Representing Images (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Computer Science): Revision Note
Exam code: 0478 & 0984
Bitmap Images
What is a bitmap?
A bitmap image is made up of squares called pixels
A pixel is the smallest element of a bitmap image
Each pixel is stored as a binary code
Binary codes are unique to the colour in each pixel
A typical example of a bitmap image is a photograph
The more colours and more detail in the image, the higher the quality of the image and the more binary that needs to be stored
Resolution & Colour Depth
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Cambridge IGCSE 0478 expects you to define resolution and colour depth, explain how both affect file size, and use formulas like width × height × colour depth to calculate storage needs. This page keeps everything focused on exam-ready phrasing and examples.
What is resolution?
Resolution is the total amount of pixels that make up a bitmap image
The resolution is calculated by multiplying the height and width of the image (in pixels)
In general, the higher the resolution the more detail in the image (higher quality)
Resolution can also refer to the total amount of pixels horizontally in a display, such as:
Computer monitors - 1440p means 1440 pixels horizontally compared to 4K which is 3840 pixels (roughly 4 thousand)
TVs - HD (high definition) channels have a resolution of 1080p, 1080 pixels horizontally compared to newer UHD (ultra high definition) channels with 3840 pixels (4K)
YouTube - The quality button allows a user to change the video playback resolution from 144p (144 pixels horizontally) up to 4K
What is colour depth?
Colour depth is the number of bits stored per pixel in a bitmap image
The colour depth is dependent on the number of colours needed in the image
In general, the higher the colour depth the more detail in the image (higher quality)
In a black & white image the colour depth would be 1, meaning 1 bit is enough to create a unique binary code for each colour in the image (1=white, 0=black)

In an image with a colour depth of 2, you would have 00, 01, 10 & 11 available binary codes, so 4 colours
As colour depth increases, so does the amount of colours available in an image
The amount of colours can be calculated as 2n (n = colour depth)
Colour Depth | Amount of Colours |
|---|---|
1 bit | 2 (B&W) |
2 bit | 4 |
4 bit | 16 |
8 bit | 256 |
24 bit | 16,777,216 (True Colour) |
What is the impact of resolution and colour depth?
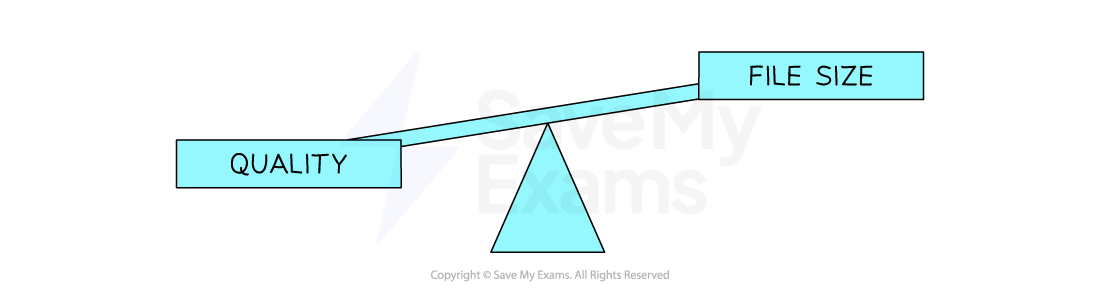
As the resolution and/or colour depth increases, the bigger the size of the file becomes on secondary storage
The higher the resolution, the more pixels are in the image, the more bits are stored
The higher the colour depth, the more bits per pixel are stored
Striking a balance between quality and file size is always a consideration
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In casual use, people say "higher resolution = better quality". But in the exam, focus on what it actually means:
“Resolution is the number of pixels in an image”
Avoid vague terms like “better” and give technical impact: “more bits needed = larger file size.”
Worked Example
1. Define the term Pixel [1]
2. If an image has a colour depth of 2 bits, how many colours can the image represent? [1]
3. Describe the impact of changing an images resolution from 500x500 to 1000x1000 [2]
Answers
The smallest element of a bitmap image (1 square)
4
The image quality would be higher [1] the file size would be larger [1]

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?