Types of Graphs (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE International Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 0607
Types of Graphs
What graphs do I need to know?
You need to be able to recognise the following lines:
Straight lines
y = mx + c
Such as y = 3x + 2, y = 5x - 1, ...
Two important ones are y = x and y = -x
Horizontal lines
y = c
Such as y = 4, y = -10, ...
Vertical lines
x = k
Such as x = 2, x = -1, ...
You need to be able to recognise quadratic graphs
y = x2
y = -x2
y = ax2 + bx + c
What does a quadratic graph look like?
The equation of a quadratic graph is y = ax2 + bx + c
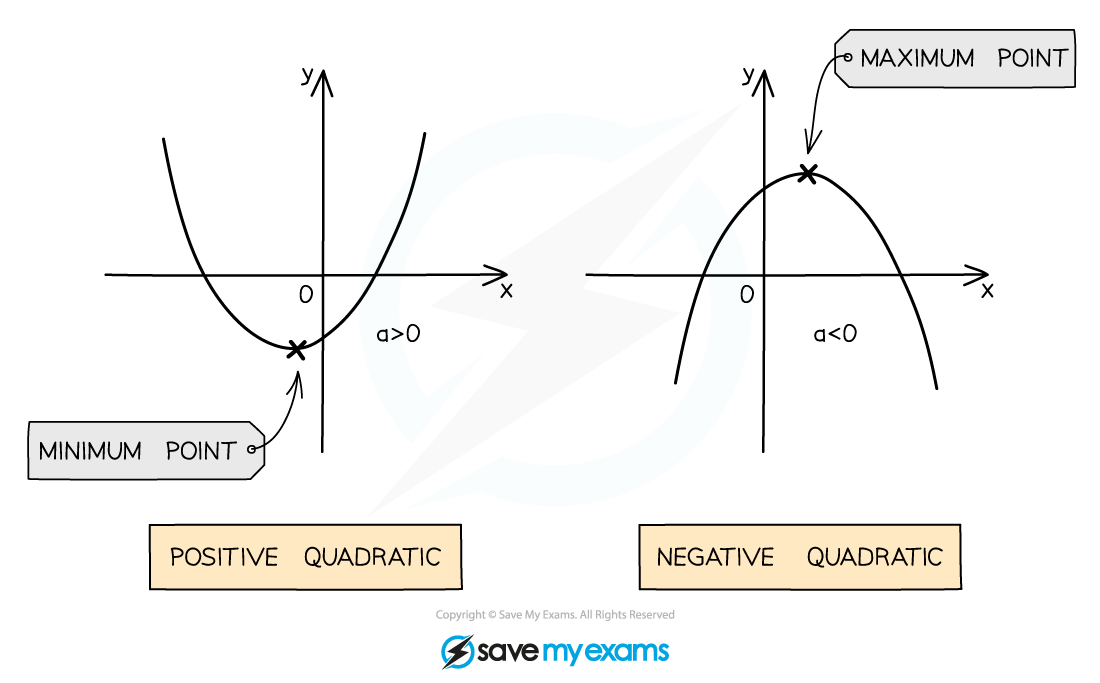
A quadratic graph has either a u-shape or an n-shape
This type of shape is called a parabola
u-shapes are called positive quadratics
because the number in front of x2 is positive
For example, y = 2x2 + 3x + 4
n-shapes are called negative quadratics
because the number in front of x2 is negative
For example, y = -3x2 + 2x + 4
You can plot quadratic graphs using a table of values
What are the key features of a quadratic graph?
The point where the graph turns is called the vertex
Positive quadratics have a minimum point
The bottom of the u-shape
Negative quadratics have a maximum point
The top of the n-shape
Quadratic graphs always have a vertical line of symmetry down the middle
The equation of the vertical line of symmetry is x = k
k is the x-coordinate of the minimum or maximum point
Quadratic graphs do not have to cross the x-axis
If they do, two x-intercepts are created, called roots
If the curve just touches the x-axis, only 1 root is created
Roots are symmetric about the vertical line of symmetry
Quadratic graphs always have one y-intercept
Worked Example
In each of the cases below, state the letter of the graph that corresponds to the equation given.

(a)
This is a straight-line graph, y = mx + c
Graph D
(b)
This is a quadratic graph, y = ax2 + bx + c (a = -1, b = 3, c = 2)
The number in front of x2 is negative so it has an n-shape
Graph C

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?