Layout (Edexcel IGCSE ICT): Revision Note
Exam code: 4IT1
Layout
How can you edit the layout of a document?
Editing the layout changes the overall look and feel of a document
Layout relates to how content is positioned on a page
There are many different way this can be achieved, such as using:
Headings
Sub-headings
Lists
Templates
Orientation (portrait & landscape)
Breaks
Headings & sub-headings
Make documents consistent
Predetermined styles can be applied (size, colour, font style etc.)
Allows for the use of auto index creation
Lists
Present information in a clear, concise and easy to read way
Allows users to find key points without being bogged down by paragraphs

Templates
Streamlines document production, saving time
Pre-set formatting included with templates
Help create a consistent look and feel

Orientation
Weather the page is vertical (portrait) or horizontal (landscape)
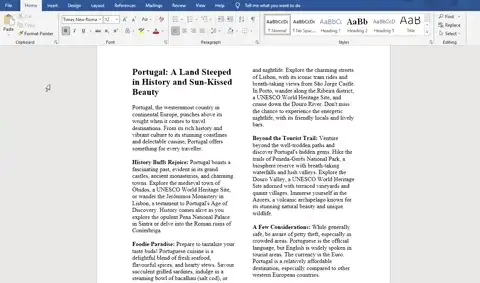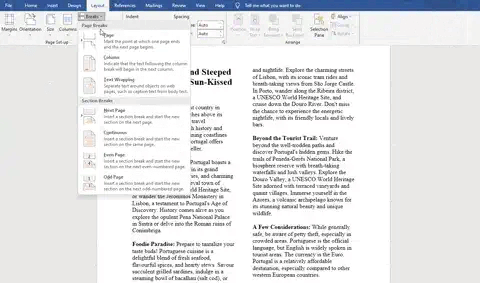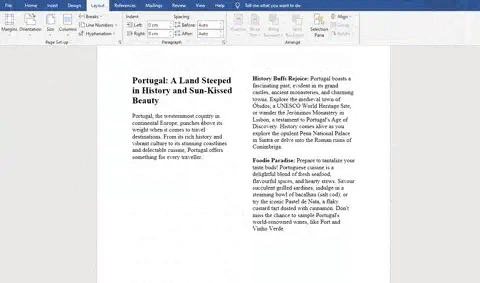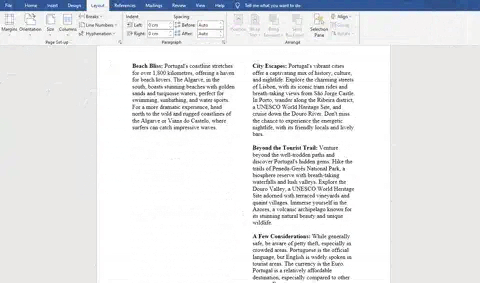
Breaks
Breaks are a method of dividing information into manageable chunks to control the layout and organisation of a document
Breaks can be used in:
Printed materials
Websites and applications
Page breaks
A page break forces content to start on a new page even when there is still space available.
Common uses include:
Starting a new chapter or section
Separating graphics and tables from surrounding text to improve readability
Ensuring all page elements appear at the top of a page
Column breaks
A column break divides a page into multiple columns to suit specific content types
Common uses include:
Creating a newsletter or brochure
Formatting content for easier viewing on screen
Section breaks
A section break creates independent sections that can be formatted differently
Common uses include:
Changing page orientation for a specific section
Applying different column layouts in the same document
Headers & footers
What is the purpose of headers & footers?
Headers and footers are areas at the top (header) and bottom (footer) of documents that can be used to help identify them
Headers and footers can contain:
Document name
Author
Company logo
Headers and footers only need to be added once and are replicated on each page, saving time and reducing the chance of data errors
Automated objects
Headers and footers can also contain automated objects to enhance the professionalism of a document
Examples of automated objects include:
Date/time
Page numbering
Total number of pages
Aligning contents
The contents of headers and footers can be aligned consistently within a document
They can be aligned to the:
Left margin
Right margin
Centred within margins

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?