Bar Charts & Pictograms (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE International Maths) : Revision Note
Bar Charts & Pictograms
What is a bar chart?
A bar chart is a visual way to represent discrete data
Discrete data is data that can be counted
This can be numerical like shoe sizes in a class
Or non-numerical (categorical) like colours of cars down a road
The horizontal axis shows the different outcomes
The vertical axis shows the frequency
The heights of the bars show the frequency
Bars should be separated by gaps
Bars should have equal widths
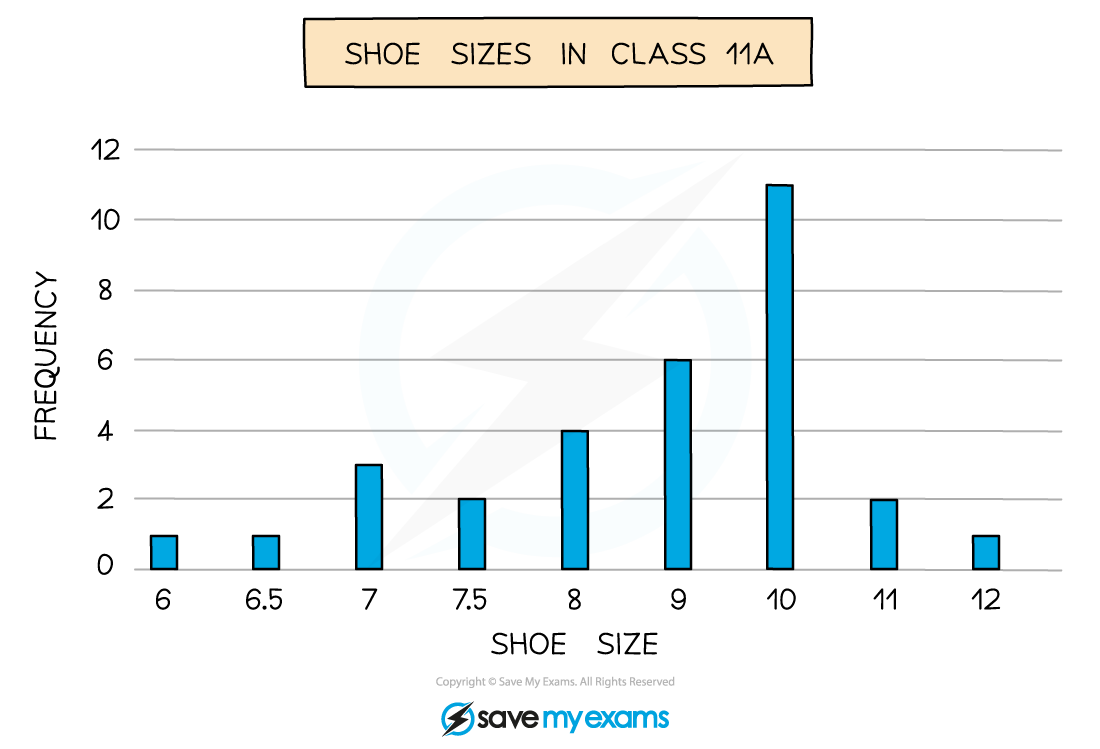
The mode is the outcome with the highest bar
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you need to find the median for data given in a bar chart
Turn the data from the bar chart into a table
Then use the method for finding the median in the 'Averages from Tables' revision note
You can also get dual bar charts to compare two data sets
Bars are in pairs (side-by-side) for each outcome
What is a pictogram?
A pictogram is an alternative to a bar chart
It is used in the same situations
There are no axes
Frequency is represented by symbols
A key shows the value of 1 symbol
For example, 1 symbol represents a frequency of 2
Half and quarter symbols are often used

The pictogram above shows the shoe sizes of students in a class
As 1 picture of a shoe represents 2 students
Half a shoe represents 1 student
The number of students with a shoe size of 7, is 3
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If asked to draw a bar chart, find the largest frequency and choose a scale which makes that fit in the space provided
If asked to draw a pictogram, pick a symbol that is easy to duplicate and draw half (or quarter) of
Worked Example
Mr Barr teaches students in Year 7 and Year 8.
He records the number of pets that students in each year have.
His results are shown below.
