Separation & Purification Techniques (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences (Double Award)): Revision Note
Exam code: 0654 & 0973
Filtration & crystallisation
The choice of separation technique depends on the substances being separated
All techniques rely on a difference in properties of the chemicals in the mixture
This is usually a physical property such as boiling point
Separating a mixture of solids
Differences in solubility can be used to separate solids
For a difference in solubility, a suitable solvent must be carefully chosen
Only the desired substance should dissolve in the solvent
Other substances or impurities in the mixture should not dissolve in the solvent
For example, to separate a mixture of sand and salt:
Water is a suitable solvent because salt is soluble in water, but sand is insoluble in water
Filtration
This technique is used to separate an undissolved solid from a mixture of the solid and a liquid / solution ( e.g. sand from a mixture of sand and water)
Centrifugation can also be used for this mixture
A filter paper is placed in a filter funnel above another beaker
The mixture of insoluble solid and liquid is poured into the filter funnel
The filter paper will only allow small liquid particles to pass through in the filtrate
Solid particles are too large to pass through the filter paper so will stay behind as a residue
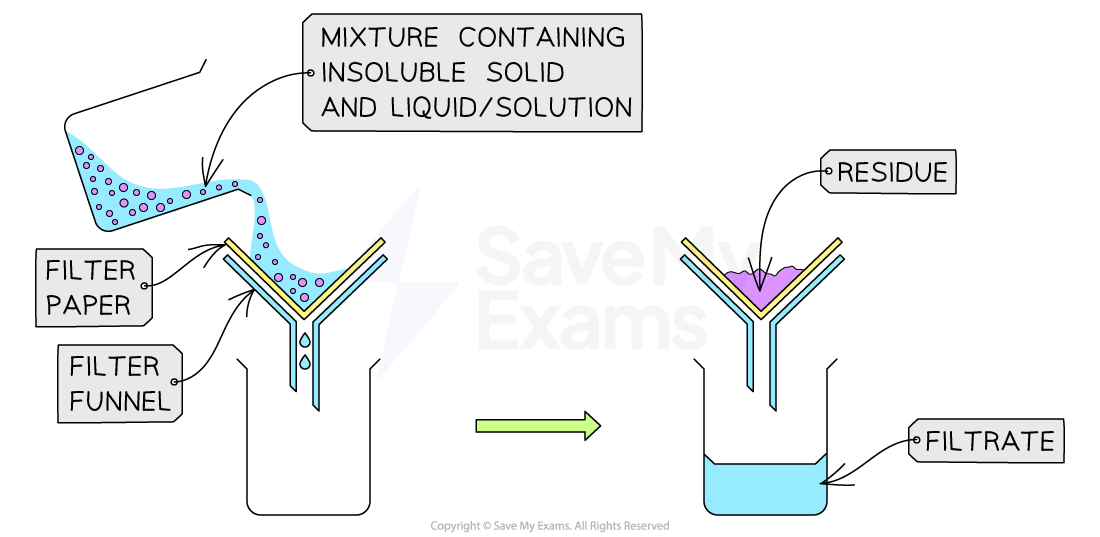
Filtration of a mixture of sand and water
Crystallisation
This method is used to separate a dissolved solid from a solution
A simple application of this is to heat a solution to boiling, remove the heat and leave the solvent to evaporate
A more common application of this is sometimes called crystallisation
This is when the solid is more soluble in hot solvent than in cold, e.g. copper sulphate from a solution of copper(II) sulphate
The solution is heated, allowing the solvent to evaporate and leaving a saturated solution behind
You can test if the solution is saturated by dipping a clean, dry, cold glass rod into the solution
If the solution is saturated, crystals will form on the glass rod when it is removed and allowed to cool
The saturated solution is allowed to cool slowly
Solids will come out of the solution as the solubility decreases
This will be seen as crystals growing
The crystals are collected by filtration
They are then washed with distilled water to remove any impurities
Finally, they are allowed to dry
Common places to dry crystals are between sheets of filter paper or in a drying oven
The process of crystallisation
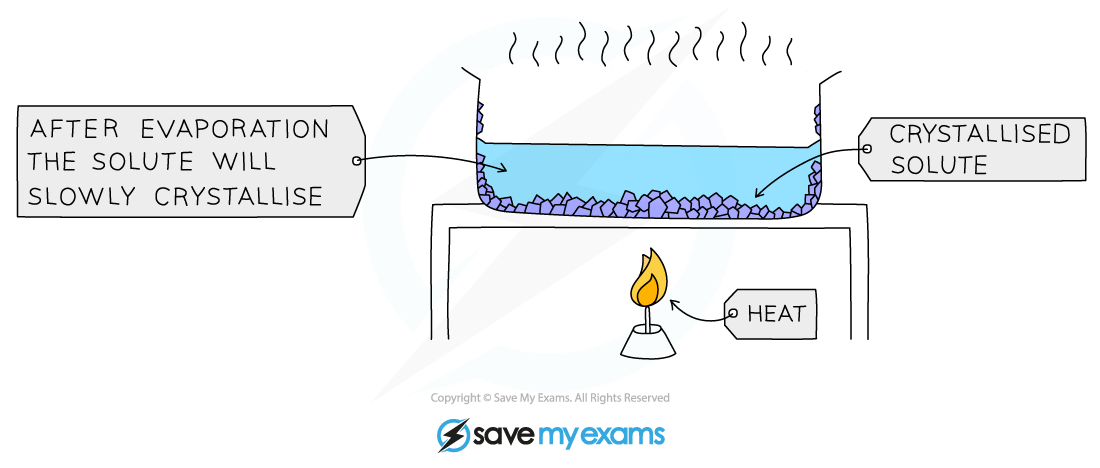
The solution is slowly heated to remove around half of the liquid. The remaining liquid will evaporate slowly
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In exams, you need to be specific that no more than half of the solution is removed by direct heating or you may lose a mark.
