Air (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences (Double Award)): Revision Note
Exam code: 0654 & 0973
The composition of air
The composition of gases in the atmosphere has not changed much in 200 million years
The composition of clean, dry air is approximately:
78% nitrogen
21% oxygen
The remaining gases include carbon dioxide and trace quantities of the noble gases
Pie chart of the current atmosphere
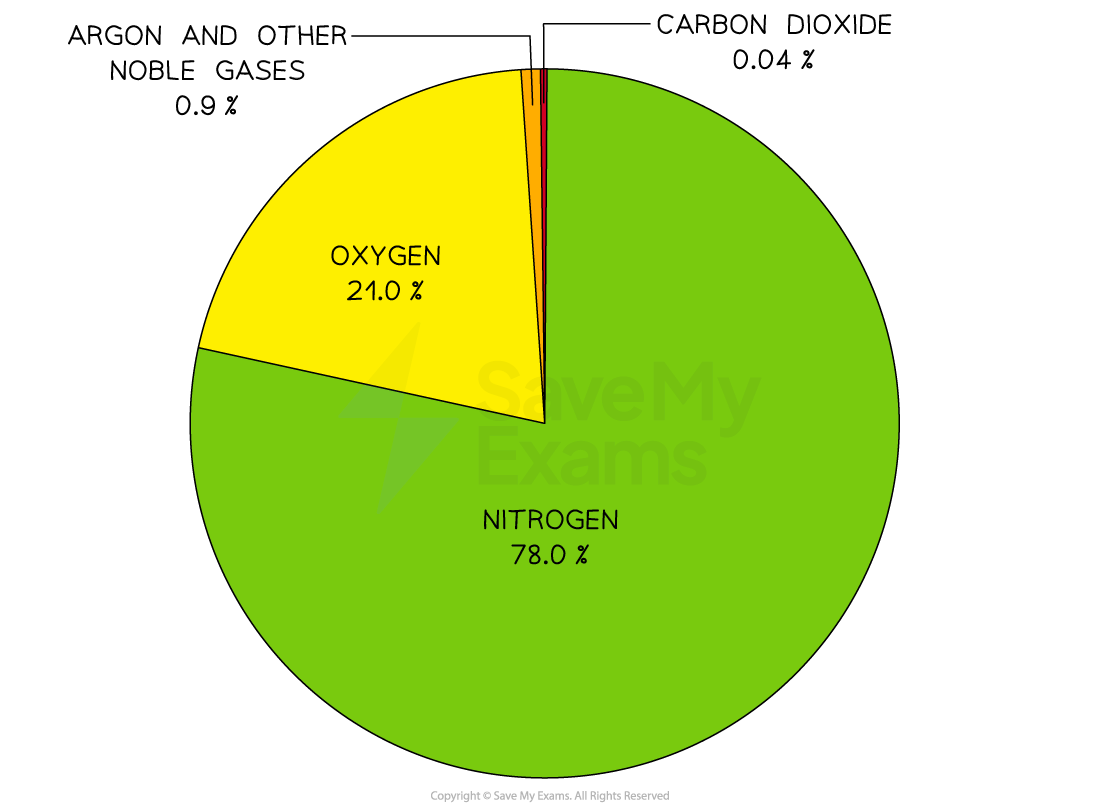
The two main gases in the air are nitrogen and oxygen
Did this video help you?
Air pollution
In addition to the gases present naturally in our atmosphere, other gases are present due to human activities and are classed as air pollutants
Carbon dioxide
Sources:
Complete combustion of carbon-containing fuels such as fossil fuels
For example, the complete combustion of methane:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
Adverse effects:
Increases global warming, which leads to climate change
Carbon monoxide
Sources:
Incomplete combustion of carbon-containing fuels such as fossil fuels
For example, the incomplete combustion of gasoline / octane:
C8H18 + 10O2 → 5CO + 3CO2 + 9H2O
Adverse effects:
Toxic / poisonous
It combines with haemoglobin in the blood and prevents it from carrying oxygen
Particulates
Sources:
Incomplete combustion of carbon-containing fuels such as fossil fuels can also produce particulates of carbon (soot)
For example, the incomplete combustion of methane can produce CO and C:
2CH4 + 3O2→ 2CO + 4H2O
CH4 + O2→ C + 2H2O
Adverse effects:
Respiratory problems
Cancer
Methane
Sources:
Waste gases from digestive processes of animals
Decomposition of vegetation
Bacterial action in swamps, rice paddy fields and landfill sites
Adverse effects:
Increases global warming, which leads to climate change
Oxides of nitrogen
Sources:
Reaction of nitrogen with oxygen in the presence of high temperatures, e.g. in car engines, high-temperature furnaces and when lightning occurs
It is also a product of bacterial action in the soil
Adverse effects:
Produces photochemical smog
Dissolves in rain to form acid rain which causes corrosion to metal structures, buildings and statues made of carbonate rocks, damage to aquatic organisms
Pollutes crops and water supplies
Irritates lungs, throats and eyes and causes respiratory problems
Sulfur dioxide
Sources:
Combustion of fossil fuels containing sulfur compounds:
S + O2 → SO2
Power stations are a major source of sulfur dioxide
Adverse effects:
Dissolves in rain to form acid rain with similar effects as the acid rain caused by oxides of nitrogen

How acid rain is produced
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Complete and incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons produce different products.
Complete combustion occurs in excess oxygen and produces CO2 and H2O.
Incomplete combustion occurs in oxygen-deficient conditions and produces CO, H2O and sometimes particulates of carbon (soot).

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
