Selection (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Computer Science): Revision Note
Exam code: 0478 & 0984
What is Selection?
Selection is when the flow of a program is changed, depending on a set of conditions
The outcome of this condition will then determine which lines or block of code is run next
Selection is used for validation, calculation and making sense of a user's choices
There are two ways to write selection statements:
if... then... else...
case...
If Statements
What is an If statement?
As If statements allow you to execute a set of instructions if a condition is true
They have the following syntax:
IF <condition>
THEN
<statement>
ENDIFA detailed look at a Python IF statement:
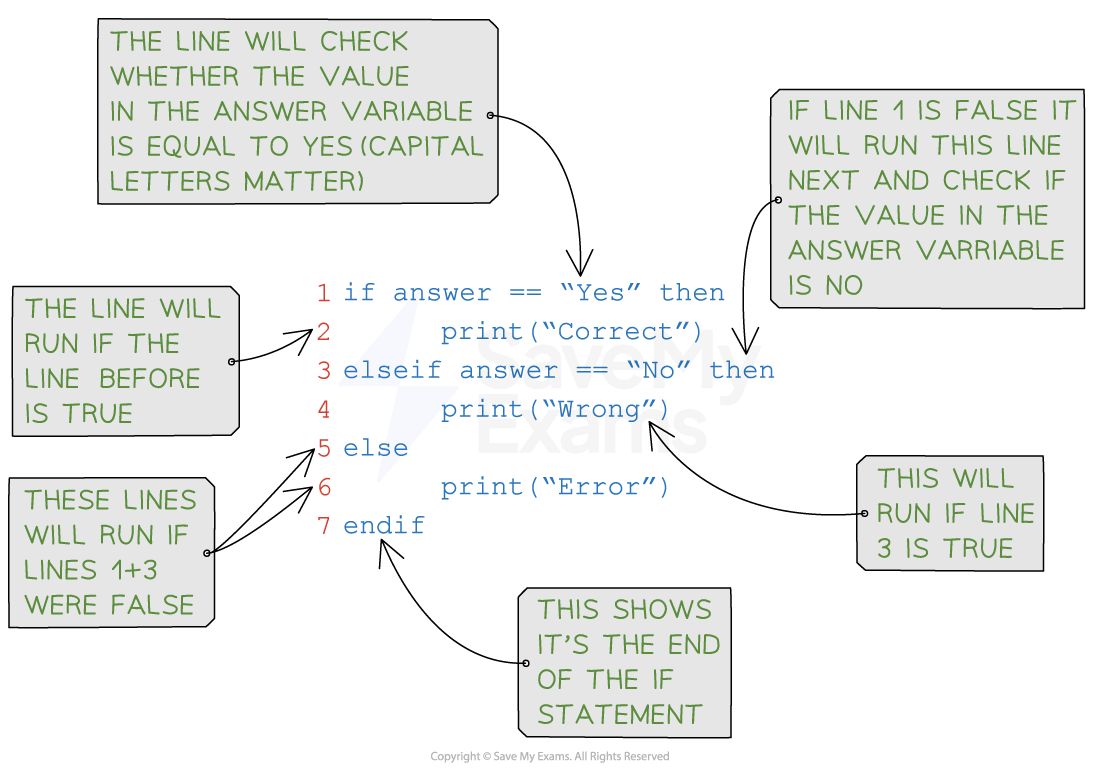
Example
Concept | Pseudocode | Python |
|---|---|---|
IF-THEN-ELSE | | |
Nested Selection
What is nested selection?
Nested selection is a selection statement within a selection statement, e.g. an If inside of another If
Nested means to be 'stored inside the other'
Example
Pseudocode |
|---|
|
Python |
|---|
|
Case Statements
What is a case statement?
A case statement can mean less code but it only useful when comparing multiple values of the same variable
If statements are more flexible and are generally used more in languages such as Python
The format of a CASE statement is:
CASE OF <identifier>
<value 1> : <statement>
<value 2>: <statement>
....
OTHERWISE <statement>
ENDCASE
Concept | Pseudocode | Python |
|---|---|---|
CASE | | |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure to include all necessary components in the selection statement:
the condition,
the statement(s) to execute when the condition is true
any optional statements to execute when the condition is false
Use proper indentation to make the code easier to read and understand
Be careful with the syntax of the programming language being used, as it may differ slightly between languages
Make sure to test the selection statement with various input values to ensure that it works as expected
Worked Example
Write an algorithm using pseudocode that:
Inputs 3 numbers
Outputs the largest of the three numbers
[3]
Exemplar answer
Pseudocode |
|---|
|
Python |
|---|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?