Distillation: simple & fractional
Simple distillation
Distillation is used to separate a liquid and soluble solid from a solution (e.g. water from a solution of saltwater) or a pure liquid from a mixture of liquids
The solution is heated and pure water evaporates producing a vapour which rises through the neck of the round-bottomed flask
The vapour passes through the condenser, where it cools and condenses, turning into pure water which is collected in a beaker
After all the water is evaporated from the solution, only the solid solute will be left behind
Simple distillation apparatus
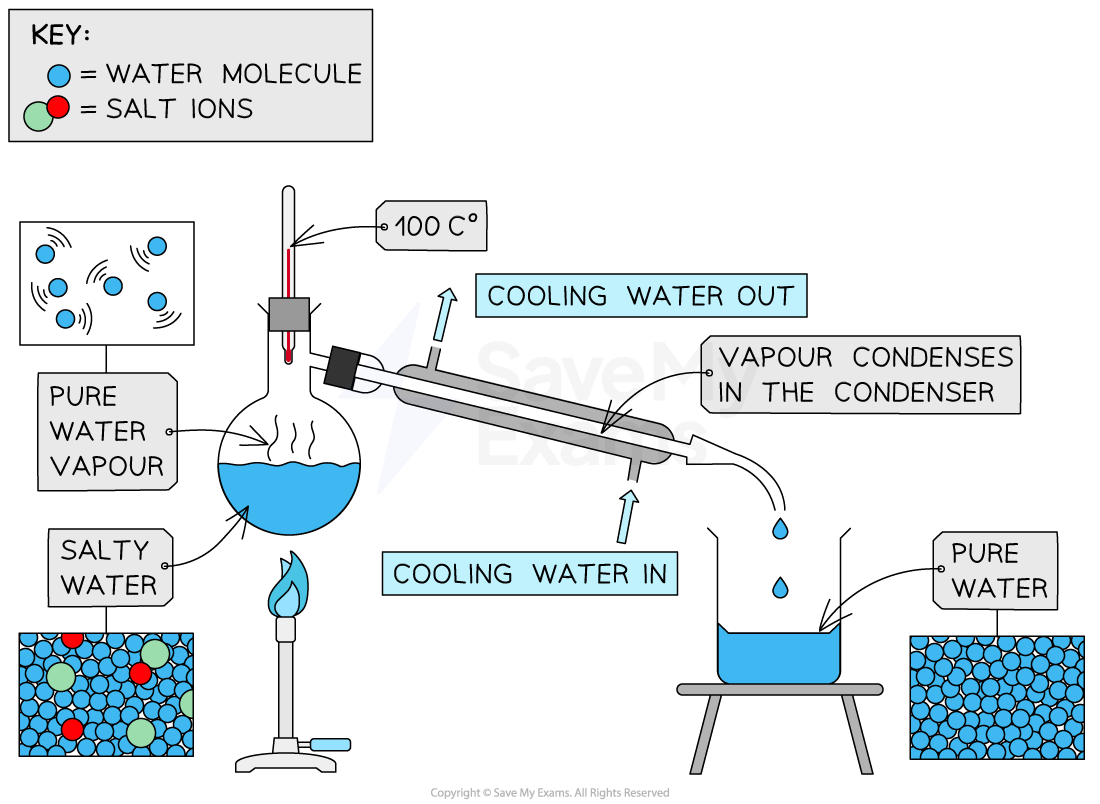
Diagram showing the distillation of a mixture of salt and water
Simple distillation can be used to separate the products of fermentation, such as alcohol and water
However, fractional distillation is a more effective separation technique, commonly used when the boiling points of the liquids are close and/or a higher degree of purity is required, such as crude oil
Fractional distillation
Used to separate two or more liquids that are miscible with one another (e.g. ethanol and water from a mixture of the two)
The solution is heated to the temperature of the substance with the lowest boiling point
This substance will rise and evaporate first
The vapours will pass through a condenser, where they cool and condense
The condensed liquid is then collected in a beaker
