Water Treatment (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences (Double Award)): Revision Note
Exam code: 0654 & 0973
Did this video help you?
Water treatment
Untreated water contains soluble and insoluble impurities
Insoluble impurities include soil, pieces of plants and other organic matter
Soluble impurities include dissolved calcium, metallic compounds and inorganic pollutants
The first step of water treatment is sedimentation / filtration
Water is pumped into sedimentation tanks and allowed to stand for a few hours
Mud, sand and other particles will fall to the bottom of the tank due to gravity and form a layer of sediment
The water is then filtered through sand and gravel to remove smaller particles
The second step is filtration / treatment with carbon (charcoal)
This removes unpleasant tastes and odours
The final step is chlorination
Bacteria and other microorganisms are too small to be trapped by the filters
So, chlorine is carefully added to the water supply to kill bacteria and other microorganisms
Cholera and typhoid are examples of bacterial diseases which can arise from the consumption of untreated water
Diagram showing the stages in the treatment of water
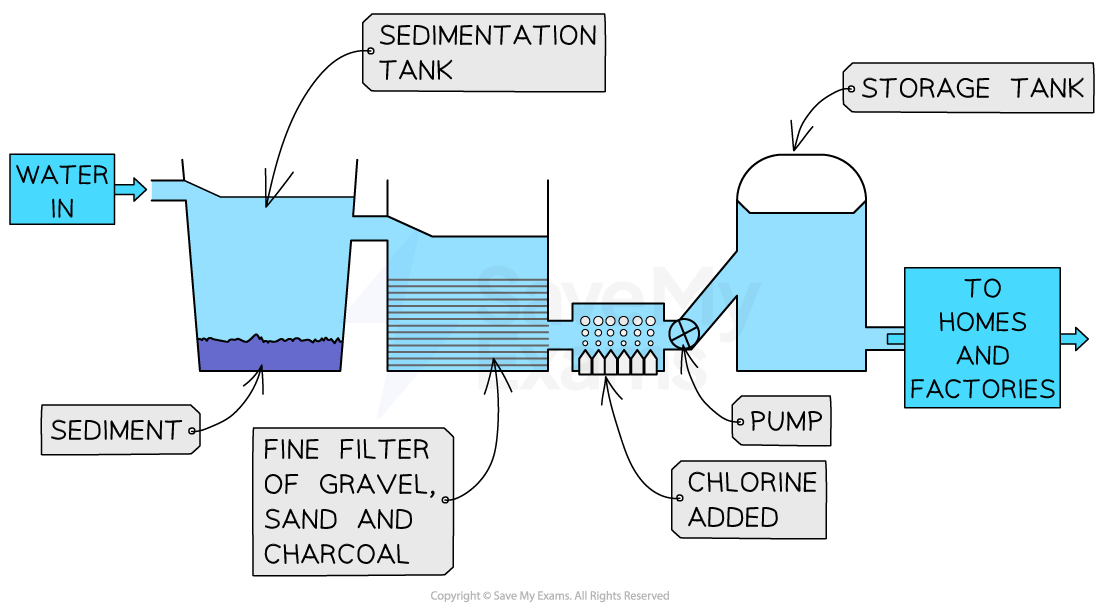
The stages of treating water are sedimentation, filtration with carbon and chlorination
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Exam questions on water treatment often focus on the purpose of each stage of the process.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?