Combustion of Fuels (Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry (Modular)) : Revision Note
Combustion of fuels
The combustion of fossil fuels
A fuel is a substance that, when burned, releases heat energy (exothermic reaction)
The combustion of fossil fuels is the major source of atmospheric pollution
Fossil fuels include: coal, oil, natural gas, oil shales and tar sands
Non-renewable fossil fuels are obtained from crude oil by fractional distillation
Petrol is used as a fuel in cars, kerosene is used to fuel aircraft and diesel oil is used as a fuel in some cars, trucks and heavy vehicles such as tanks and trains
Coal is used in power stations and also steel production
Natural gas consists mainly of methane, CH4
There are finite amounts of fossil fuels and they all contribute to pollution and global warming
All these fuels contain carbon, hydrogen and small quantities of sulfur
Combustion products
The burning of fossil fuels releases the gases carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, oxides of nitrogen and oxides of sulfur
In addition incomplete combustion of the fuels gives rise to unburned hydrocarbons and carbon particulates
When the fuel is a hydrocarbon then water and carbon dioxide are the products formed
Hydrocarbon compounds undergo complete and incomplete combustion
Complete combustion
Complete combustion occurs when there is excess oxygen
For example, the combustion equation for propane is:
C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
Incomplete combustion
Incomplete combustion occurs when there is insufficient oxygen to burn
It occurs in some appliances such as boilers and stoves as well as in internal combustion engines
The products of these reactions are unburnt fuel (soot), carbon monoxide and water
Methane for example undergoes incomplete combustion in an oxygen-poor environment:
2CH4 + 3O2→ 2CO + 4H2O
CH4 + O2→ C + 2H2O
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You don't need to learn these equations, but you do need to be able to predict the products of combustion given the composition of the fuel and the conditions.
Carbon monoxide
Why is carbon monoxide dangerous?
Carbon monoxide is a toxic and odourless gas which can cause dizziness, loss of consciousness and eventually death
The CO binds well to haemoglobin which therefore cannot bind oxygen
Oxygen is transported to organs
Carbon monoxide binding to haemoglobin
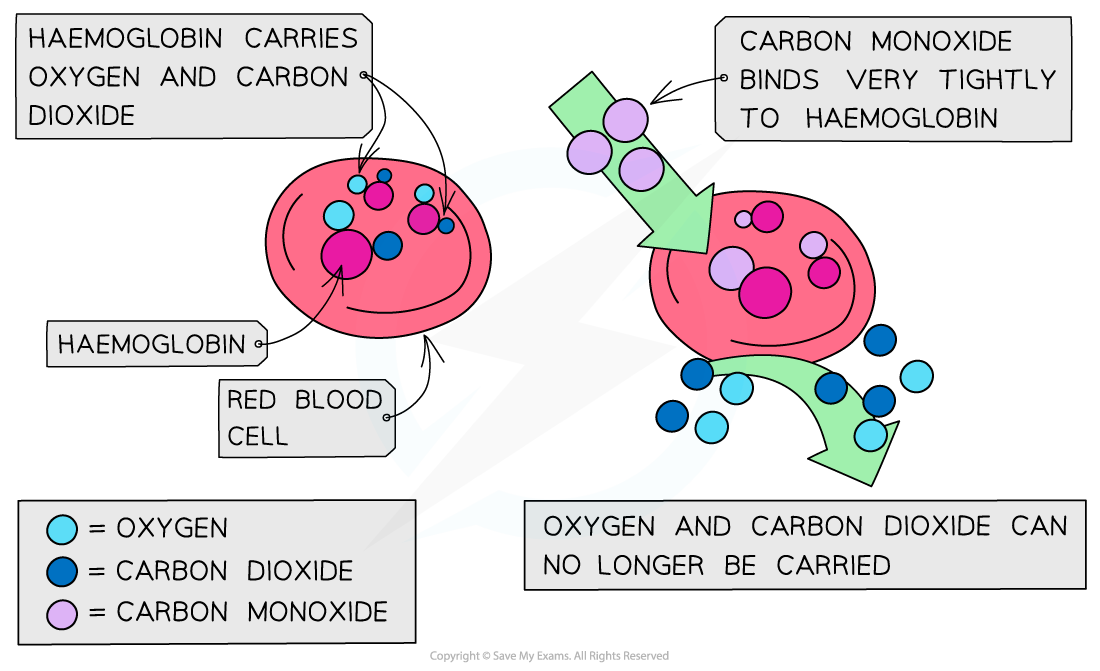
The high affinity of CO to haemoglobin prevents it from binding to O2
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Though CO2 is not a toxic gas, it is still a pollutant causing global warming and climate change.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?

