Using Differentiation for Kinematics (Edexcel IGCSE Maths A): Revision Note
Exam code: 4MA1
Did this video help you?
Kinematics
What does kinematics mean?
Kinematics is the study of the motion of an object
It is a branch of Physics
Objects are called particles
They are modelled as single moving points
Over time, the particles move and
can be at different distances from a fixed origin (displacement)
can move with different speeds in different directions (velocity)
can speed up or slow down (acceleration)
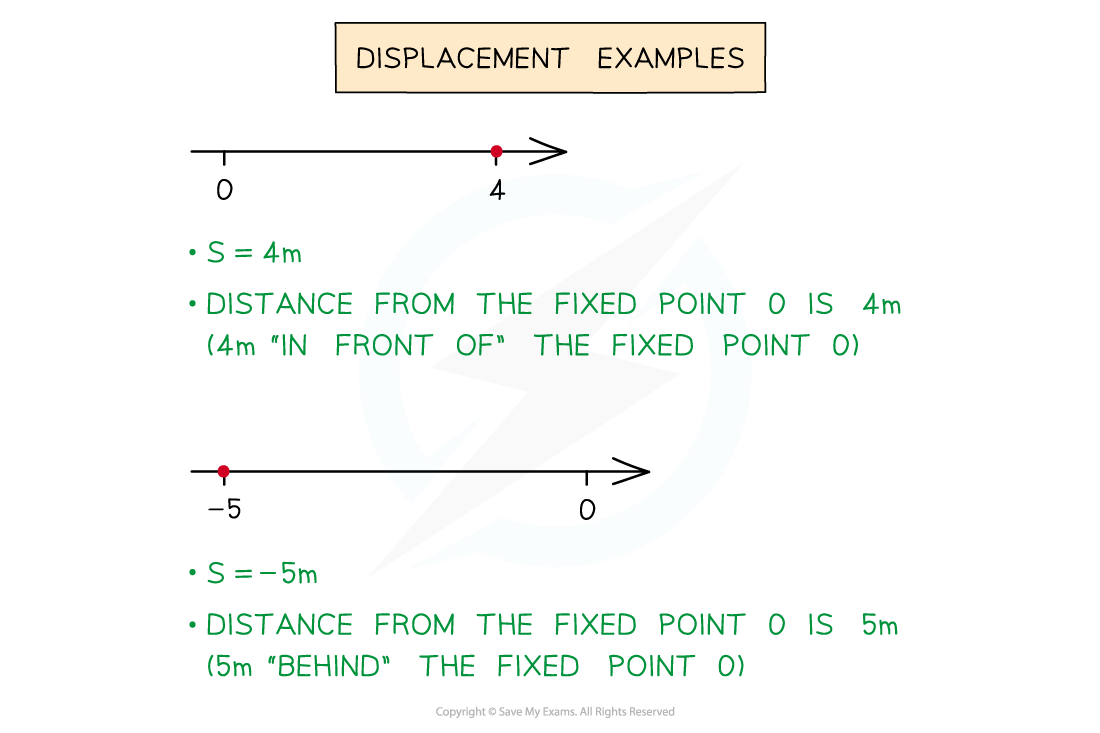
What is displacement?
The displacement of an object is how far away it is from a fixed origin
It can be positive (in front of the origin)
or negative (behind the origin)
Do not confuse displacement with distance
Distance is always positive!
Displacement can have a
sign
Displacement is given the letter
in kinematics
Do not confuse this letter for speed!
Displacement is measured in metres
What is a displacement function?
The displacement of an object,
metres, can be written as a function of time,
seconds
Substitute a value of time in to find its displacement at that time
For example,
Initially,
gives
(1 metre in front of the origin)
After 3 seconds,
gives
(2 metres behind the origin)
What is the velocity and how do I find it?
Velocity is the speed and direction of an object
It is positive if moving forwards
It is negative if moving backwards
Do not confuse velocity and speed
Speed is always positive!
To find the velocity of an object,
metres per second, differentiate its displacement function
For example, if
then
(by differentiation)
The initial velocity (
) is
ms-1
The velocity after 1 second (
) is
ms-1
Its speed is 3 ms-1
If a velocity is zero at any point in time, it is said to be at instantaneous rest
It is stationary (not moving) at that instant in time
but not stationary all the time
To find the times at which the particle is at rest, set
and solve to find
What is the acceleration and how do I find it?
Acceleration is rate at which the velocity changes
It is positive if speeding up (when moving forwards)
It is negative if slowing down (when moving forwards)
A negative acceleration is also called a deceleration
The magnitude of acceleration is always positive
To find the acceleration of an object,
metres per second per second, differentiate its velocity function
For example, if
then
You can substitute times in to find accelerations
It the acceleration is always zero then the particle moves at a constant speed
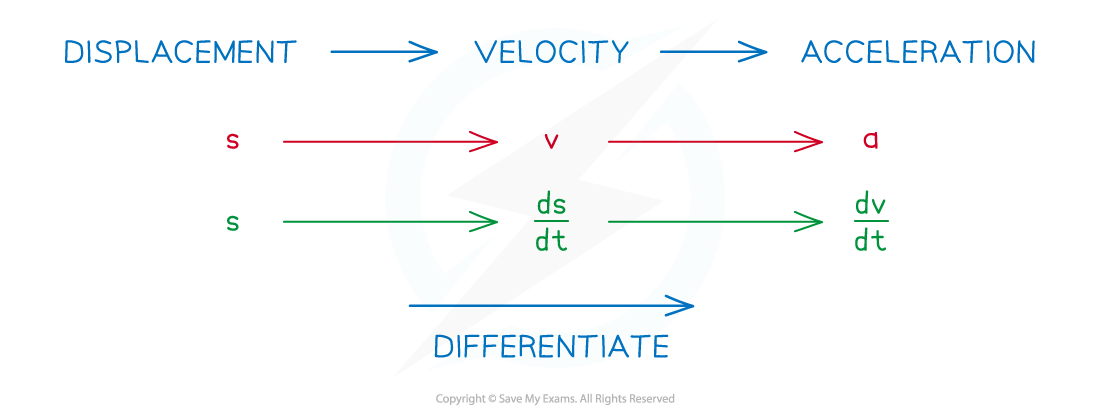
How do I find the acceleration from the displacement?
You differentiate displacement to get velocity, then differentiate velocity to get acceleration
So you differentiate displacement twice to get acceleration
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Harder exam questions may jump back and forth between displacement, velocity and acceleration
so make sure you use the labels
,
and
to make your working clear
Worked Example
A particle moves along a straight line.
The displacement of the particle from a fixed point, O, on the line at time seconds is
metres, where
(a) Find the initial distance of the particle from O.
Answer:
Initial means
Substitute into
to find the initial displacement
Distance is always positive, so convert -3 into 3
The particle is initially at a distance of 3 metres from O
(b) Find an expression for the velocity, ms-1, at time
seconds.
Answer:
To find the velocity, differentiate the displacement
This is an expression for the velocity in terms of time,
ms-1
(c) Find how long, after , it takes for the particle to come to rest.
Answer:
The particle is at rest when
Set and solve to find
or
After the next point of rest is
After , it takes 4 seconds for the particle to come to rest
(d) Find the time at which the particle is decelerating at 3 ms-2.
Answer:
A deceleration of 3 means an acceleration of -3
Differentiate the velocity function to find acceleration
Set and solve for
The particle is decelerating at 3 ms-2 at 1.5 seconds

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?