Interpreting Chromatograms (Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry (Modular)) : Revision Note
Interpreting chromatograms
We can use a chromatogram to compare the substances present in a mixture to known substances and make assumptions
Pure substances will produce only one spot on the chromatogram
Impure substances will produce more than one spot on the chromatogram
If two or more substances are the same, they will produce identical chromatograms
If the substance is a mixture, it will separate on the paper to show all the different components as separate spots
It is common practice to include a known compound as a reference spot
This can help match up to an unknown spot or set of spots in order to identify it
Interpreting chromatograms

Diagram showing the analysis of a mixture and pure substances using chromatography
We can draw several conclusions from this chromatogram:
The brown ink is a mixture as there are three dots
Red, yellow and blue are pure as there is only one dot for each
The brown ink contains red, blue and yellow as the dots are in line with one another horizontally
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Chromatograms in exams will be in black and white so to identify whether a mixture contains a known sample, the dots need to be in line with one another.
Rf Values
Rf values are used to identify the components of mixtures
The Rf value of a particular compound is always the same
However, it does depend on the solvent used
If the solvent is changed then the Rf value changes
Calculating the Rf value allows chemists to identify unknown substances because it can be compared with the Rf values of known substances under the same conditions
The retention factor, Rf, is calculated by the equation:
The Rf value:
Is a ratio
Has no units
Will always be less than
Worked Example
A student obtained the following chromatogram when carrying out chromatography.
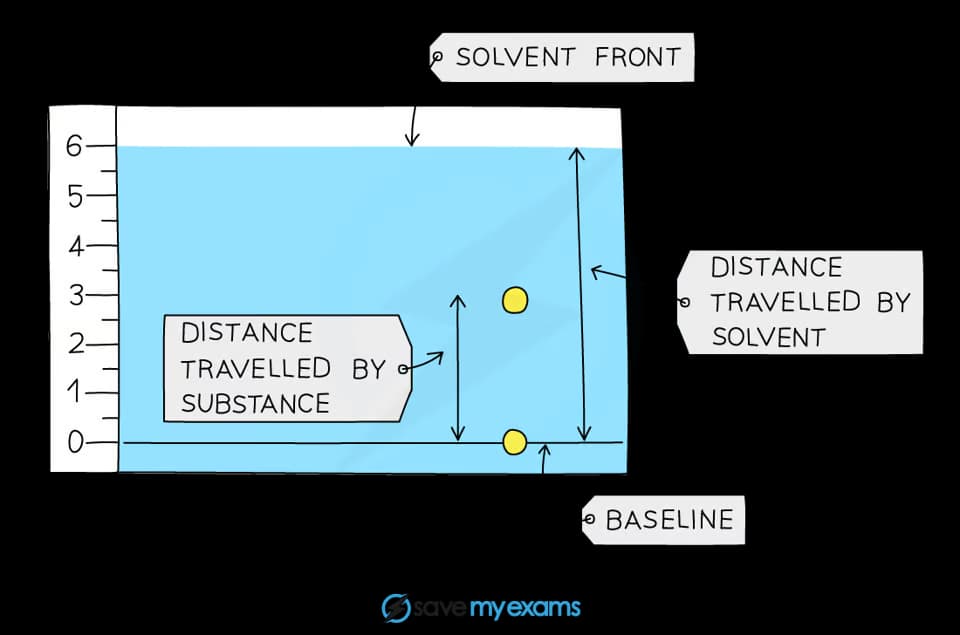
Calculate the Rf value of the substance.
Answer:
The Rf value of the substances in the chromatogram above can be calculated by:
Rf =
=
= 0.5
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When you calculate Rf values in exams, make sure to use your ruler carefully to measure the distance moved by the solvent and the substance as mark schemes can be strict about the values accepted for these.
For both measurements, the distance should be measured from the baseline to the centre of the dot.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?

