Image Types (Edexcel IGCSE ICT): Revision Note
Exam code: 4IT1
Bitmaps & vectors
Computers represent all data in binary, including images that are seen on a screen, TV or other output device
Images can be stored in binary as Bitmap or Vector
What is a bitmap?
A bitmap image is made up of squares called pixels
A pixel is the smallest element of a bitmap image
Each pixel is stored as a binary code
Binary codes are unique to the colour in each pixel
A typical example of a bitmap image is a photograph
The more colours and more detail in the image, the higher the quality of the image and the more binary that needs to be stored
What is a vector?
A vector image is created from mathematical equations and points
Only the mathematics used to create the image are stored
For example, to create a circle the data stored would be:
Centre point (x, y coordinates)
Radius
Typical examples of vector images are logos and clipart
Vector images are infinitely scalable
Ideal for situations where the same image will be made bigger and smaller and a loss of quality is unacceptable. For example, the same logo used on both a pencil and a billboard
Editing images
What is image editing?
Image editing is the process of modifying and enhancing digital photographs, illustrations or any other visual media
Placing an image with precision
This refers to positioning an image accurately within a document or other media
You can usually do this by selecting the image and dragging it to the desired location
Some software allows for more precision through the use of coordinates or alignment tools
Resizing an image
This means changing the dimensions of an image
You can often do this by selecting the image and dragging its corners or edges
Maintaining the aspect ratio means the image's width and height change at the same rate, preventing distortion
Adjusting the aspect ratio can change the shape and proportions of the image
Cropping an image
This involves cutting out and discarding parts of an image
Cropping tools usually allow you to select a portion of the image to keep and discard the rest
Rotating an image
This means turning the image around a central point
Most software allows rotation to any angle, and common rotations such as 90 degrees or 180 degrees are often provided as options
Reflecting (flipping) an image
This means creating a mirror image of the original
An image can be flipped horizontally (left to right) or vertically (top to bottom)
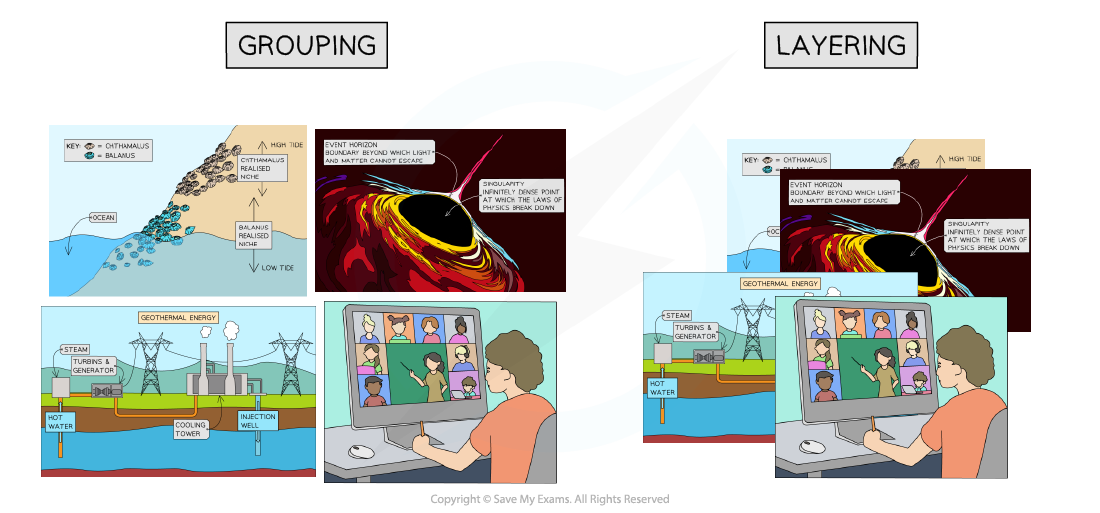
Grouping and layering images
These techniques help to organise multiple images
Grouping combines images so they can be moved or transformed as a single unit
Layering involves placing images on top of each other
You can change the order of layered images, moving them to the front or back

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?