All of the substance is evaporated and collected, leaving behind the other component(s) of the mixture
For water and ethanol:
Ethanol has a boiling point of 78 ºC
Water has a boiling point of of 100 ºC
The mixture is heated until it reaches 78 ºC, at which point the ethanol distills out of the mixture and into the beaker
When the temperature starts to increase to 100 ºC heating should be stopped as the water and ethanol are now separated
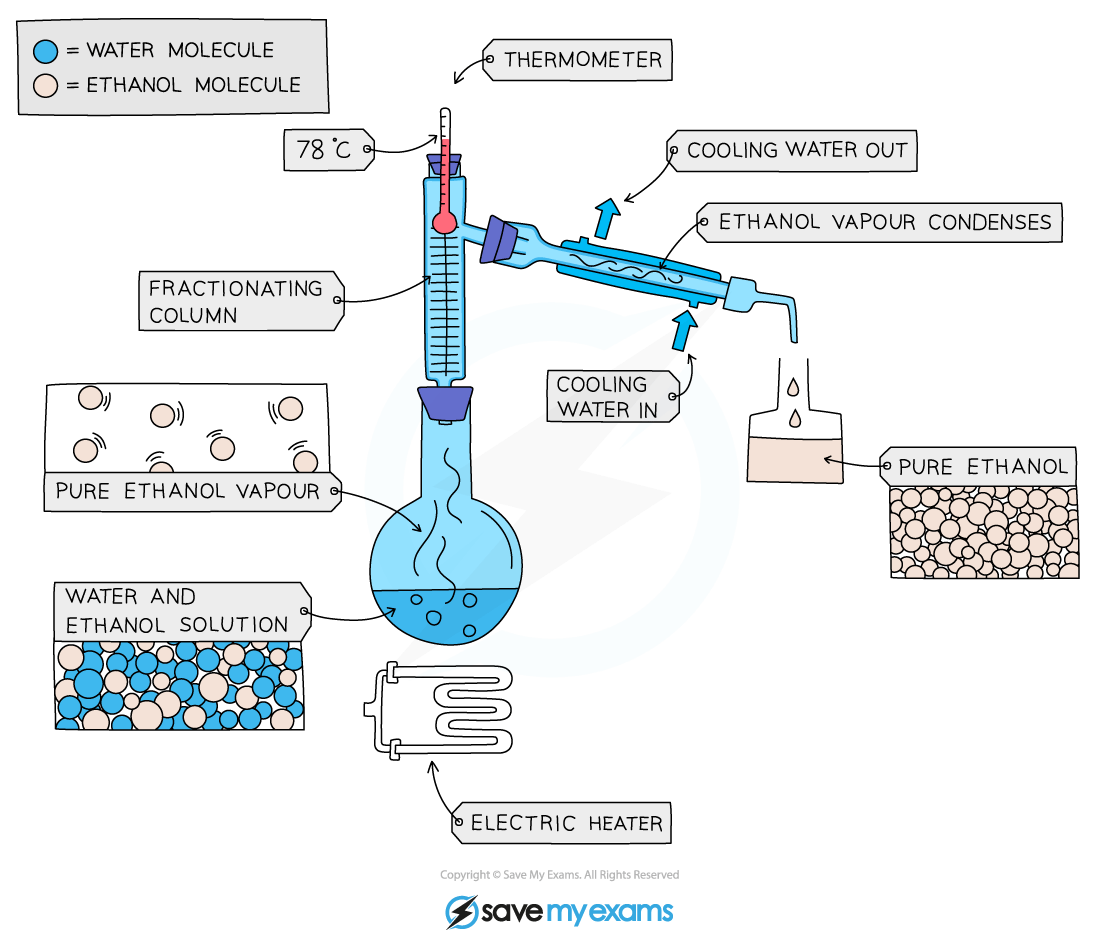
Fractional distillation of a mixture of ethanol and water
An electric heater is safer to use when there are flammable liquids present
The separation of the components in petroleum is achieved by fractional distillation on an industrial scale
Fractional distillation of crude oil is not carried out in school laboratories due to the toxic nature of some of the components of the crude oil, but it can sometimes be simulated using a synthetic crude oil made specially for the demonstration
Worked Example
A student is given a mixture of calcium sulfate, magnesium chloride and water. The table below shows some information about calcium sulfate and magnesium chloride.
substance | solubility in water | state at room temperature |
calcium sulfate | insoluble | solid |
magnesium chloride | soluble | solid |
How does the student obtain magnesium chloride crystals from the mixture?