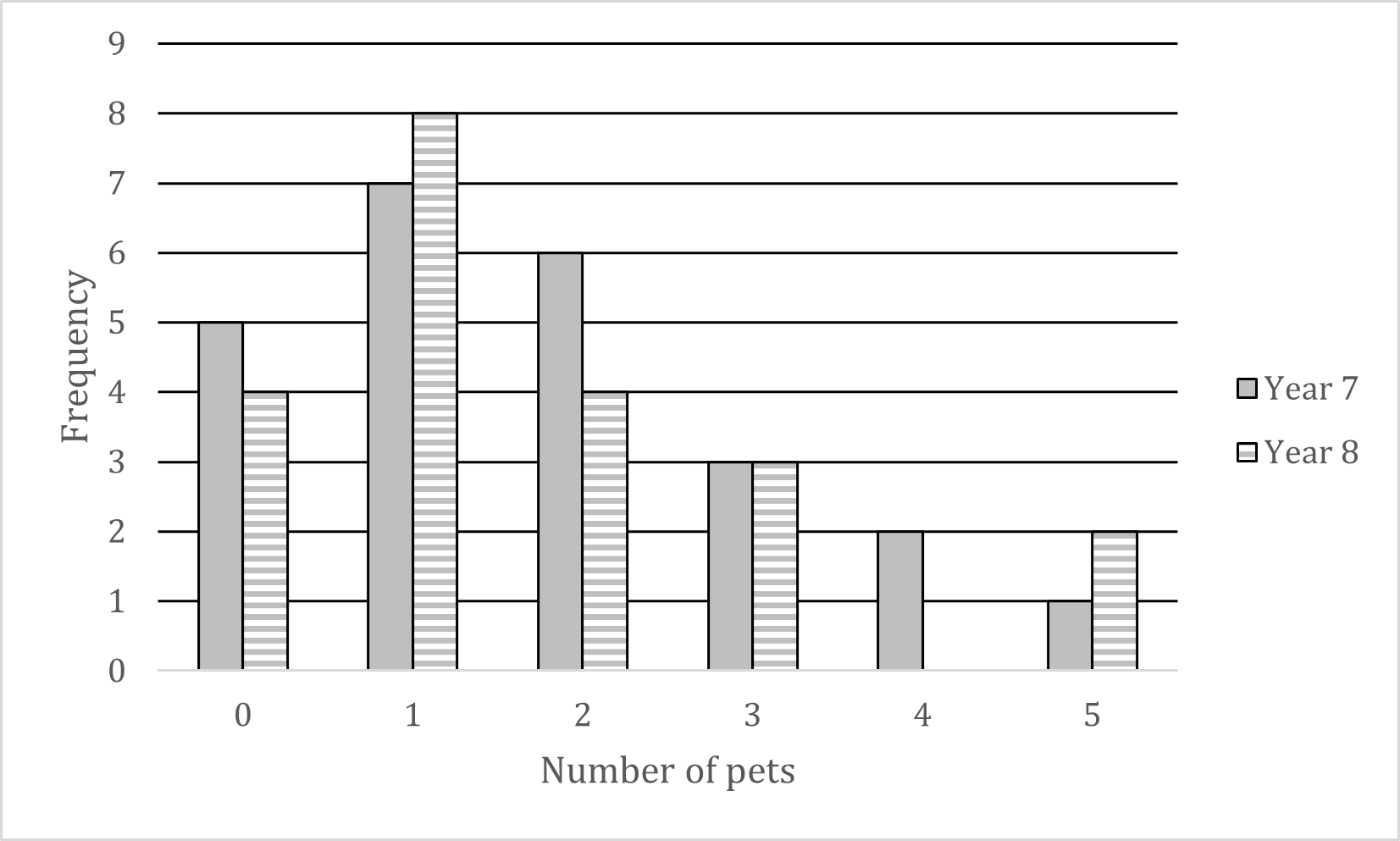
(a) Write down the modal number of pets for his Year 7 students.
The modal number (mode) is the number of pets that occurs the most
Visually, this will be the highest bar for Year 7s
The mode for Year 7 is 1 pet
(b) How many Year 8 students does he teach?
Add up all the heights (frequencies) of the Year 8 bars
4 + 8 + 4 + 3 + 0 + 2
He teaches 21 Year 8 students

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

