Planes of Symmetry (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE International Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 0607
Planes of symmetry
What is a plane of symmetry?
A plane is a flat surface that can be any 2D shape
A plane of symmetry is a plane that splits a 3D shape into two congruent (identical) halves
If a 3D shape has a plane of symmetry, it has reflection symmetry
The two congruent halves are identical, mirror images of each other
All prisms have at least one plane of symmetry
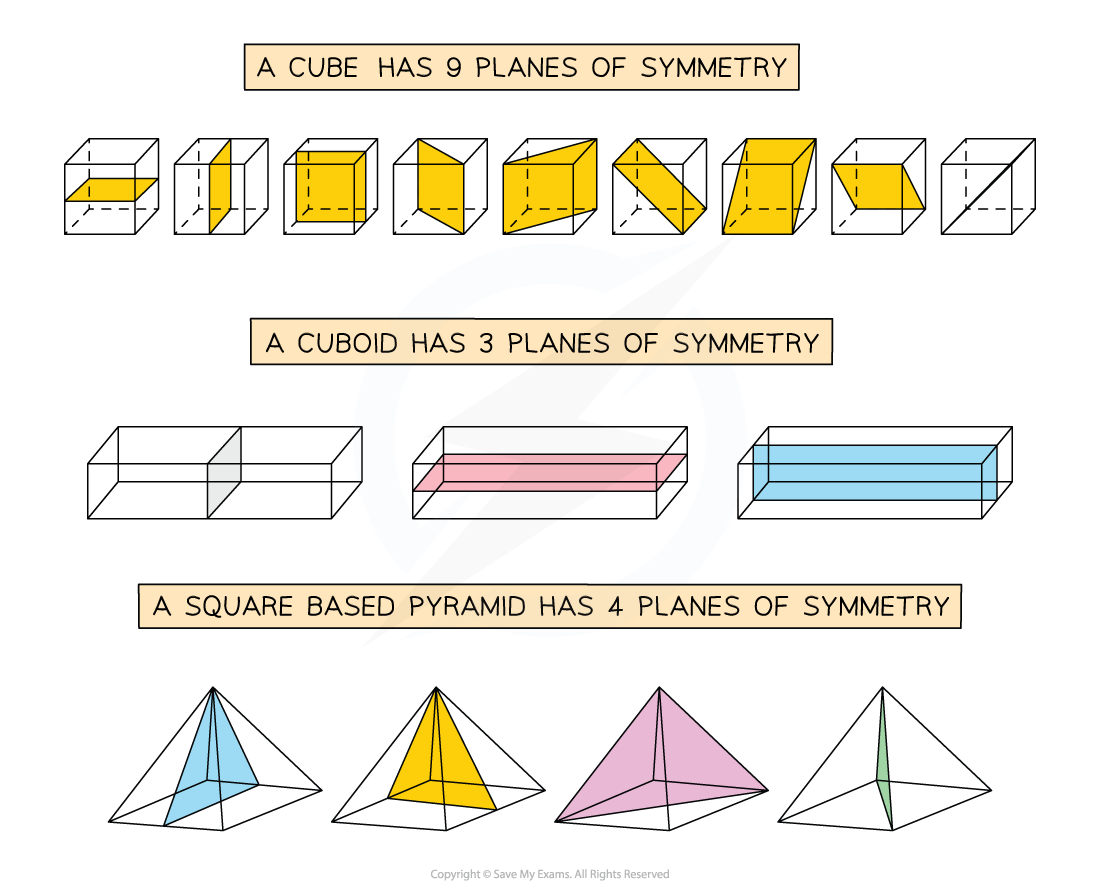
Cubes have 9 planes of symmetry
Cuboids have 3 planes of symmetry
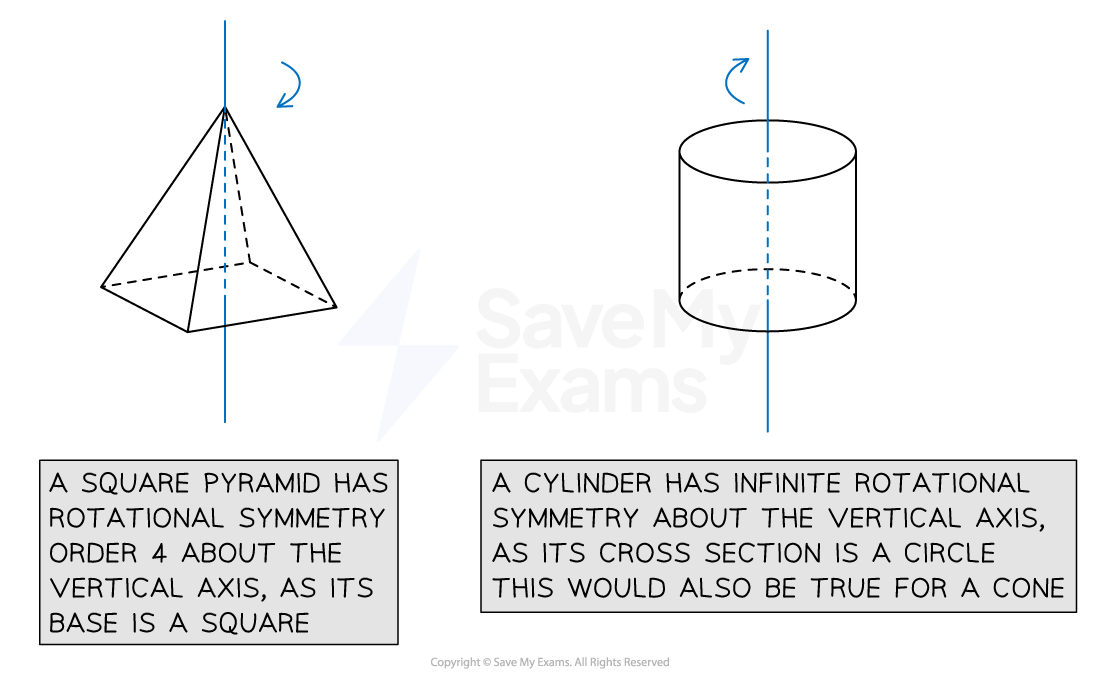
Cylinders have an infinite number of planes of symmetry
The number of planes of symmetry in other prisms will be equal to the number of lines of symmetry in its cross-section plus 1
Pyramids can have planes of symmetry too
The number of planes of symmetry in pyramids will be equal to the number of lines of symmetry in its 2D base
If the base of the pyramid is a regular polygon of n sides, it will have n planes of symmetry
Can a 3D shape have rotational symmetry?
