Introduction to Column Vectors (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE International Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 0607
Did this video help you?
Basic vectors
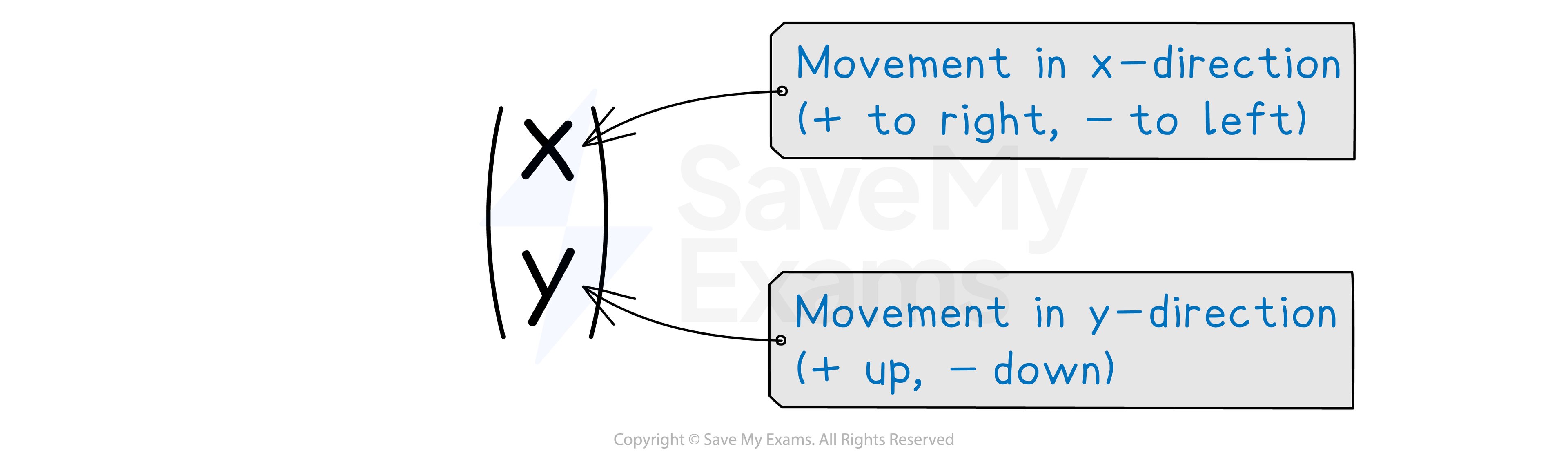
What are column vectors?
A column vector can be used to describe how to get from one point to another point
This is also called a translation vector
means 6 units to the right and 3 units up
How do I add and subtract column vectors?
Adding and subtracting vectors is done by looking at the top numbers and bottom numbers separately
To add column vectors
Add the top numbers together
Add the bottom numbers together
To subtract column vectors
Subtract the second top number from the first
Subtract the second bottom number from the first
How do I multiply a vector by a scalar?
A scalar is a number not a vector
It does not have a direction
To multiply a column vector by a scalar
Multiply the top number by the scalar
Multiply the bottom number by the scalar
How do I write an expression as a single column vector?
You need to follow the order of operations
STEP 1
Multiply each vector by the scalar in front of itSTEP 2
Add or subtract the new column vectors
Worked Example
and
.
Given that , find the value of
and the value of
.
Answer:
Write the left-side side as one vector
Multiply each vector by the scalar in front of it
Add the vectors together
The top components are equal
Form and solve an equation
The bottom components are equal
and

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
