Tangents & Normals (Edexcel IGCSE Further Pure Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 4PM1
Tangents & Normals
What is a tangent?
At any point on the graph of a (non-linear) function
the tangent is the straight line that touches the graph at the point without cutting through it
Its gradient is given by the derivative of the function
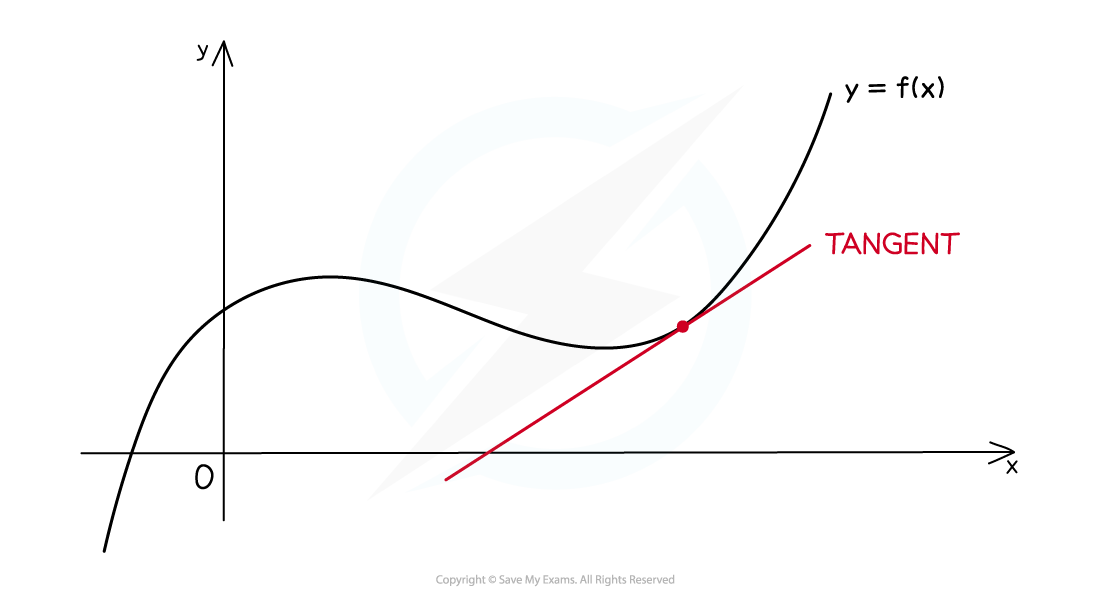
How do I find the equation of a tangent?
You need a point and the gradient to find the equation of a straight line
The gradient of the tangent to the function
at the point
is
Therefore to find the equation of the tangent to the function
at the point
Find
Substitute
into
to find the gradient
,
Use the
form of the line equation
Rearrange the equation into whatever form the question requires
What is a normal?
At any point on the graph of a (non-linear) function
the normal is the straight line that passes through that point
and is perpendicular to the tangent
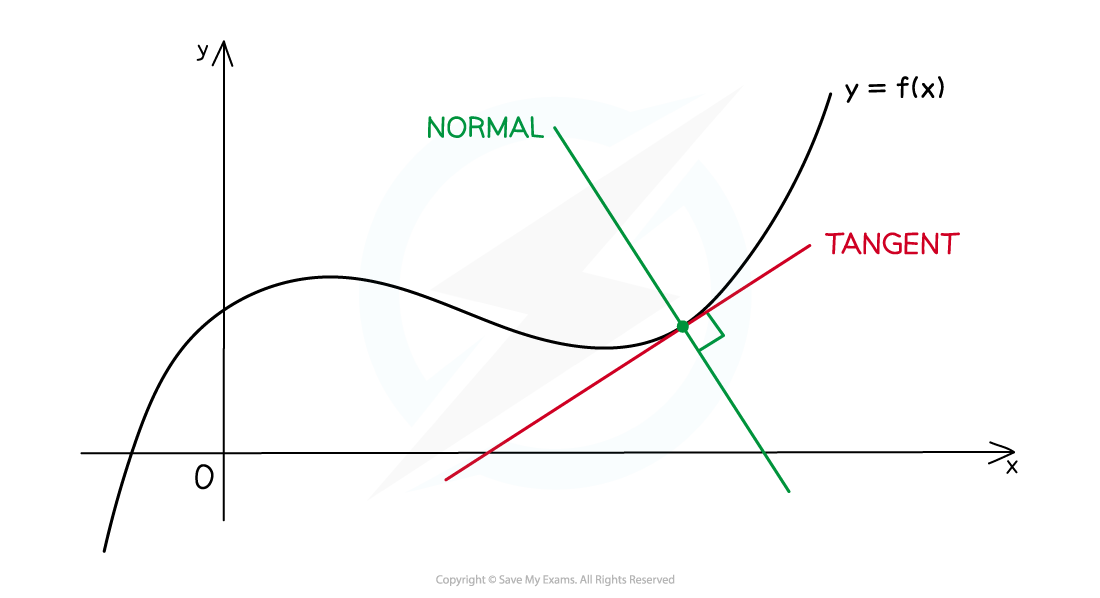
How do I find the equation of a normal?
You need a point and the gradient to find the equation of a straight line
The tangent and the normal are perpendicular
Therefore the gradient of the normal to the function
at the point
is
To find the equation of the normal to the function
at the point
Find
Substitute
into
to find the gradient of the tangent
Use that to find the gradient of the normal
Use the
form of the line equation
Rearrange the equation into whatever form the question requires
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure you are confident with finding the equation of a straight line
In particular when you know the gradient and one point on the line
This is an essential skill for finding tangents and normals
Worked Example
The function is defined by
a) Find an equation for the tangent to the curve at the point where
, giving your answer in the form
.
Substitute into
to find the
-coordinate of the point
So the point in question is
Now differentiate to find , first using laws of indices to rewrite
as
Substitute into
to find the gradient of the tangent at the point
Now use to find the equation of the line
Here and
b) Find an equation for the normal to the curve at the point where
, giving your answer in the form
, where
,
and
are integers.
The normal and tangent are perpendicular
So the gradient of the normal will be
Now use to find the equation of the line
Here and
Multiply both sides by 2 to get rid of the fractions
Then rearrange into the required form

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?