3D shapes are able to be rotated around different axes
Depending on which axis the shape is rotated around, 3D shapes can have rotational symmetry
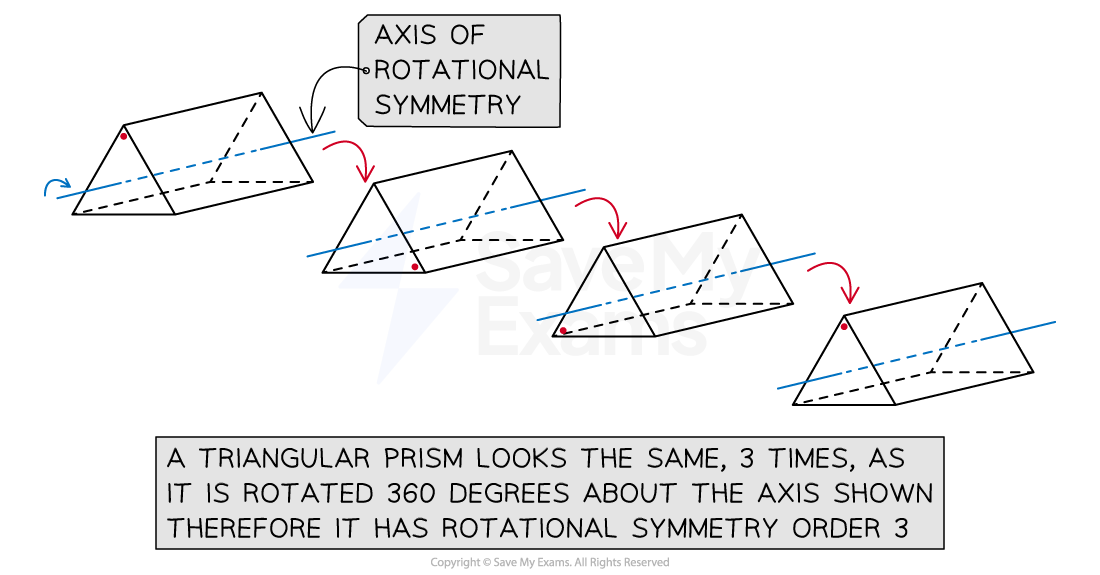
Recall that rotational symmetry is how many times the shape looks the same (congruent) when rotated through 360 degrees
See the example of the triangular prism where the cross-section is an equilateral triangle
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you’re unsure in the exam, consider the properties of the 3D shape.
Is it a prism or a pyramid?
How many lines of symmetry are there in the 2D faces or cross-section?
Worked Example
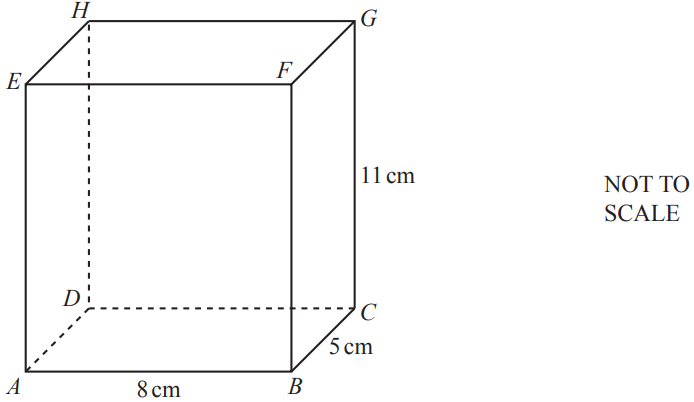
The diagram below shows a cuboid of length 8 cm, width 5 cm and height 11 cm.
Write down the number of planes of symmetry of this cuboid.
Answer:
A plane of symmetry is where a shape can be "sliced" such that it is symmetrical
A cuboid with three different pairs of opposite rectangles has 3 planes of symmetry
3 planes of symmetry

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?