Basic Coordinate Geometry (Edexcel IGCSE Further Pure Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 4PM1
Basic Coordinate Geometry
What are Cartesian coordinates?
Cartesian coordinates are the coordinates used in the x-y coordinate system
They allow us to label where things are in a two-dimensional plane
In the 2D Cartesian system, the horizontal axis is labelled x and the vertical axis is labelled y
What can I do with coordinates?
If you have two points with coordinates
and
then you should be able to find
The distance between the two points
The point that divides the line between the two points in a given ratio
The gradient of the line joining the two points
How do I find the distance between two points?
The distance
between two points with coordinates
and
can be found using the formula
is the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle
The differences between the
-coordinates and the
-coordinates give the other two side lengths
So by Pythagoras’ Theorem
How do I divide the line between two points in a given ratio?
The coordinates of the point dividing the line joining
and
in the ratio
are given by
If
then the point is closer to
If
then the point is closer to
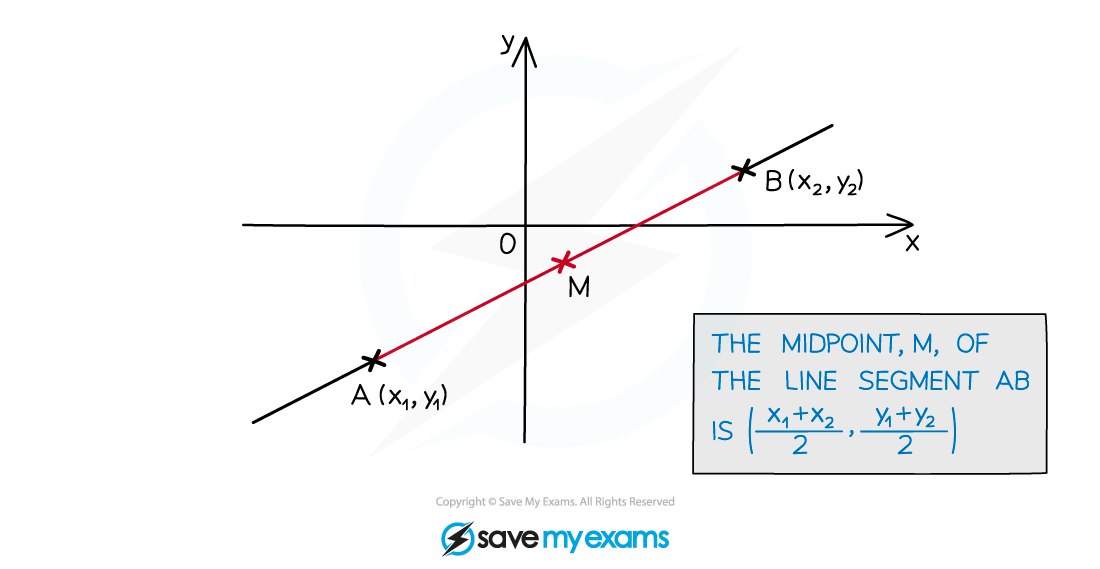
How do I find the midpoint between two points?
The midpoint is the point halfway between the two points
This is just 'dividing in a given ratio' where the ratio is
The coordinates of the midpoint will be
How do I find the gradient of a straight line joining two points?
The gradient
of a line between two points with coordinates
and
can be found using the formula
This is also known as
Worked Example
Point has coordinates
and point
has coordinates
.
(a) Calculate the distance between points and
.
Let be 'point 1', so
and
Let be 'point 2', so
and
Use the formula
(or
or 14.4 to 3 s.f.)
(b) Find the gradient of the line joining points A and B.
Let be 'point 1', so
and
Let be 'point 2', so
and
Use the formula
Simplify the fraction
(c) Find point that divides the line joining points A and B in the ratio .
Let be 'point 1', so
and
Let be 'point 2', so
and
Use the formula with
and

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?