Crystallisation followed by distillation
Crystallisation followed by filtration
Distillation followed by crystallisation
Filtration followed by crystallisation
Answer
The correct answer is D because:
The difference in solubility in water means the first step is to make a solution
The magnesium chloride will dissolve, but the solid calcium sulfate will be left behind
The mixture is filtered to remove the calcium sulfate and then evaporated and crystallised to obtain magnesium chloride crystals
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You may be asked how to separate a mixture of gases:
One method involves cooling the gaseous mixture sufficiently to liquefy all of the gases, which are then separated by fractional distillation.
They can also be separated by diffusion, where the boiling points are very close or it is impractical or expensive to use fractional distillation.
Assessing purity
Pure substances melt and boil at specific and sharp temperatures
For example, water has a boiling point of 100°C and a melting point of 0°C
Mixtures have a range of melting and boiling points as they consist of different substances that melt or boil at different temperatures
Therefore, melting and boiling point data can be used to distinguish pure substances from mixtures
An unknown pure substance can be identified by experimentally determining its melting point and boiling point and comparing them to literature values / data tables
Boiling points are commonly determined by distillation
Melting point analysis is routinely used to assess the purity of drugs for example
This is done using a melting point apparatus which allows you to slowly heat up a small amount of the sample, making it easier to observe the exact melting point
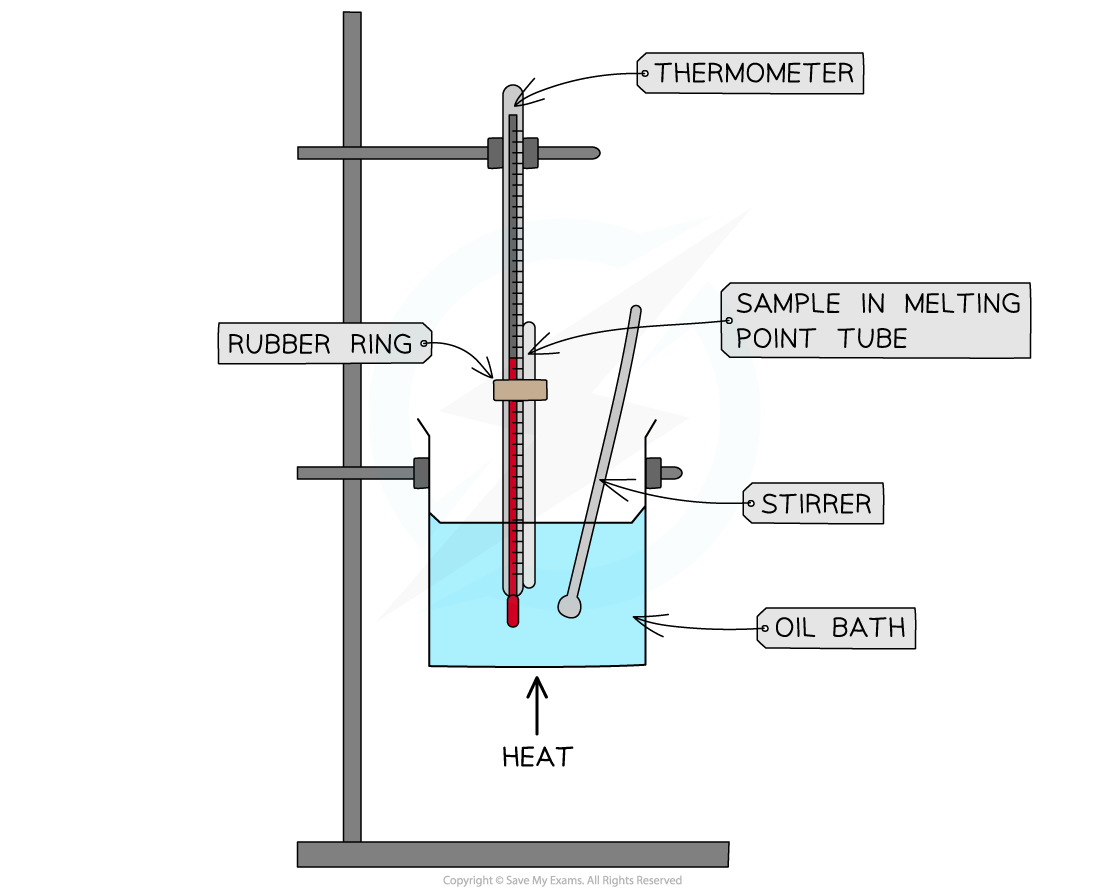
Melting point test using an oil bath
This is then compared to data tables
The closer the measured value is to the actual melting or boiling point, the purer the sample is
If the sample contains impurities:
The boiling point may appear higher than the sample's actual boiling point
The melting point may appear lower than the sample's actual melting point

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
