Exponential Graphs (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE International Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 0607
Exponential Graphs
What is an exponential graph?
An exponential graph is of the form
When
,
represents exponential growth
Values of y increase as x increases
When
,
represents exponential decay
is positive but less than 1
Values of y decrease as x increases
Graphs of both exponential growth and exponential decay
have a horizontal asymptote at
do not have a vertical asymptote
have a
-intercept of


Exponential decay can also be identified by a negative power using index laws
This has the form
where
How do I compare exponential graphs?
For
where
:
The graph with a higher value of
is the “higher” graph for
but the "lower" graph for

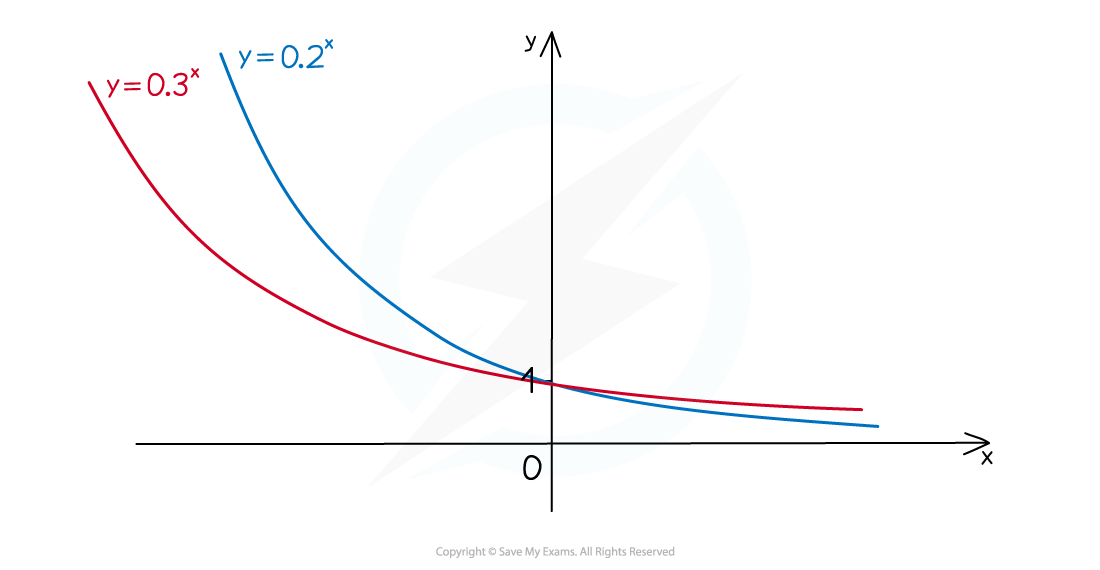
For
where
:
The graph with a higher value of
is the “higher” graph for
but the "lower" graph for
Worked Example
(a) Identify the equation that shows exponential decay.
A:
B:
C:
D:
A is an exponential graph as the x is in the power
The base number is greater than 1 so it is exponential growth (not decay)
B has the x as the denominator in a fraction
It is a reciprocal graph
C is an exponential graph as the x is in the power
The base number is between 0 and 1 so it is exponential decay
D has x raised to the power 3
It is a cubic graph
C: shows exponential decay
(b) On the same set of axes, sketch the graphs of and
.
Both graphs will have the "typical" exponential growth shape for
will be the "higher" graph for
and "lower" graph for
Both graphs go through and have an asymptote along the
-axis


Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?