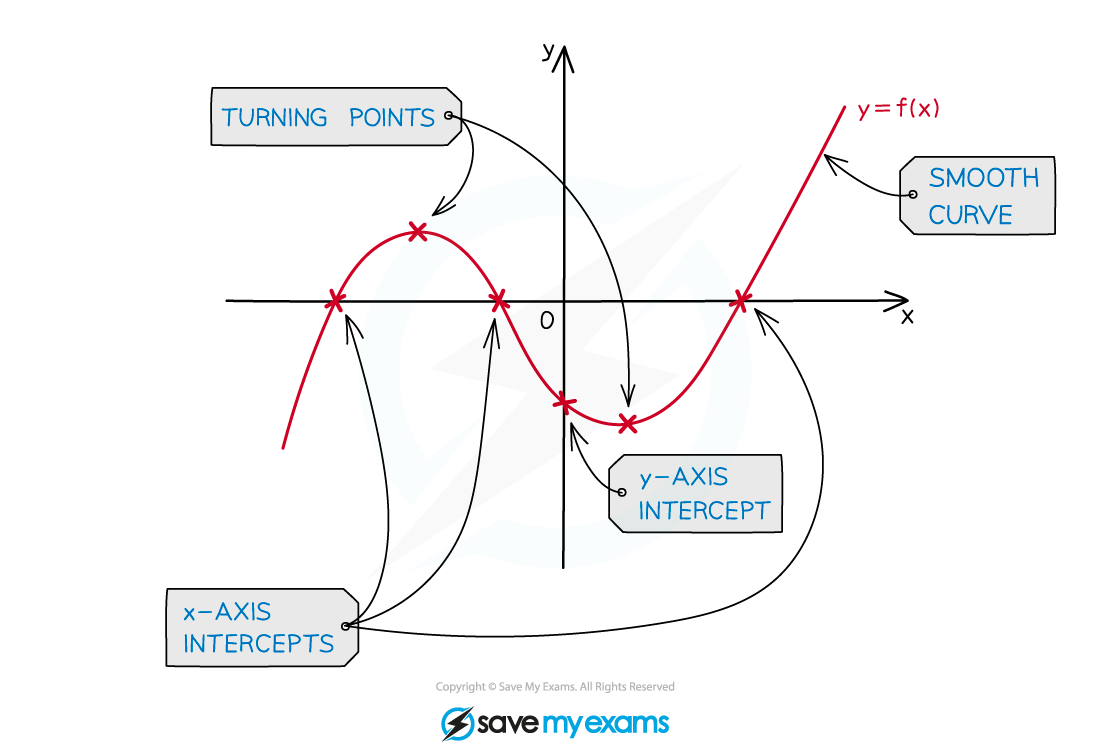
Cubics can have two turning points
a maximum point and a minimum point
However, note that the graphs of
and
:
Do not have a maximum or minimum (turning points)
Only cross the
-axis once, at
Worked Example
Match the graphs to the equations.
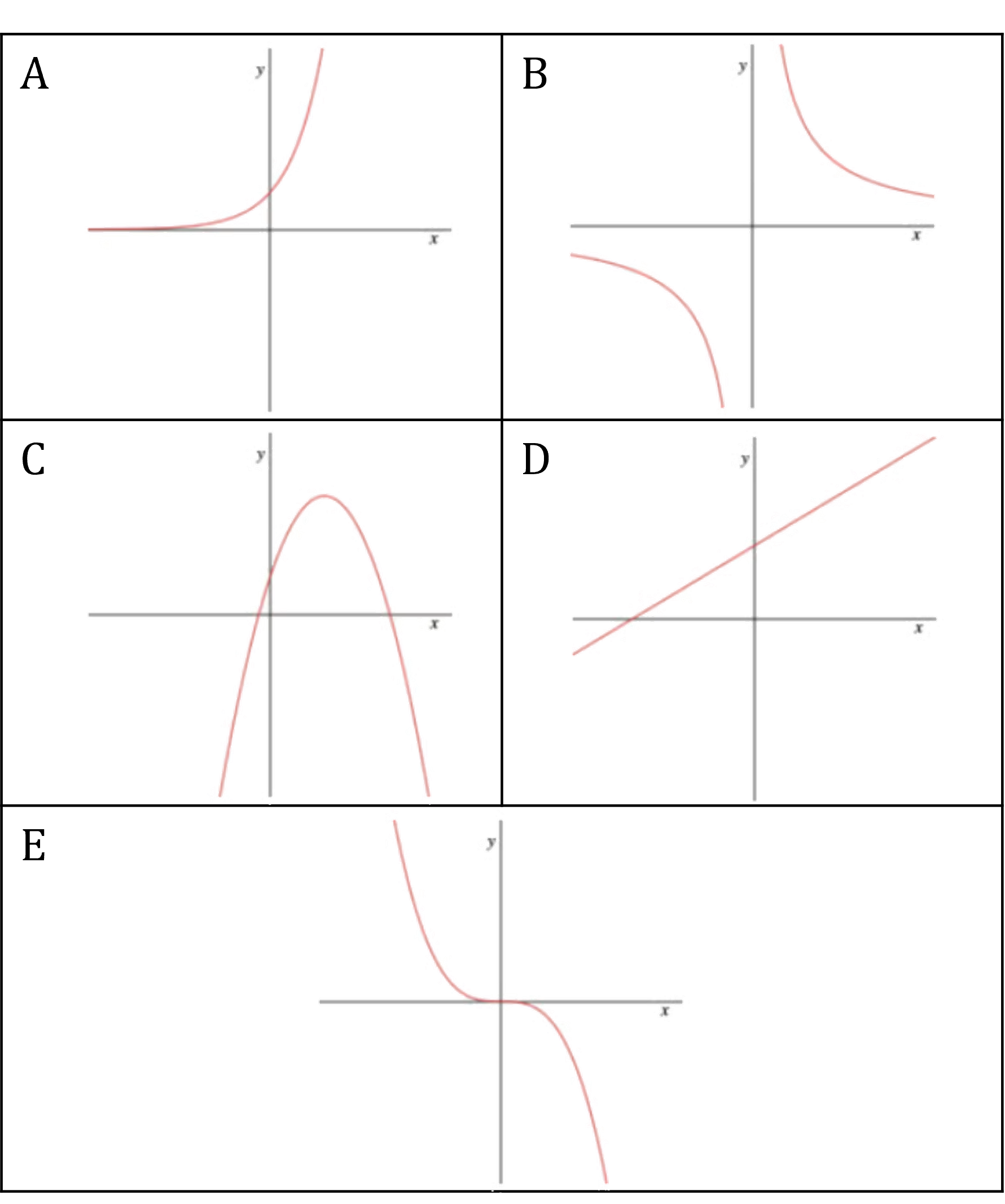
(1) , (2)
, (3)
, (4)
, (5)
Answer:
Starting with the equations,
(1) is a linear equation (y = mx + c) so matches the only straight line, graph D
(3) is a cubic equation with a negative coefficient so matches graph E
(4) is a reciprocal equation with a positive coefficient so matches graph B
(5) is a quadratic equation with a negative coefficient so matches graph C
(2) is the only equation not yet used, so by elimination it is graph A
Graph A → Equation 2
Graph B → Equation 4
Graph C → Equation 5
Graph D → Equation 1
Graph E → Equation 3

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?