Trigonometric Functions (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Additional Maths) : Revision Note
Trigonometric Functions
What are the trigonometric functions?
The three standard trigonometric functions are: sine, cosine and tangent
The functions are many-to-one mappings
They do not have inverses unless their domain is restricted
Function | Notation | Domain | Range |
Sine | |||
Cosine | |||
Tangent |
How can I use the trigonometric functions with right-angled triangles?
The three trigonometric functions sine, cosine and tangent give the ratios of side lengths in right-angled triangles
For an acute angle in a right-angled triangle:
Sine of the angle is the length of the side opposite the angle divided by the hypotenuse
Cosine of the angle is the length of the side adjacent to the angle divided by the hypotenuse
Tangent of the angle is the length of the opposite side divided by the length of the adjacent side
You can use the acronym SOHCAHTOA to help you remember these

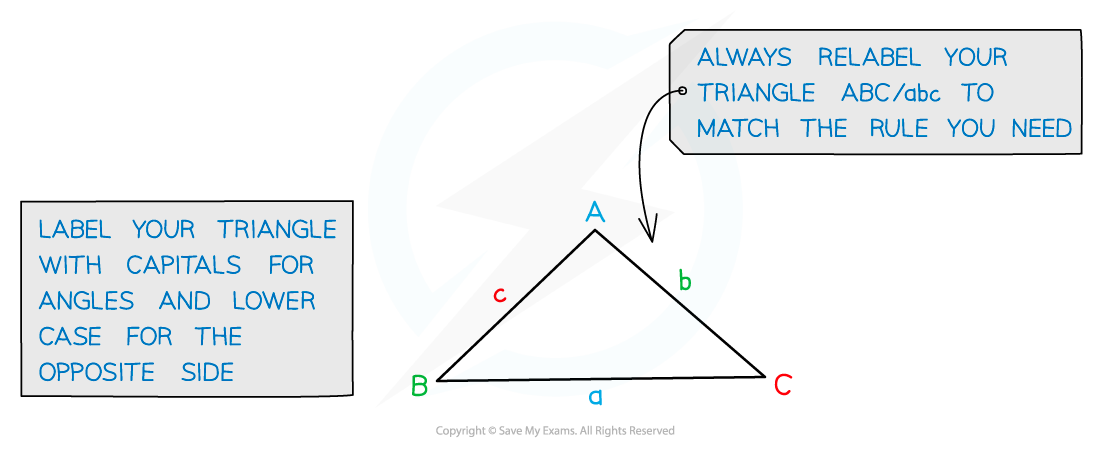
How can I use the trigonometric functions with non-right-angled triangles?
You can find missing angles and the lengths of missing sides using the sine rule and the cosine rule
You can also use the area formula



Reciprocal Trig Functions
What are the reciprocal trig functions?
There are three reciprocal trig functions that each correspond to either sin, cos or tan
Secant (sec x)
Cosecant (cosec x)
Cotangent (cot x)
A good way to remember which function is which is to look at the third letter in each of the reciprocal trig functions
cot x is 1 over tan x etc
Each of the reciprocal trig functions are undefined for certain values of x
sec x is undefined for values of x for which cos x = 0
cosec x is undefined for values of x for which sin x = 0
cot x is undefined for values of x for which tan x = 0
When tan x is undefined, cot x = 0
Be careful not to confuse the reciprocal trig functions with the inverse trig functions
Worked Example
Without the use of a calculator, find the values of
a)
The third letter of sec is c so it is the reciprocal of cos.
Write down the value of .
Simplify.
b)
The third letter of cot is t so it is the reciprocal of tan.
Write down the value of tan(45°).

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
