Protectionism (Edexcel IGCSE Economics): Revision Note
Exam code: 4EC1
Introduction to Protectionism
Free trade aims to maximise global output through specialisation at a national level, e.g. Germany specialises in highly technical capital goods
However, there are numerous reasons why countries would seek to limit free trade in order to protect their markets and employment from too much competition
This is called protectionism and may take the form of:
Import tariffs
Export subsidies
The use of quotas or embargoes
Reasons for Protectionism
Trading partners may retaliate to any methods of protectionism and they should be carefully considered before any implementation
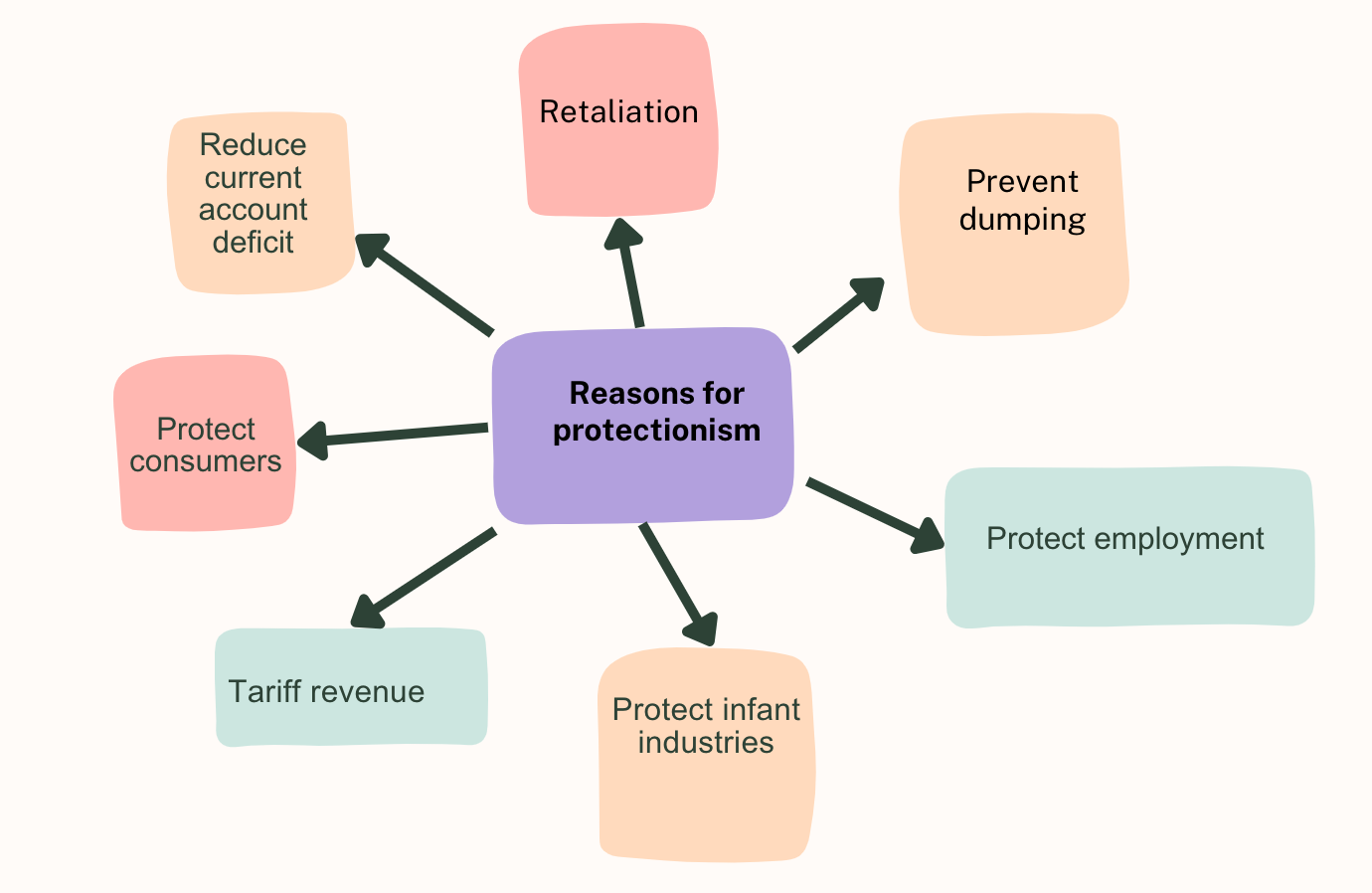
Reasons for Protectionism
Reason | Explanation |
|---|---|
Prevent dumping |
|
Protect employment |
|
Protect infant industries |
|
Tariff revenue |
|
Protect consumers |
|
Reduce current account deficit |
|
Retaliation |
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Most countries wish to impose protectionism to protect their own markets but do not wish to experience protectionism against their own exports. Retaliation against protectionism is often swiftly put in place. It may end up damaging both economies as trade is reduced and consumers are left worse off.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?